Digital nomad visas offer remote professionals legal permission to live and work temporarily in foreign countries without local employment restrictions. Work permits, typically tied to specific employers, grant foreigners the right to engage in on-site jobs within host nations under regulated terms. Explore the distinct advantages and application processes of digital nomad visas versus traditional work permits to determine the best fit for your international career goals.
Why it is important
Understanding the difference between digital nomad visas and work permits is crucial for legal employment and tax compliance across countries. Digital nomad visas allow remote workers to live and work legally without engaging in the local job market, often with simplified tax obligations. Work permits grant authorization to physically work for employers in the host country, subject to local labor laws and tax systems. Knowing these distinctions helps avoid legal penalties and ensures proper employment benefits and taxation.
Comparison Table
| Aspect | Digital Nomad Visas | Work Permits |
|---|---|---|
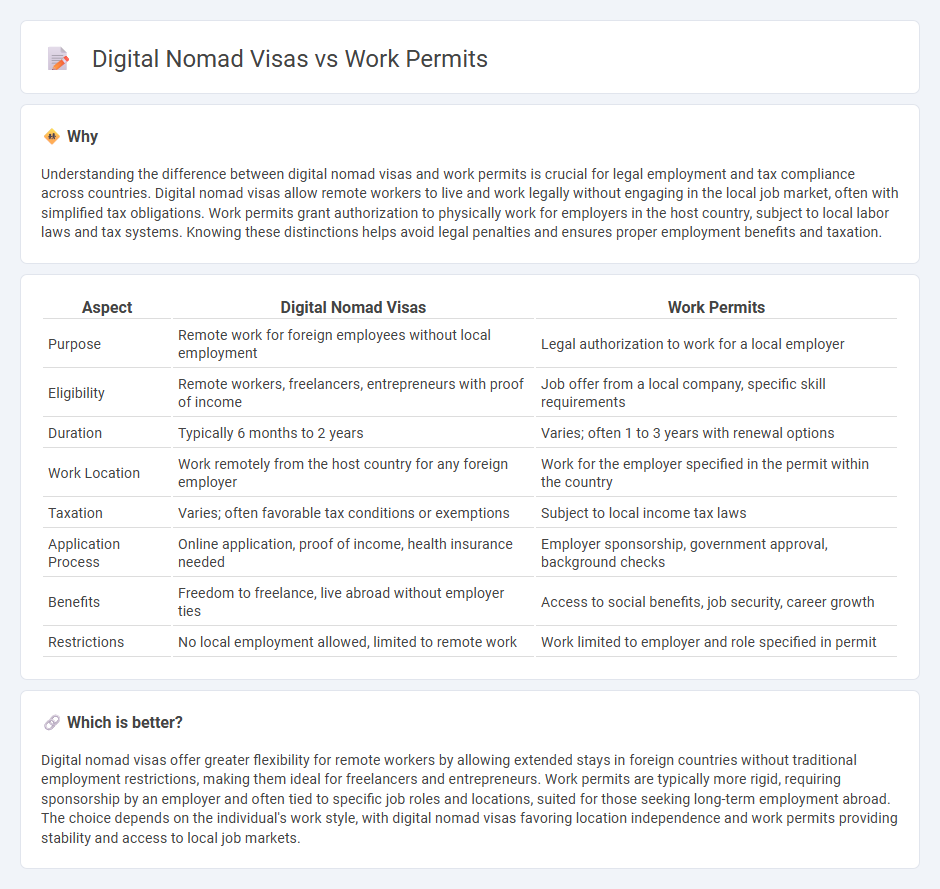
| Purpose | Remote work for foreign employees without local employment | Legal authorization to work for a local employer |
| Eligibility | Remote workers, freelancers, entrepreneurs with proof of income | Job offer from a local company, specific skill requirements |
| Duration | Typically 6 months to 2 years | Varies; often 1 to 3 years with renewal options |
| Work Location | Work remotely from the host country for any foreign employer | Work for the employer specified in the permit within the country |
| Taxation | Varies; often favorable tax conditions or exemptions | Subject to local income tax laws |
| Application Process | Online application, proof of income, health insurance needed | Employer sponsorship, government approval, background checks |
| Benefits | Freedom to freelance, live abroad without employer ties | Access to social benefits, job security, career growth |
| Restrictions | No local employment allowed, limited to remote work | Work limited to employer and role specified in permit |
Which is better?
Digital nomad visas offer greater flexibility for remote workers by allowing extended stays in foreign countries without traditional employment restrictions, making them ideal for freelancers and entrepreneurs. Work permits are typically more rigid, requiring sponsorship by an employer and often tied to specific job roles and locations, suited for those seeking long-term employment abroad. The choice depends on the individual's work style, with digital nomad visas favoring location independence and work permits providing stability and access to local job markets.
Connection
Digital nomad visas and work permits facilitate remote work by legally allowing individuals to reside and work in foreign countries without traditional local employment contracts. These permits are designed to attract global talent, boosting local economies through increased spending and cultural exchange. The synergy between digital nomad visas and work permits creates flexible employment opportunities while ensuring compliance with immigration and labor regulations.
Key Terms
Authorization
Work permits grant foreign nationals legal authorization to work within a specific country, usually tied to a particular employer and duration. Digital nomad visas provide flexible legal permission for remote workers to reside and work digitally from a host country without traditional employment restrictions. Explore the detailed differences in authorization criteria to determine which option best suits your professional and lifestyle needs.
Remote Work
Work permits typically require employer sponsorship and limit remote work to specific countries or roles, while digital nomad visas allow individuals to live and work remotely from a foreign country without local employment restrictions. Digital nomad visas often provide greater flexibility for remote professionals, freelancers, and entrepreneurs seeking to maintain their home employment status while experiencing new cultures. Explore the key differences and advantages of both options to determine the best path for your remote work lifestyle.
Residency
Work permits often require employer sponsorship and typically restrict the holder to specific job roles within the host country, ensuring legal residency tied directly to employment status. In contrast, digital nomad visas grant temporary residency based on remote work capabilities without local job sponsorship, offering greater flexibility for location-independent professionals. Explore detailed comparisons of residency rights, application processes, and duration to determine which option best suits your global mobility needs.
Source and External Links
Work in the U.S. with a work permit (EAD) | USAGov - To work in the U.S. as a nonimmigrant, you may apply for a work permit (Employment Authorization Document, EAD) by filing Form I-765, which allows employment for any employer typically for 1 or 2 years depending on your category.
Working in the United States | USCIS - Work permits often require a petition filed by a U.S. employer with USCIS for temporary nonimmigrant workers, and eligibility depends on visa status and job classification, with permanent work possible through employment-based immigrant visas.
Work Permits for Minors - Jefferson Parish Schools - Minors aged 14-17 must have a work permit to be employed, which requires a job offer, completed paperwork, and official ID, issued during specified hours at designated locations.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com