Blue collar tech jobs involve hands-on, skilled labor roles such as equipment maintenance, manufacturing, and technical installations, often requiring physical presence at worksites. Remote workers typically engage in digital or knowledge-based tasks like software development, customer support, or marketing, leveraging internet connectivity to perform their duties from any location. Explore more to understand how these employment types impact productivity and career growth.
Why it is important
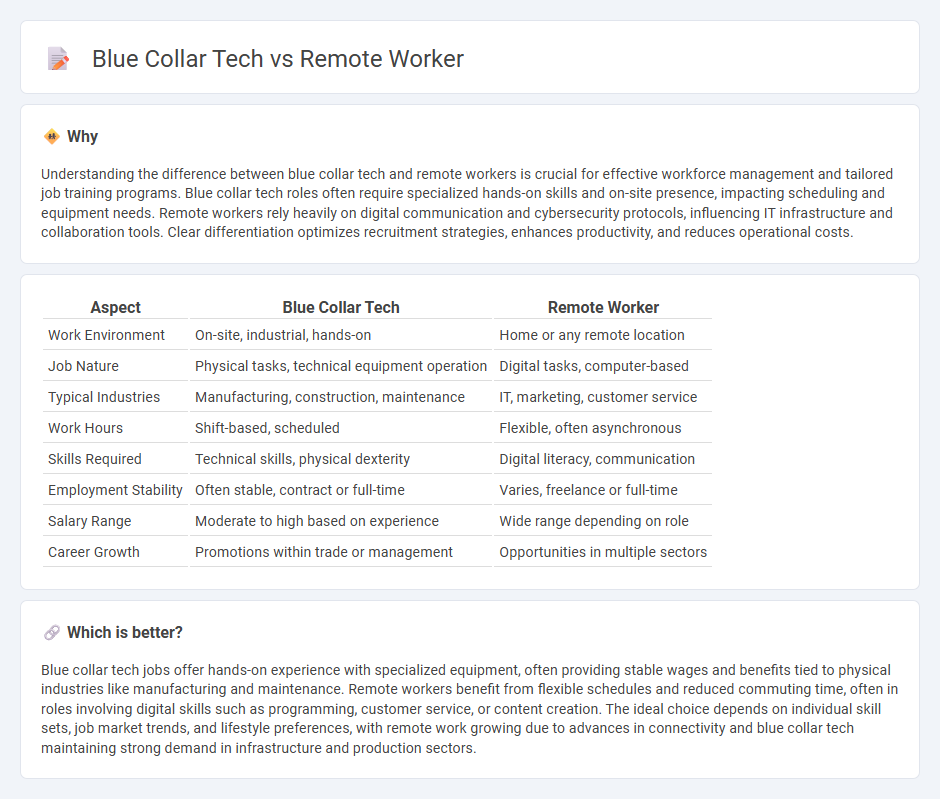
Understanding the difference between blue collar tech and remote workers is crucial for effective workforce management and tailored job training programs. Blue collar tech roles often require specialized hands-on skills and on-site presence, impacting scheduling and equipment needs. Remote workers rely heavily on digital communication and cybersecurity protocols, influencing IT infrastructure and collaboration tools. Clear differentiation optimizes recruitment strategies, enhances productivity, and reduces operational costs.
Comparison Table
| Aspect | Blue Collar Tech | Remote Worker |
|---|---|---|
| Work Environment | On-site, industrial, hands-on | Home or any remote location |
| Job Nature | Physical tasks, technical equipment operation | Digital tasks, computer-based |
| Typical Industries | Manufacturing, construction, maintenance | IT, marketing, customer service |
| Work Hours | Shift-based, scheduled | Flexible, often asynchronous |
| Skills Required | Technical skills, physical dexterity | Digital literacy, communication |
| Employment Stability | Often stable, contract or full-time | Varies, freelance or full-time |
| Salary Range | Moderate to high based on experience | Wide range depending on role |
| Career Growth | Promotions within trade or management | Opportunities in multiple sectors |
Which is better?
Blue collar tech jobs offer hands-on experience with specialized equipment, often providing stable wages and benefits tied to physical industries like manufacturing and maintenance. Remote workers benefit from flexible schedules and reduced commuting time, often in roles involving digital skills such as programming, customer service, or content creation. The ideal choice depends on individual skill sets, job market trends, and lifestyle preferences, with remote work growing due to advances in connectivity and blue collar tech maintaining strong demand in infrastructure and production sectors.
Connection
Blue collar tech workers leverage specialized skills in trades and technology, enabling them to perform remote tasks such as equipment monitoring, technical support, and system diagnostics through digital platforms. Remote work expands employment opportunities for blue collar tech professionals by reducing geographical barriers and facilitating flexible work environments. Integration of IoT devices and cloud computing enhances remote management and collaboration, strengthening the connection between blue collar tech roles and remote work models.
Key Terms
Work Location
Remote workers primarily operate from home or satellite offices, leveraging digital tools and internet connectivity to perform tasks across various industries. Blue collar tech employees usually work on-site in industrial, construction, or maintenance environments, using specialized machinery and hands-on technical skills. Explore the nuances of work location dynamics between remote professionals and blue collar tech workers for deeper insights.
Skill Set
Remote workers primarily emphasize digital skills such as software proficiency, communication tools, and self-management competencies essential for virtual collaboration. Blue collar tech workers combine traditional hands-on abilities with emerging technologies like automation, IoT, and advanced machinery operation, requiring physical presence and technical expertise. Explore detailed skill set comparisons to understand how these roles evolve in today's tech-driven labor market.
Compensation Structure
Remote workers often receive a compensation structure based on salaries or hourly rates tied to digital roles, with bonuses linked to project completion or performance metrics. Blue collar tech roles typically feature hourly wages with overtime pay, union-negotiated benefits, and skill-based pay scales reflecting hands-on technical expertise. Discover more about how these compensation models impact worker satisfaction and industry trends.
Source and External Links
Q&A: What Is Remote Work? - Remote work, also known as telecommuting or working from home, refers to work done outside a traditional office environment, allowing employees to perform tasks flexibly without daily commuting.
The Remote Work Paradox: Higher Engagement, Lower ... - Remote workers tend to be more engaged at work due to increased autonomy and flexibility but often experience isolation, stress, and emotional strain that employers should address.
What is the definition of remote work? - Remote work is a flexible arrangement where employees perform their duties at an alternative worksite away from the main agency office, typically under a formal remote work agreement.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com