Labor hoarding involves maintaining employment levels despite reduced demand to preserve skilled workforce and morale, often seen during economic downturns. Automation replaces human labor with technology to increase efficiency and reduce costs but may lead to job displacement. Explore the trade-offs between labor hoarding and automation to understand their impacts on workforce dynamics and business strategy.
Why it is important
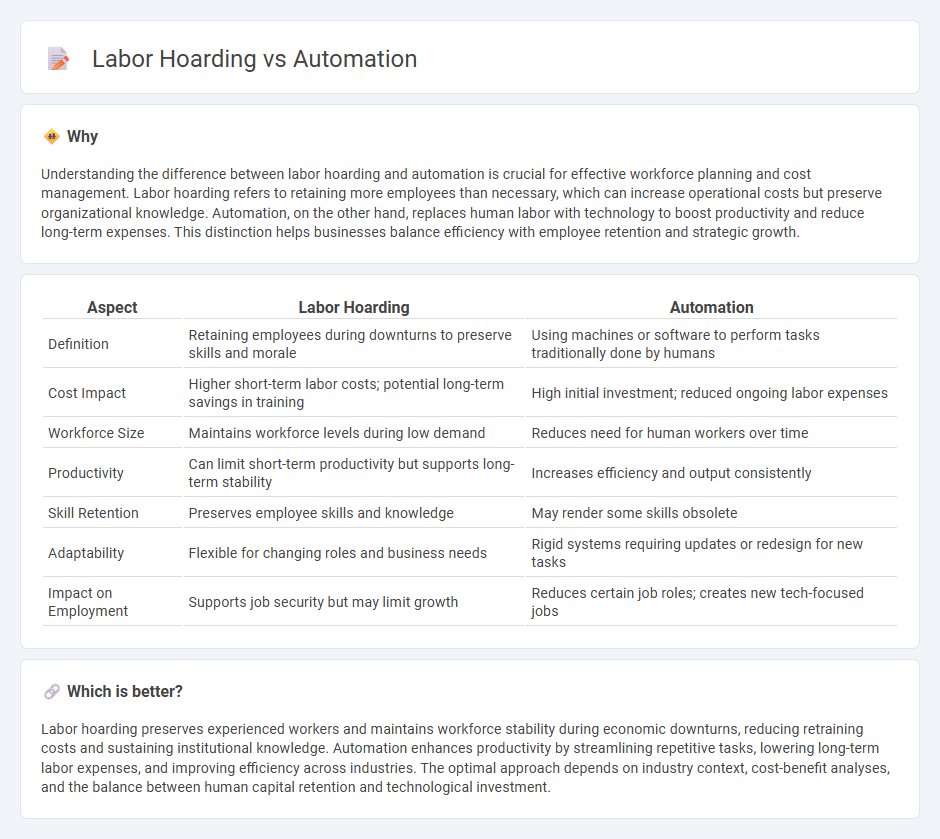
Understanding the difference between labor hoarding and automation is crucial for effective workforce planning and cost management. Labor hoarding refers to retaining more employees than necessary, which can increase operational costs but preserve organizational knowledge. Automation, on the other hand, replaces human labor with technology to boost productivity and reduce long-term expenses. This distinction helps businesses balance efficiency with employee retention and strategic growth.
Comparison Table
| Aspect | Labor Hoarding | Automation |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Retaining employees during downturns to preserve skills and morale | Using machines or software to perform tasks traditionally done by humans |
| Cost Impact | Higher short-term labor costs; potential long-term savings in training | High initial investment; reduced ongoing labor expenses |
| Workforce Size | Maintains workforce levels during low demand | Reduces need for human workers over time |
| Productivity | Can limit short-term productivity but supports long-term stability | Increases efficiency and output consistently |
| Skill Retention | Preserves employee skills and knowledge | May render some skills obsolete |
| Adaptability | Flexible for changing roles and business needs | Rigid systems requiring updates or redesign for new tasks |
| Impact on Employment | Supports job security but may limit growth | Reduces certain job roles; creates new tech-focused jobs |
Which is better?
Labor hoarding preserves experienced workers and maintains workforce stability during economic downturns, reducing retraining costs and sustaining institutional knowledge. Automation enhances productivity by streamlining repetitive tasks, lowering long-term labor expenses, and improving efficiency across industries. The optimal approach depends on industry context, cost-benefit analyses, and the balance between human capital retention and technological investment.
Connection
Labor hoarding occurs when companies retain more employees than immediately necessary to preserve skills and capacity during downturns. Automation impacts this by enabling firms to streamline operations and reduce reliance on excess labor, but it can also lead to selective hoarding of specialized human roles. The interplay between labor hoarding and automation influences workforce stability, productivity, and long-term employment strategies.
Key Terms
Workforce Optimization
Automation enhances workforce optimization by streamlining repetitive tasks and increasing productivity through advanced technologies like robotics and AI. Labor hoarding, characterized by retaining excess staff during downturns, may impede efficiency and raise operational costs without immediate revenue gains. Explore the strategic balance between automation and labor hoarding to maximize workforce potential and drive sustainable business growth.
Job Displacement
Automation often leads to job displacement as machines and algorithms replace repetitive tasks traditionally performed by human labor, reducing the demand for certain skill sets in the workforce. Labor hoarding occurs when companies retain more employees than necessary during economic downturns to preserve institutional knowledge and avoid rehiring costs, which can temporarily mitigate job losses but may impact long-term efficiency. Explore the dynamics between automation and labor hoarding to understand their complex effects on employment stability.
Productivity
Automation enhances productivity by streamlining processes, reducing human error, and enabling faster task completion compared to traditional labor-intensive methods. Labor hoarding, while preserving jobs, often leads to inefficiencies and suboptimal output during fluctuating demand periods. Explore the impact of automation versus labor hoarding on productivity to understand the optimal workforce strategy for business growth.
Source and External Links
Automation - Wikipedia - Automation refers to technologies that reduce human intervention in processes by predetermining decisions and actions, using devices ranging from mechanical to computer systems, improving efficiency and accuracy in industries like manufacturing, aviation, and banking.
What Is Automation? - IBM - Automation is the use of technology, robotics, or processes to achieve results with minimal human input, widely applied across industries to increase productivity, reduce errors, and free workers from repetitive tasks.
Understanding automation - Red Hat - Automation involves using technology to perform repetitive tasks with less human assistance, spanning IT automation, cloud automation, business process automation, robotic process automation, and industrial automation, often enhanced by AI and machine learning.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com