Ghost work involves performing tasks anonymously for clients or platforms, often via digital labor marketplaces, offering flexibility but limited job security and benefits. Self-employment grants individuals full control over their business operations and income, yet demands higher responsibility and risk management. Explore the differences further to determine which employment model suits your career goals.
Why it is important
Understanding the difference between ghost work and self-employment is crucial for workers to secure appropriate labor rights and benefits, as ghost work involves invisible, often low-paid tasks managed by platforms, while self-employment offers greater autonomy and control over one's business. Misclassifying ghost workers as self-employed can lead to disparities in minimum wage, health insurance, and social security access. Accurate classification ensures fair treatment under labor laws and protects workers from exploitation in the gig economy. Recognizing these distinctions helps policymakers design targeted employment regulations that reflect the realities of modern work environments.
Comparison Table
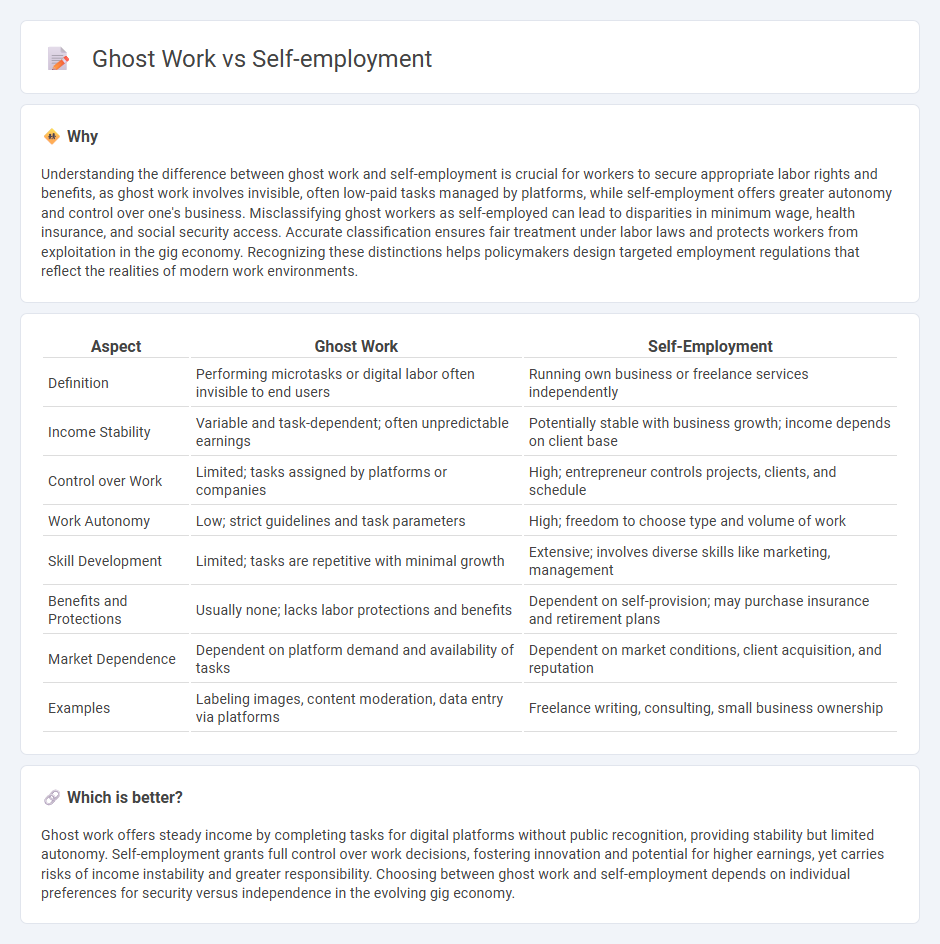
| Aspect | Ghost Work | Self-Employment |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Performing microtasks or digital labor often invisible to end users | Running own business or freelance services independently |
| Income Stability | Variable and task-dependent; often unpredictable earnings | Potentially stable with business growth; income depends on client base |
| Control over Work | Limited; tasks assigned by platforms or companies | High; entrepreneur controls projects, clients, and schedule |
| Work Autonomy | Low; strict guidelines and task parameters | High; freedom to choose type and volume of work |
| Skill Development | Limited; tasks are repetitive with minimal growth | Extensive; involves diverse skills like marketing, management |
| Benefits and Protections | Usually none; lacks labor protections and benefits | Dependent on self-provision; may purchase insurance and retirement plans |
| Market Dependence | Dependent on platform demand and availability of tasks | Dependent on market conditions, client acquisition, and reputation |
| Examples | Labeling images, content moderation, data entry via platforms | Freelance writing, consulting, small business ownership |
Which is better?
Ghost work offers steady income by completing tasks for digital platforms without public recognition, providing stability but limited autonomy. Self-employment grants full control over work decisions, fostering innovation and potential for higher earnings, yet carries risks of income instability and greater responsibility. Choosing between ghost work and self-employment depends on individual preferences for security versus independence in the evolving gig economy.
Connection
Ghost work, involving tasks performed remotely without direct recognition, often intersects with self-employment as individuals independently offer digital services on gig platforms or freelance marketplaces. This blend allows workers to control their schedules and client base while navigating the challenges of inconsistent income and limited labor protections. The rise of digital economies increasingly ties ghost work to self-employment trends, influencing labor market dynamics and employment structures.
Key Terms
Autonomy
Self-employment offers greater autonomy by allowing individuals to set their own schedules, choose projects, and control their work environment, fostering a sense of independence. In contrast, ghost work often involves performing tasks with limited visibility into the overall project, restricted decision-making power, and adherence to strict guidelines imposed by platforms or employers. Explore the nuanced differences between self-employment and ghost work to better understand how autonomy shapes each labor model.
Attribution
Self-employment offers clear attribution as individuals directly own their work and brand, establishing personal accountability and recognition for their output. Ghost work involves labor performed anonymously for companies, where the contributions remain uncredited, limiting visibility and acknowledgment. Explore deeper distinctions and implications of attribution in self-employment versus ghost work to understand their impact on worker identity and rights.
Compensation
Self-employment often offers variable income driven by client acquisition and project completion, while ghost work typically provides hourly or per-task wages set by a platform. Compensation in self-employment depends heavily on skills, reputation, and market demand, whereas ghost workers face limited earning potential due to task standardization and low transparency. Explore further to understand how compensation structures impact financial stability in both work models.
Source and External Links
Self-employment - Wikipedia - Self-employment means working for oneself rather than for an employer, with levels rising in the U.S. and contributing significantly to economic revenue and job creation, especially in non-metropolitan areas.
Self-employment | Explore Careers - CareerOneStop - Self-employment includes gig work, freelancing, and starting a business, offering flexible work tied to personal skills but requiring self-motivation and business management capabilities.
Self-employment: What to know to be your own boss : Career Outlook - Being self-employed entails being your own boss and requiring key technical skills, business knowledge, and preparation, while offering independence but also significant challenges and risks.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com