Polyworking involves managing multiple part-time jobs or projects simultaneously, offering diverse income streams and skill development opportunities. The gig economy centers on short-term, flexible work arrangements facilitated by digital platforms, emphasizing convenience and on-demand labor. Explore the distinctions between polyworking and the gig economy to determine which model suits your career goals.
Why it is important
Understanding the difference between polyworking and the gig economy is crucial for optimizing career strategies and managing financial stability. Polyworking involves holding multiple part-time roles simultaneously across various industries, promoting skill diversification and consistent income streams. In contrast, the gig economy focuses on short-term, task-based jobs often facilitated by digital platforms, which can lead to income volatility and limited benefits. Recognizing these distinctions helps individuals make informed decisions about job security, work-life balance, and long-term career growth.
Comparison Table
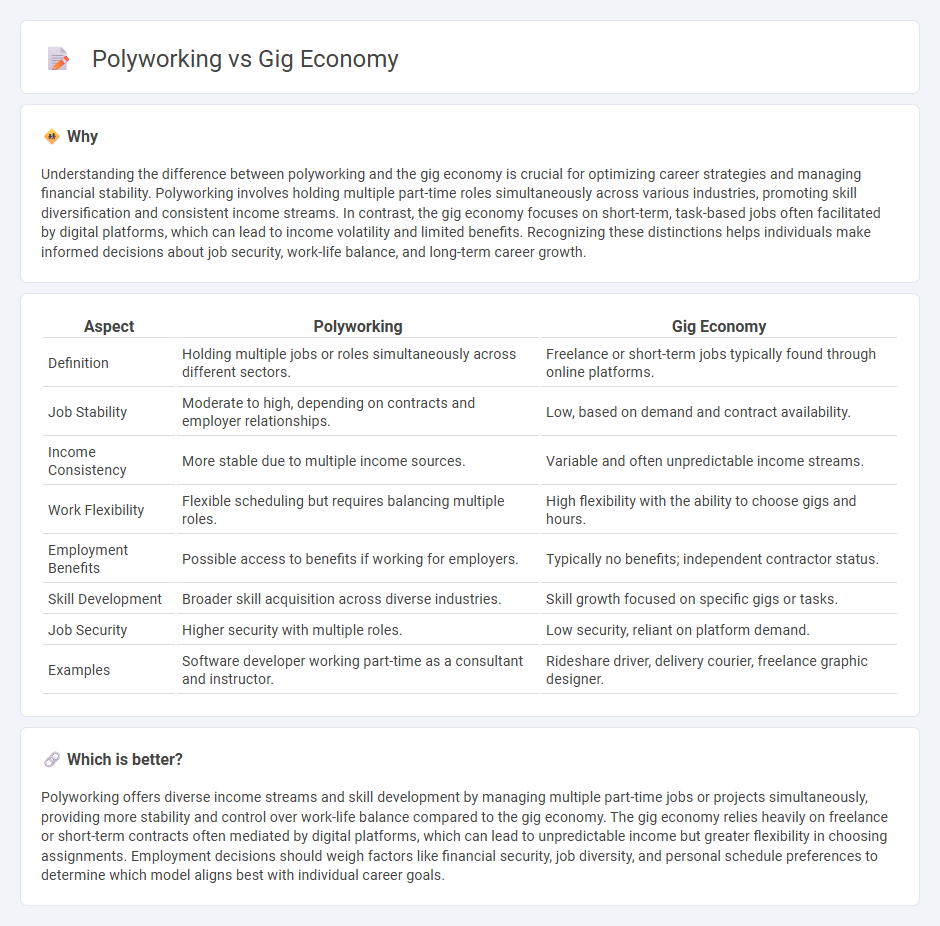
| Aspect | Polyworking | Gig Economy |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Holding multiple jobs or roles simultaneously across different sectors. | Freelance or short-term jobs typically found through online platforms. |
| Job Stability | Moderate to high, depending on contracts and employer relationships. | Low, based on demand and contract availability. |
| Income Consistency | More stable due to multiple income sources. | Variable and often unpredictable income streams. |
| Work Flexibility | Flexible scheduling but requires balancing multiple roles. | High flexibility with the ability to choose gigs and hours. |
| Employment Benefits | Possible access to benefits if working for employers. | Typically no benefits; independent contractor status. |
| Skill Development | Broader skill acquisition across diverse industries. | Skill growth focused on specific gigs or tasks. |
| Job Security | Higher security with multiple roles. | Low security, reliant on platform demand. |
| Examples | Software developer working part-time as a consultant and instructor. | Rideshare driver, delivery courier, freelance graphic designer. |
Which is better?
Polyworking offers diverse income streams and skill development by managing multiple part-time jobs or projects simultaneously, providing more stability and control over work-life balance compared to the gig economy. The gig economy relies heavily on freelance or short-term contracts often mediated by digital platforms, which can lead to unpredictable income but greater flexibility in choosing assignments. Employment decisions should weigh factors like financial security, job diversity, and personal schedule preferences to determine which model aligns best with individual career goals.
Connection
Polyworking and the gig economy are interconnected through their reliance on flexible, independent job roles that allow workers to engage in multiple income streams simultaneously. The gig economy fuels polyworking by providing diverse short-term projects and freelance opportunities across platforms like Uber, Fiverr, and TaskRabbit. This synergy enables professionals to diversify skill sets, increase earnings, and maintain adaptable work schedules in an evolving labor market.
Key Terms
Flexibility
The gig economy offers flexible work opportunities by allowing individuals to pick short-term tasks, while polyworking combines multiple jobs or roles simultaneously for broader income streams and skill diversification. Flexibility in the gig economy is often task-oriented with varying schedules, whereas polyworking requires advanced time management to balance diverse responsibilities. Explore more to understand how these approaches can reshape your work-life balance and career growth.
Income sources
The gig economy centers on short-term, task-based jobs primarily through platforms like Uber or Fiverr, offering income from varied but often unpredictable sources. Polyworking involves maintaining multiple stable roles or businesses simultaneously, diversifying income streams through complementary skills or professions for financial resilience. Explore how these income strategies influence work flexibility and economic stability.
Job security
Job security in the gig economy is often precarious due to the lack of long-term contracts and benefits, with workers relying on platforms like Uber or Fiverr that offer fluctuating income without guaranteed stability. In contrast, polyworking involves diversifying income streams across multiple professions or projects, potentially enhancing job security by not depending on a single employer or platform. Explore how adopting polyworking strategies can mitigate risks associated with gig economy instability.
Source and External Links
Gig Economy - Overview, Advantages, Disadvantages - The gig economy is a flexible market where labor and resources are exchanged through digital platforms, with workers hired as independent contractors for temporary jobs, enabling cheaper and more flexible services primarily operated via the internet.
The Pros and Cons of the Gig Economy - The gig economy allows individuals to work short-term projects or freelance jobs outside traditional employment, connecting workers to services like transportation and deliveries, and is growing rapidly with millions engaged today.
What is the Gig Economy?| Definition from TechTarget - The gig economy is a free market system with widespread temporary jobs where employers hire independent workers for short-term commitments, facilitated by digital technologies that enable remote work and increase workforce mobility.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com