Rage applying involves submitting numerous job applications impulsively in response to frustration or dissatisfaction at work, often without strategic planning. Career cushioning focuses on building a safety net by discreetly exploring job opportunities and skill development to ensure stability before leaving a current position. Discover effective strategies for balancing immediate job search impulses with long-term career security.
Why it is important
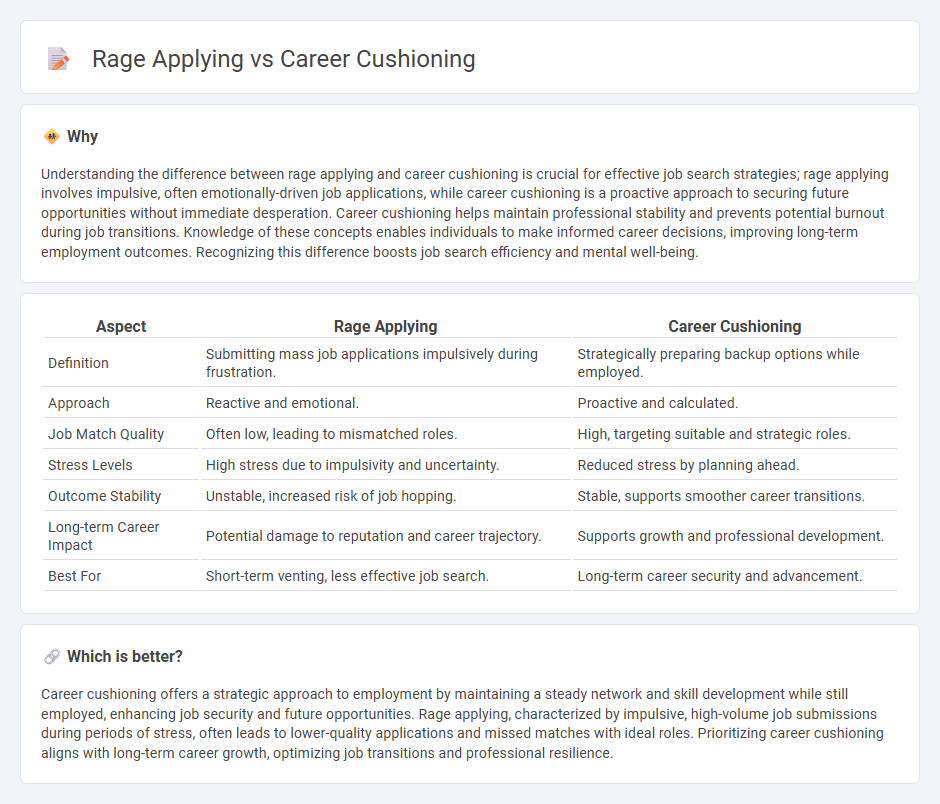
Understanding the difference between rage applying and career cushioning is crucial for effective job search strategies; rage applying involves impulsive, often emotionally-driven job applications, while career cushioning is a proactive approach to securing future opportunities without immediate desperation. Career cushioning helps maintain professional stability and prevents potential burnout during job transitions. Knowledge of these concepts enables individuals to make informed career decisions, improving long-term employment outcomes. Recognizing this difference boosts job search efficiency and mental well-being.
Comparison Table
| Aspect | Rage Applying | Career Cushioning |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Submitting mass job applications impulsively during frustration. | Strategically preparing backup options while employed. |
| Approach | Reactive and emotional. | Proactive and calculated. |
| Job Match Quality | Often low, leading to mismatched roles. | High, targeting suitable and strategic roles. |
| Stress Levels | High stress due to impulsivity and uncertainty. | Reduced stress by planning ahead. |
| Outcome Stability | Unstable, increased risk of job hopping. | Stable, supports smoother career transitions. |
| Long-term Career Impact | Potential damage to reputation and career trajectory. | Supports growth and professional development. |
| Best For | Short-term venting, less effective job search. | Long-term career security and advancement. |
Which is better?
Career cushioning offers a strategic approach to employment by maintaining a steady network and skill development while still employed, enhancing job security and future opportunities. Rage applying, characterized by impulsive, high-volume job submissions during periods of stress, often leads to lower-quality applications and missed matches with ideal roles. Prioritizing career cushioning aligns with long-term career growth, optimizing job transitions and professional resilience.
Connection
Rage applying occurs when job seekers urgently submit multiple applications in response to workplace dissatisfaction or job insecurity, which directly ties into career cushioning--a strategy of maintaining backup job options to manage employment risks. Both concepts highlight proactive measures individuals take to safeguard their careers amid uncertain labor market conditions. Understanding the link between rage applying and career cushioning reveals how emotional responses influence practical career management tactics.
Key Terms
Job Security
Career cushioning involves discreetly exploring new job opportunities to enhance job security without immediate intention to leave, reducing the risk of unemployment. Rage applying, driven by frustration or anger after negative work experiences, often leads to impulsive job applications that may not align with long-term career goals or stability. Discover how adopting strategic career cushioning can safeguard your professional future and improve job security.
Employee Motivation
Career cushioning involves discreetly preparing backup job options to maintain security and motivation during uncertain employment periods, helping employees feel more in control and less stressed. Rage applying, characterized by impulsively submitting numerous job applications out of frustration, often leads to diminished motivation and suboptimal job matches. Explore strategies to harness career cushioning effectively while managing emotional impulses for sustained employee motivation.
Career Transition
Career cushioning involves discreetly preparing for a job transition by updating skills and networking, minimizing risk while maintaining current employment stability. Rage applying reflects impulsive job applications driven by frustration or dissatisfaction, often leading to misaligned opportunities and increased stress during career changes. Explore effective strategies to navigate career transitions with confidence and intentionality.
Source and External Links
What is Career Cushioning and How Can it Impact Business? - Indeed - Career cushioning is when employees keep other career options and relationships open due to uncertainty about their current job, involving strategies like building networks, upskilling, or side gigs to prepare for worst-case scenarios and maintain career stability.
The importance of career cushioning in today's job market - Career cushioning is a response to professional volatility, acting as an insurance policy by upskilling, reskilling, or securing alternative paths to protect against unexpected career disruptions.
What Is Career Cushioning and Can It Lead to Success? - BetterUp - Career cushioning is a backup plan strategy involving job searching, freelance work, or skill development to ensure readiness for career changes, with pros like quicker job transitions and cons including potential distraction or stress.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com