No-collar work, characterized by roles in emerging technology sectors such as AI development and renewable energy, emphasizes innovation and flexible skill sets distinct from traditional service industry positions that focus on customer interaction and routine tasks. The service industry encompasses jobs like retail, hospitality, and food service, which require strong interpersonal abilities and adaptability in dynamic environments. Explore the evolving landscape of employment to understand the distinctive opportunities and demands of no-collar versus service industry roles.
Why it is important
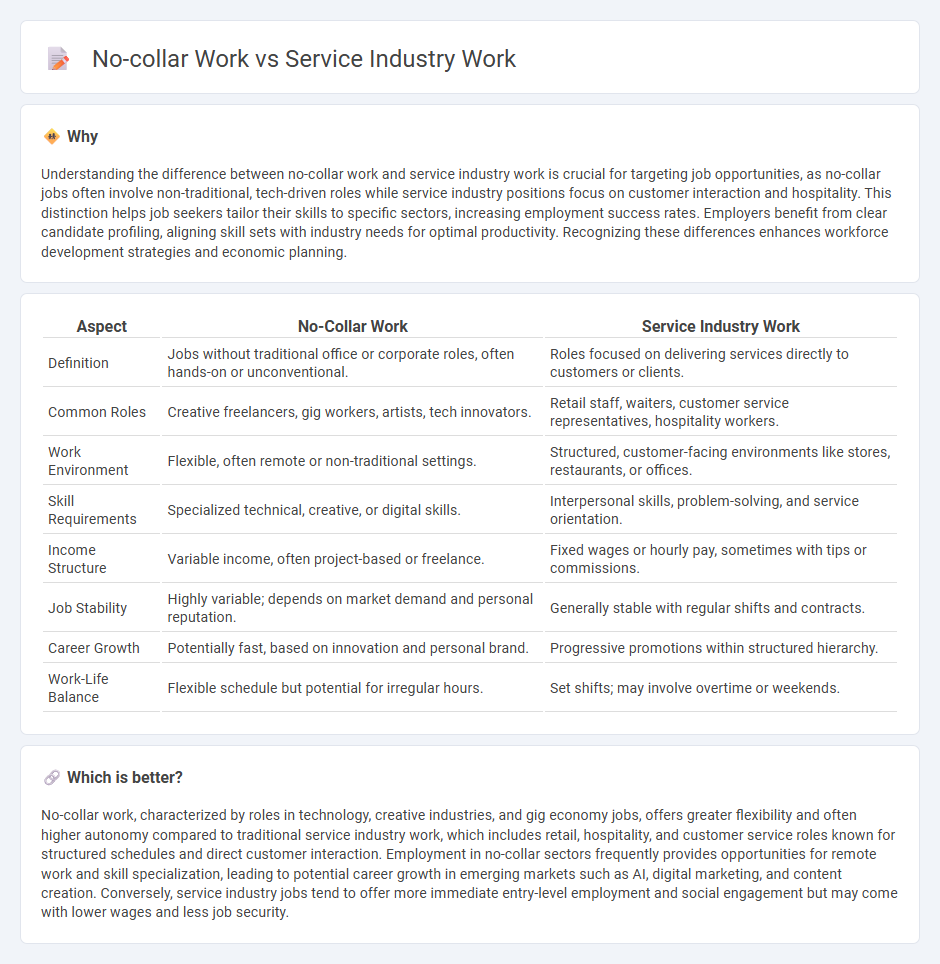
Understanding the difference between no-collar work and service industry work is crucial for targeting job opportunities, as no-collar jobs often involve non-traditional, tech-driven roles while service industry positions focus on customer interaction and hospitality. This distinction helps job seekers tailor their skills to specific sectors, increasing employment success rates. Employers benefit from clear candidate profiling, aligning skill sets with industry needs for optimal productivity. Recognizing these differences enhances workforce development strategies and economic planning.
Comparison Table
| Aspect | No-Collar Work | Service Industry Work |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Jobs without traditional office or corporate roles, often hands-on or unconventional. | Roles focused on delivering services directly to customers or clients. |
| Common Roles | Creative freelancers, gig workers, artists, tech innovators. | Retail staff, waiters, customer service representatives, hospitality workers. |
| Work Environment | Flexible, often remote or non-traditional settings. | Structured, customer-facing environments like stores, restaurants, or offices. |
| Skill Requirements | Specialized technical, creative, or digital skills. | Interpersonal skills, problem-solving, and service orientation. |
| Income Structure | Variable income, often project-based or freelance. | Fixed wages or hourly pay, sometimes with tips or commissions. |
| Job Stability | Highly variable; depends on market demand and personal reputation. | Generally stable with regular shifts and contracts. |
| Career Growth | Potentially fast, based on innovation and personal brand. | Progressive promotions within structured hierarchy. |
| Work-Life Balance | Flexible schedule but potential for irregular hours. | Set shifts; may involve overtime or weekends. |
Which is better?
No-collar work, characterized by roles in technology, creative industries, and gig economy jobs, offers greater flexibility and often higher autonomy compared to traditional service industry work, which includes retail, hospitality, and customer service roles known for structured schedules and direct customer interaction. Employment in no-collar sectors frequently provides opportunities for remote work and skill specialization, leading to potential career growth in emerging markets such as AI, digital marketing, and content creation. Conversely, service industry jobs tend to offer more immediate entry-level employment and social engagement but may come with lower wages and less job security.
Connection
No-collar work emphasizes skills and creativity over traditional office roles, aligning closely with service industry jobs that require customer interaction and problem-solving abilities. The service sector often employs no-collar workers who focus on flexible, adaptive tasks rather than rigid job descriptions. This connection drives economic growth by fostering innovation and improving customer experience across various service fields.
Key Terms
Customer Interaction
Service industry work centers on direct customer interaction, requiring strong communication skills and empathy to ensure satisfaction and repeat business. No-collar work, often associated with tech and creative sectors, may involve limited or virtual customer engagement but emphasizes innovation and problem-solving. Explore how these distinct customer interaction styles shape career paths and workplace dynamics.
Knowledge-based Tasks
Service industry work often involves routine, customer-facing tasks requiring interpersonal skills and basic problem-solving. No-collar work emphasizes knowledge-based tasks such as innovation, creativity, and advanced data analysis, driven largely by technology and intellectual capital. Explore the distinct advantages and evolving trends in knowledge-driven roles across both sectors for a comprehensive understanding.
Soft Skills
The service industry heavily relies on soft skills such as communication, empathy, and problem-solving to enhance customer satisfaction and operational efficiency. No-collar work, characterized by flexible and often technology-driven roles, demands adaptability, creativity, and emotional intelligence to navigate dynamic environments and collaborative teams. Explore deeper insights into how soft skills shape success in both sectors and impact career development.
Source and External Links
13 Service Industry Jobs (With Duties and Salaries) | Indeed.com - The service industry involves jobs that provide intangible services rather than products, including roles in travel, hospitality, finance, education, healthcare, and entertainment, requiring strong communication and customer service skills.
What Is a Service Industry? (With Examples) | Indeed.com - The service industry delivers nonmaterial goods such as consulting, education, healthcare, maintenance, and customer service, focusing on tasks useful to customers and businesses instead of tangible products.
What are positive things about the service industry? - Career Village - The service industry offers diverse career paths, emphasizes customer satisfaction, enables global reach, provides work flexibility, and makes significant social impacts in sectors like healthcare and education.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com