Companies often struggle to balance ghost jobs--positions advertised but never intended to be filled--with internal hiring strategies that prioritize existing employees. Ghost jobs create inefficiencies in the recruitment process, whereas internal hiring boosts employee retention and morale by offering career advancement opportunities. Discover how organizations can optimize staffing by understanding the impact of ghost jobs and leveraging internal talent pipelines.
Why it is important
Understanding the difference between ghost jobs and internal hiring is crucial for accurate labor market analysis and effective workforce planning. Ghost jobs, which are fictitious job postings, can distort employment data and mislead job seekers about actual opportunities. Internal hiring focuses on promoting current employees, enhancing retention and organizational culture. Recognizing these distinctions helps employers optimize recruitment strategies and candidates make informed career decisions.
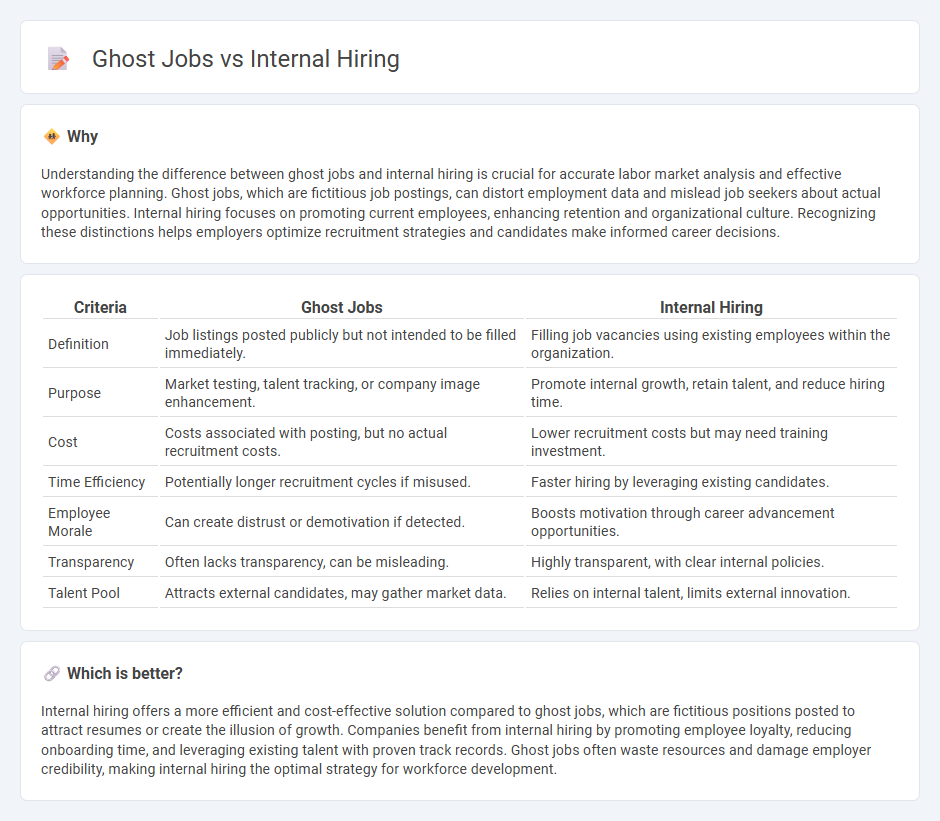
Comparison Table
| Criteria | Ghost Jobs | Internal Hiring |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Job listings posted publicly but not intended to be filled immediately. | Filling job vacancies using existing employees within the organization. |
| Purpose | Market testing, talent tracking, or company image enhancement. | Promote internal growth, retain talent, and reduce hiring time. |
| Cost | Costs associated with posting, but no actual recruitment costs. | Lower recruitment costs but may need training investment. |
| Time Efficiency | Potentially longer recruitment cycles if misused. | Faster hiring by leveraging existing candidates. |
| Employee Morale | Can create distrust or demotivation if detected. | Boosts motivation through career advancement opportunities. |
| Transparency | Often lacks transparency, can be misleading. | Highly transparent, with clear internal policies. |
| Talent Pool | Attracts external candidates, may gather market data. | Relies on internal talent, limits external innovation. |
Which is better?
Internal hiring offers a more efficient and cost-effective solution compared to ghost jobs, which are fictitious positions posted to attract resumes or create the illusion of growth. Companies benefit from internal hiring by promoting employee loyalty, reducing onboarding time, and leveraging existing talent with proven track records. Ghost jobs often waste resources and damage employer credibility, making internal hiring the optimal strategy for workforce development.
Connection
Ghost jobs, defined as unadvertised positions existing mainly to create the illusion of opportunity, often overlap with internal hiring processes where companies prioritize promoting current employees. This strategy enhances talent retention and reduces recruitment costs by filling roles internally rather than seeking external candidates, aligning workforce planning with corporate culture. By leveraging ghost jobs through internal hiring, organizations streamline succession planning and ensure a motivated workforce ready for advancement.
Key Terms
Talent Pipeline
Internal hiring enhances talent pipeline strength by promoting employee growth and retention, ensuring a skilled and motivated workforce. Ghost jobs misrepresent organizational needs, creating confusion and inefficiency in talent acquisition processes. Discover effective strategies to optimize your talent pipeline and avoid pitfalls associated with ghost jobs.
Job Transparency
Internal hiring practices enhance job transparency by openly communicating available positions to current employees, fostering trust and career growth within an organization. In contrast, ghost jobs--positions advertised without intent to fill--obfuscate hiring processes and mislead candidates, undermining employer credibility. Explore more about how transparent hiring can transform workforce dynamics and boost employee engagement.
Workforce Mobility
Internal hiring enhances workforce mobility by promoting talent development and retention within the organization, ensuring employees have access to growth opportunities. Ghost jobs, or unadvertised positions, hinder transparency and limit employee movement by restricting access to open roles. Explore effective strategies to balance internal hiring and workforce mobility for organizational success.
Source and External Links
8 Internal Recruitment Methods You Need to Know - This article highlights eight internal recruitment methods, including promotions, transfers, and hiring former employees, to utilize existing talent within a company.
HR Glossary | What is Internal Hiring? - This resource defines internal hiring as filling open positions with existing employees, noting benefits such as reduced recruitment costs and improved employee engagement.
Internal Hiring Factbook - This factbook discusses the benefits of internal hiring, including reduced hiring timelines and increased employee retention, offering insights into its impact on company performance.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com