No-collar work encompasses jobs in emerging industries like technology and creative sectors where traditional office attire is uncommon, contrasting with white-collar roles typified by professional office environments and formal dress codes. The no-collar workforce often prioritizes flexibility and innovation, while white-collar employment emphasizes structured hierarchy and routine tasks. Explore the evolving dynamics and opportunities within no-collar and white-collar work to understand modern employment trends.
Why it is important
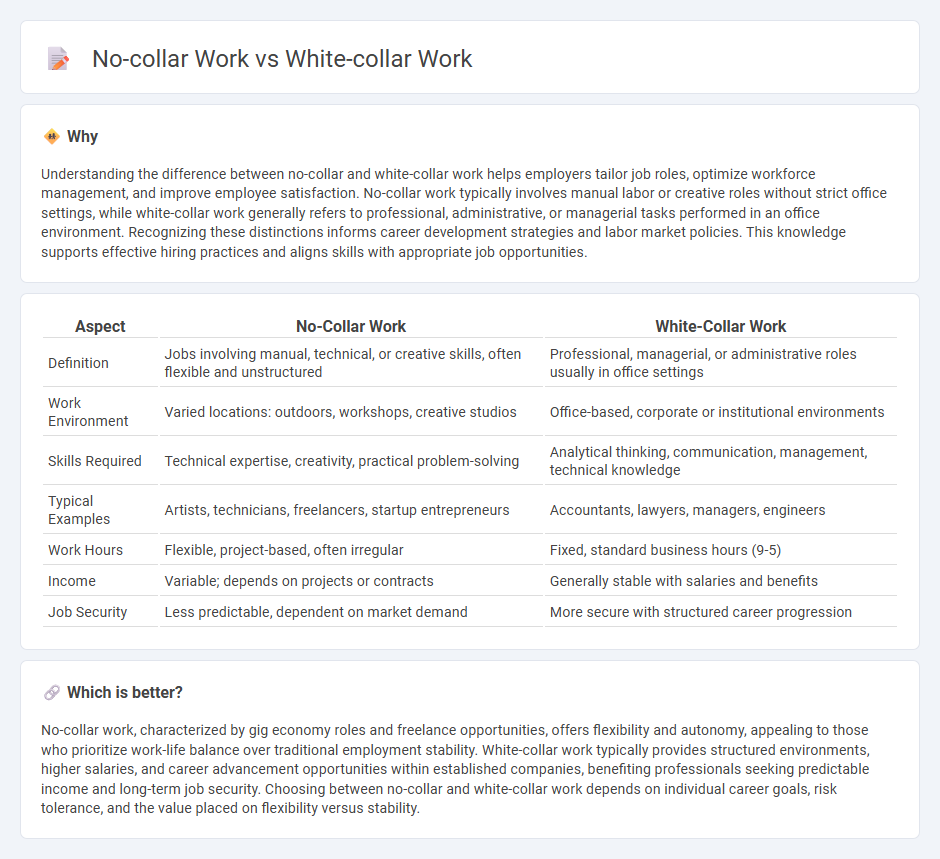
Understanding the difference between no-collar and white-collar work helps employers tailor job roles, optimize workforce management, and improve employee satisfaction. No-collar work typically involves manual labor or creative roles without strict office settings, while white-collar work generally refers to professional, administrative, or managerial tasks performed in an office environment. Recognizing these distinctions informs career development strategies and labor market policies. This knowledge supports effective hiring practices and aligns skills with appropriate job opportunities.
Comparison Table
| Aspect | No-Collar Work | White-Collar Work |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Jobs involving manual, technical, or creative skills, often flexible and unstructured | Professional, managerial, or administrative roles usually in office settings |
| Work Environment | Varied locations: outdoors, workshops, creative studios | Office-based, corporate or institutional environments |
| Skills Required | Technical expertise, creativity, practical problem-solving | Analytical thinking, communication, management, technical knowledge |
| Typical Examples | Artists, technicians, freelancers, startup entrepreneurs | Accountants, lawyers, managers, engineers |
| Work Hours | Flexible, project-based, often irregular | Fixed, standard business hours (9-5) |
| Income | Variable; depends on projects or contracts | Generally stable with salaries and benefits |
| Job Security | Less predictable, dependent on market demand | More secure with structured career progression |
Which is better?
No-collar work, characterized by gig economy roles and freelance opportunities, offers flexibility and autonomy, appealing to those who prioritize work-life balance over traditional employment stability. White-collar work typically provides structured environments, higher salaries, and career advancement opportunities within established companies, benefiting professionals seeking predictable income and long-term job security. Choosing between no-collar and white-collar work depends on individual career goals, risk tolerance, and the value placed on flexibility versus stability.
Connection
No-collar work and white-collar work intersect through the increasing integration of technology and automation in professional environments, transforming traditional office roles with digital tools and AI. Both sectors emphasize skills such as problem-solving, adaptability, and continuous learning, reflecting a shift towards more flexible and hybrid work models. The collaboration between no-collar laborers, often in creative or technical roles, and white-collar professionals drives innovation and operational efficiency across industries.
Key Terms
Office-based
White-collar work primarily involves office-based tasks such as management, administration, and professional services requiring formal education and advanced skills. No-collar work, while often associated with non-traditional or creative industries, can also include flexible office-based roles that prioritize innovation and adaptability over rigid hierarchies. Explore the evolving dynamics between white-collar and no-collar office work to understand their impact on modern workplace culture.
Gig economy
White-collar work traditionally involves office-based roles requiring specialized skills, while no-collar work in the gig economy emphasizes flexibility and project-based tasks often without formal employment contracts. The rise of platforms like Uber, Fiverr, and TaskRabbit highlights the shift toward no-collar opportunities where workers trade job security for autonomy and varied income streams. Explore how this transformation impacts career stability, worker rights, and economic trends in the evolving labor market.
Professional autonomy
White-collar work typically involves higher levels of professional autonomy, allowing employees greater control over decision-making, project management, and flexible work schedules. No-collar work, often found in creative or freelance industries, emphasizes innovation and self-direction but may lack the structured autonomy present in traditional white-collar roles. Explore the distinct nuances of professional autonomy in these work categories to understand their impact on job satisfaction and productivity.
Source and External Links
Blue Collar vs. White Collar: What's the Difference? - White-collar work generally involves mental or administrative tasks performed in office settings, requiring formal education and specialized knowledge in professional fields like finance, law, marketing, and management, typically using office equipment to perform complex intellectual or managerial duties.
White-collar worker - A white-collar worker performs knowledge-based, managerial, or administrative work usually in an office environment, encompassing professions in government, business, law, technology, and more, historically named for the white dress shirts typically worn by these workers.
What are "White-Collar" Jobs? 16 Jobs To Consider - White-collar jobs typically avoid physical labor, require education, and include roles such as customer service managers, publicists, and market researchers, who perform professional, analytical, or managerial duties in various industries.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com