Fractional work offers specialized skills on a part-time basis, allowing companies to engage experts without full-time commitments, while temporary employment fills short-term staffing needs with flexible workforce solutions. Businesses leverage fractional work to access high-level expertise efficiently, whereas temporary employment provides operational agility during peak demands or project-based tasks. Explore the advantages and applications of each employment model to determine the best fit for your organizational goals.
Why it is important
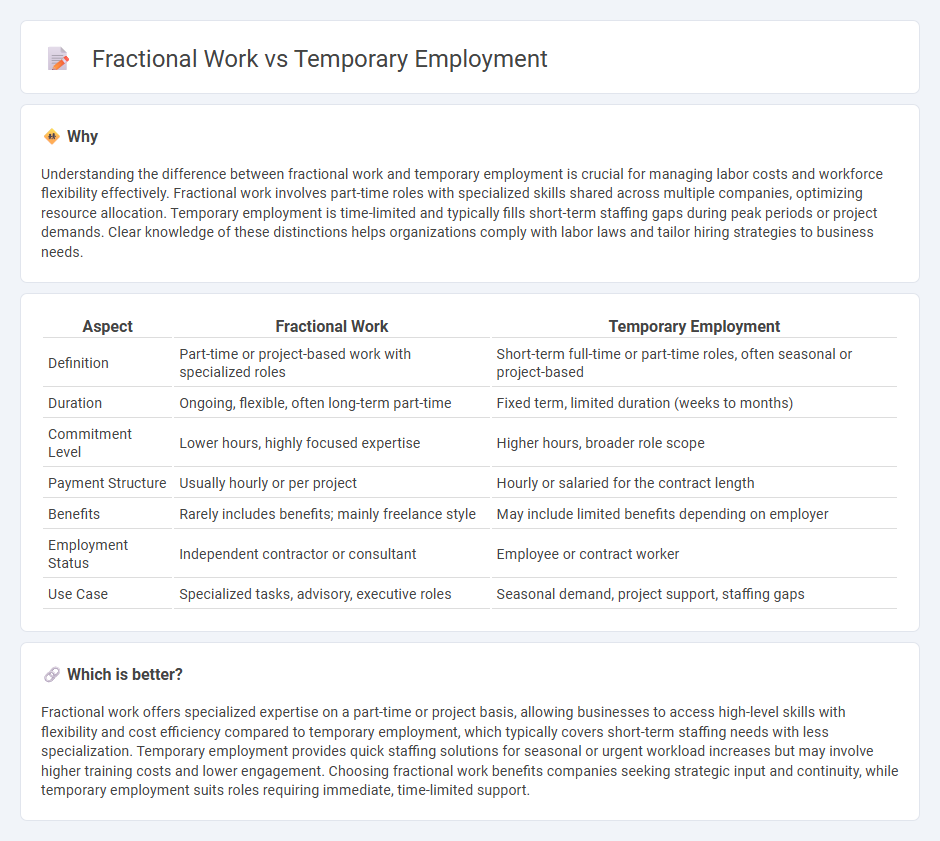
Understanding the difference between fractional work and temporary employment is crucial for managing labor costs and workforce flexibility effectively. Fractional work involves part-time roles with specialized skills shared across multiple companies, optimizing resource allocation. Temporary employment is time-limited and typically fills short-term staffing gaps during peak periods or project demands. Clear knowledge of these distinctions helps organizations comply with labor laws and tailor hiring strategies to business needs.
Comparison Table
| Aspect | Fractional Work | Temporary Employment |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Part-time or project-based work with specialized roles | Short-term full-time or part-time roles, often seasonal or project-based |
| Duration | Ongoing, flexible, often long-term part-time | Fixed term, limited duration (weeks to months) |
| Commitment Level | Lower hours, highly focused expertise | Higher hours, broader role scope |
| Payment Structure | Usually hourly or per project | Hourly or salaried for the contract length |
| Benefits | Rarely includes benefits; mainly freelance style | May include limited benefits depending on employer |
| Employment Status | Independent contractor or consultant | Employee or contract worker |
| Use Case | Specialized tasks, advisory, executive roles | Seasonal demand, project support, staffing gaps |
Which is better?
Fractional work offers specialized expertise on a part-time or project basis, allowing businesses to access high-level skills with flexibility and cost efficiency compared to temporary employment, which typically covers short-term staffing needs with less specialization. Temporary employment provides quick staffing solutions for seasonal or urgent workload increases but may involve higher training costs and lower engagement. Choosing fractional work benefits companies seeking strategic input and continuity, while temporary employment suits roles requiring immediate, time-limited support.
Connection
Fractional work and temporary employment both provide flexible labor solutions by allowing companies to hire professionals for specific periods or projects, optimizing workforce costs and adapting to fluctuating demands. They enable businesses to access specialized skills without long-term commitments, enhancing operational agility in dynamic markets. This connection supports diverse employment models that meet evolving workforce preferences and economic conditions.
Key Terms
Contract Duration
Temporary employment typically involves fixed-term contracts ranging from a few weeks to several months, designed to address immediate workforce needs or seasonal demands. Fractional work, often characterized by part-time or project-based engagement, allows skilled professionals to contribute expertise flexibly over an extended period without full-time commitment. Explore these contract duration differences further to determine which model best suits your organizational goals.
Work Hours
Temporary employment typically involves working full-time hours for a limited duration, often aligned with project needs or seasonal demands, ensuring consistent workload during that period. Fractional work offers part-time involvement where employees contribute specific expertise or tasks across multiple clients, allowing flexible allocation of work hours tailored to strategic priorities. Explore more to understand how work hour structures impact productivity and job satisfaction in these models.
Job Commitment
Temporary employment typically involves fixed-term contracts where employees commit fully to a single employer for the duration, often focusing on specific projects or seasonal needs. Fractional work allows professionals to allocate limited hours across multiple organizations, balancing diverse responsibilities with less intensive job commitment. Explore how commitment varies between these work arrangements to optimize your staffing strategy.
Source and External Links
Temporary work - Wikipedia - Temporary employment refers to jobs that are limited to a specified period, often filled through staffing agencies or freelance platforms, and includes roles described as contractual, seasonal, interim, or casual, with varying levels of benefits based on employer policy.
What Is a Temporary Employee? (With Benefits and FAQs) - Indeed - Temporary employees are hired for short-term roles, typically under one year, with clearly defined contracts, and are generally exempt from benefits--though they qualify for workers' compensation if injured on the job.
Temporary employment - OECD - Temporary employment is defined as wage and salary work with a predetermined end date, and its prevalence is measured as a percentage of all dependent employees, with national definitions sometimes varying.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com