Talent arbitrage leverages global labor cost differences by sourcing skilled workers from lower-cost regions to optimize operational expenses without compromising quality. The contingent workforce offers flexible, on-demand talent acquisition to address fluctuating business needs and project-specific demands with minimal long-term commitment. Discover how these strategic employment models can transform workforce management and drive organizational agility.
Why it is important
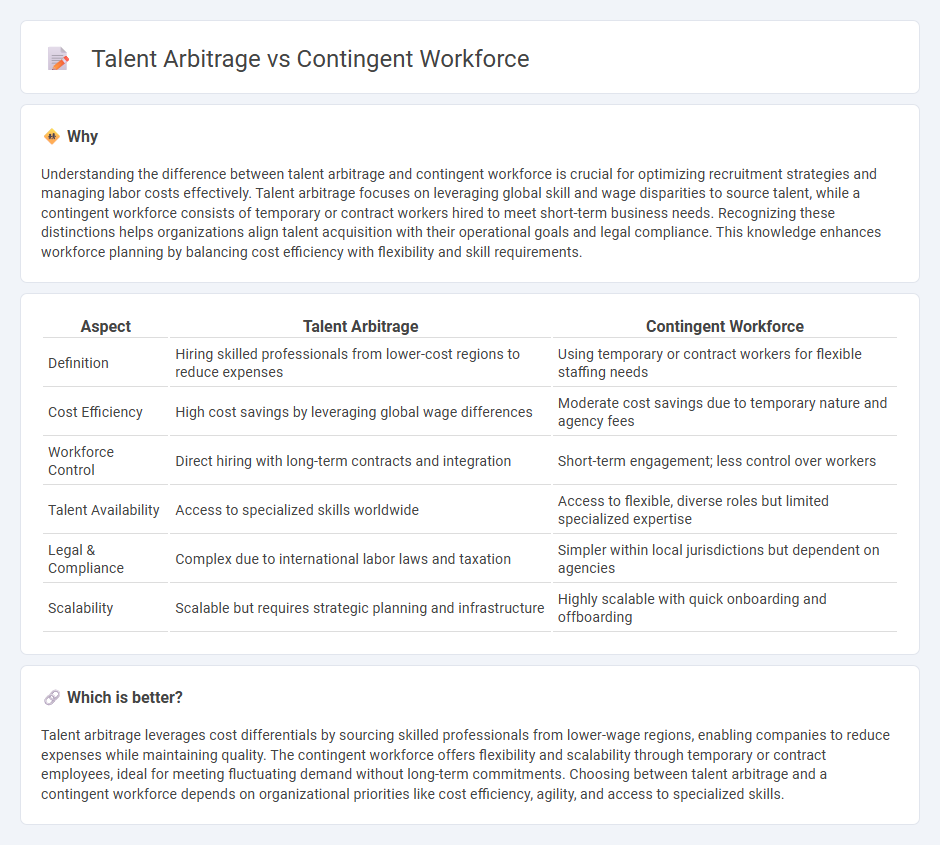
Understanding the difference between talent arbitrage and contingent workforce is crucial for optimizing recruitment strategies and managing labor costs effectively. Talent arbitrage focuses on leveraging global skill and wage disparities to source talent, while a contingent workforce consists of temporary or contract workers hired to meet short-term business needs. Recognizing these distinctions helps organizations align talent acquisition with their operational goals and legal compliance. This knowledge enhances workforce planning by balancing cost efficiency with flexibility and skill requirements.
Comparison Table
| Aspect | Talent Arbitrage | Contingent Workforce |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Hiring skilled professionals from lower-cost regions to reduce expenses | Using temporary or contract workers for flexible staffing needs |
| Cost Efficiency | High cost savings by leveraging global wage differences | Moderate cost savings due to temporary nature and agency fees |
| Workforce Control | Direct hiring with long-term contracts and integration | Short-term engagement; less control over workers |
| Talent Availability | Access to specialized skills worldwide | Access to flexible, diverse roles but limited specialized expertise |
| Legal & Compliance | Complex due to international labor laws and taxation | Simpler within local jurisdictions but dependent on agencies |
| Scalability | Scalable but requires strategic planning and infrastructure | Highly scalable with quick onboarding and offboarding |
Which is better?
Talent arbitrage leverages cost differentials by sourcing skilled professionals from lower-wage regions, enabling companies to reduce expenses while maintaining quality. The contingent workforce offers flexibility and scalability through temporary or contract employees, ideal for meeting fluctuating demand without long-term commitments. Choosing between talent arbitrage and a contingent workforce depends on organizational priorities like cost efficiency, agility, and access to specialized skills.
Connection
Talent arbitrage leverages global wage disparities by employing contingent workforce solutions, enabling companies to source skilled professionals from lower-cost regions. This strategy increases operational efficiency and reduces labor expenses through flexible, project-based staffing models. Organizations gain a competitive advantage by dynamically aligning talent supply with demand across diverse geographic markets.
Key Terms
Flexibility
Contingent workforce offers companies flexible staffing solutions by enabling rapid scaling of labor based on project demands without long-term commitments. Talent arbitrage focuses on cost efficiency by leveraging global talent pools with varied wage structures while maintaining flexibility in resource allocation. Explore the strategic benefits of flexibility in contingent workforce and talent arbitrage to optimize your business agility.
Cost Optimization
Contingent workforce involves hiring temporary or contract employees to meet fluctuating business demands, offering flexible cost control and reduced long-term liabilities. Talent arbitrage focuses on outsourcing jobs to lower-cost regions, leveraging global wage disparities to minimize expenses. Explore these strategies further to identify the best cost optimization approach for your organization.
Skill Matching
Contingent workforce strategies prioritize flexibility by matching workers' specific skills to project needs, ensuring rapid deployment and adaptability in dynamic markets. Talent arbitrage focuses on leveraging global labor cost differences by matching skills across geographies to achieve cost efficiency without compromising quality. Explore how strategic skill matching enhances workforce planning and drives competitive advantage.
Source and External Links
What Is a Contingent Workforce? - A contingent workforce consists of contractors, consultants, freelancers, and temporary workers hired on a contract basis for a defined period to fulfill specific projects or roles, offering organizations flexibility and access to specialized skills without long-term commitment.
Contingent work - Wikipedia - Contingent work refers to non-permanent employment relationships such as gig work, contract work, or part-time roles with limited job security, commonly including independent contractors, temps, and freelancers.
What is Contingent Workforce Management? - Contingent workforce management involves the strategic hiring and overseeing of non-permanent workers like temporary agency staff and independent contractors using tools such as vendor management systems (VMS) to efficiently manage flexible labor resources.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com