Blue collar tech jobs focus on skilled trades such as electrical work, plumbing, and machinery repair, emphasizing hands-on expertise and technical know-how. The creative industry encompasses careers in design, media, and the arts, highlighting innovation, original thinking, and artistic expression. Explore how these distinct employment sectors shape career opportunities and economic growth.
Why it is important
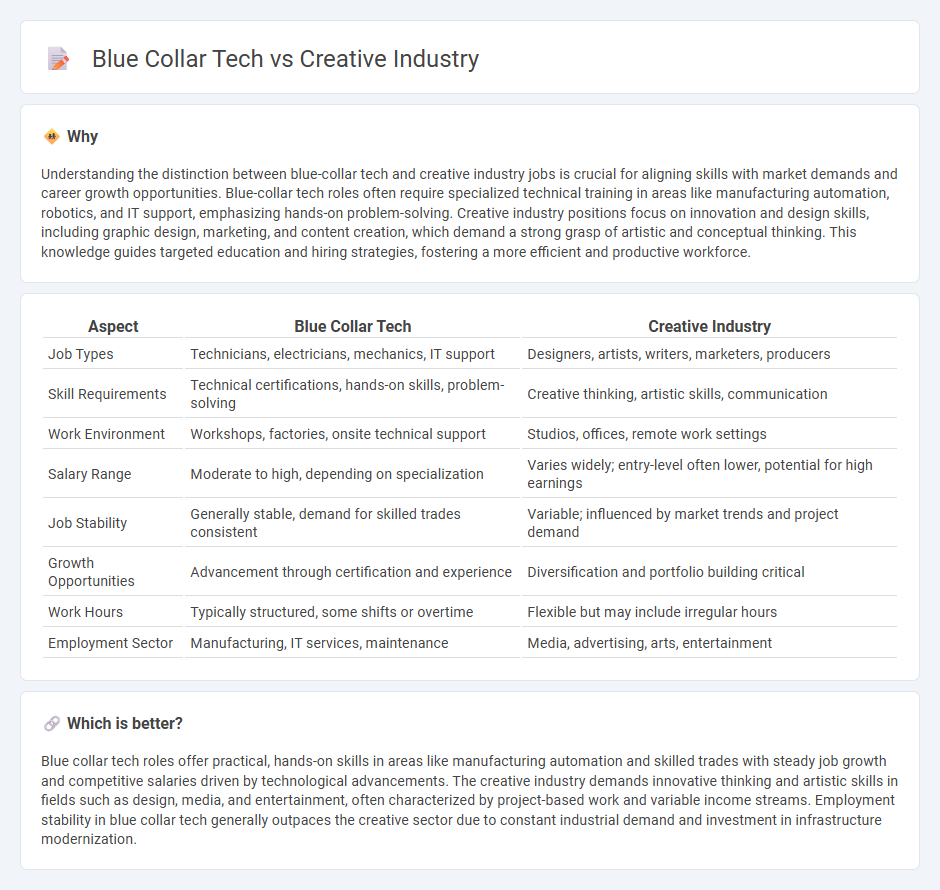
Understanding the distinction between blue-collar tech and creative industry jobs is crucial for aligning skills with market demands and career growth opportunities. Blue-collar tech roles often require specialized technical training in areas like manufacturing automation, robotics, and IT support, emphasizing hands-on problem-solving. Creative industry positions focus on innovation and design skills, including graphic design, marketing, and content creation, which demand a strong grasp of artistic and conceptual thinking. This knowledge guides targeted education and hiring strategies, fostering a more efficient and productive workforce.
Comparison Table
| Aspect | Blue Collar Tech | Creative Industry |
|---|---|---|
| Job Types | Technicians, electricians, mechanics, IT support | Designers, artists, writers, marketers, producers |
| Skill Requirements | Technical certifications, hands-on skills, problem-solving | Creative thinking, artistic skills, communication |
| Work Environment | Workshops, factories, onsite technical support | Studios, offices, remote work settings |
| Salary Range | Moderate to high, depending on specialization | Varies widely; entry-level often lower, potential for high earnings |
| Job Stability | Generally stable, demand for skilled trades consistent | Variable; influenced by market trends and project demand |
| Growth Opportunities | Advancement through certification and experience | Diversification and portfolio building critical |
| Work Hours | Typically structured, some shifts or overtime | Flexible but may include irregular hours |
| Employment Sector | Manufacturing, IT services, maintenance | Media, advertising, arts, entertainment |
Which is better?
Blue collar tech roles offer practical, hands-on skills in areas like manufacturing automation and skilled trades with steady job growth and competitive salaries driven by technological advancements. The creative industry demands innovative thinking and artistic skills in fields such as design, media, and entertainment, often characterized by project-based work and variable income streams. Employment stability in blue collar tech generally outpaces the creative sector due to constant industrial demand and investment in infrastructure modernization.
Connection
Blue collar tech roles, such as skilled technicians and equipment operators, support the creative industry by managing and maintaining the technology essential for production and design processes. These blue collar workers ensure the functionality of specialized tools, machinery, and infrastructure that enable creative professionals to innovate in fields like media, entertainment, and digital arts. The symbiotic relationship between blue collar tech expertise and creative talent drives efficiency and advances technological integration within the creative sector.
Key Terms
Intellectual Property
The creative industry centers on generating and protecting intellectual property such as copyrights, trademarks, and patents related to art, design, and media innovations. Blue collar tech emphasizes practical technical skills with a focus on equipment maintenance, installation, and operational efficiency, where intellectual property concerns often involve proprietary processes and trade secrets. Explore the distinctive intellectual property challenges and protections unique to both sectors for deeper insight.
Skilled Trades
Skilled trades within the blue collar tech sector encompass specialized professions such as electricians, welders, and HVAC technicians, delivering critical services that support infrastructure and manufacturing. The creative industry centers on innovation and design, with roles including graphic designers, filmmakers, and marketing strategists, driving brand development and entertainment. Explore detailed insights to understand the evolving roles, salary trends, and educational pathways in these dynamic career fields.
Portfolio
Creative industry professionals build portfolios showcasing diverse projects that highlight originality, design skills, and innovation across media such as graphic design, advertising, and digital content. Blue collar tech workers emphasize portfolios that demonstrate technical proficiency, problem-solving abilities, and practical experience in areas like IT support, network management, and hardware maintenance. Explore detailed comparisons to understand how specialized portfolios impact career opportunities in these fields.
Source and External Links
Creative Industries definitions - David Parrish - The creative industries encompass economic activities centered on creativity, including design, music, publishing, architecture, film, crafts, visual arts, fashion, TV, advertising, literature, computer games, and performing arts, defined by their use of individual creativity, skill, and talent to generate wealth and jobs through intellectual property exploitation.
Creative industries - Wikipedia - The creative industries refer to economic activities involved in generating or exploiting knowledge and information, often including advertising, architecture, art, design, fashion, film, music, performing arts, publishing, software, TV, and games, and are considered key to economic growth by valuing human creativity as a vital resource.
The Creative Economy - The Policy Circle - The creative economy makes up over 6.1% of global GDP, with television and visual arts being the largest revenue sources and visual arts and music leading in employment, highlighting the significant economic impact of creative industries across regions like the U.S., China, and Europe.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com