Sustainability benchmarking evaluates an organization's environmental and social performance against industry standards to identify gaps and opportunities for improvement. Materiality analysis prioritizes the most significant sustainability issues based on stakeholder impact and business relevance, guiding strategic decision-making. Explore how integrating both methodologies enhances comprehensive sustainability strategies.
Why it is important
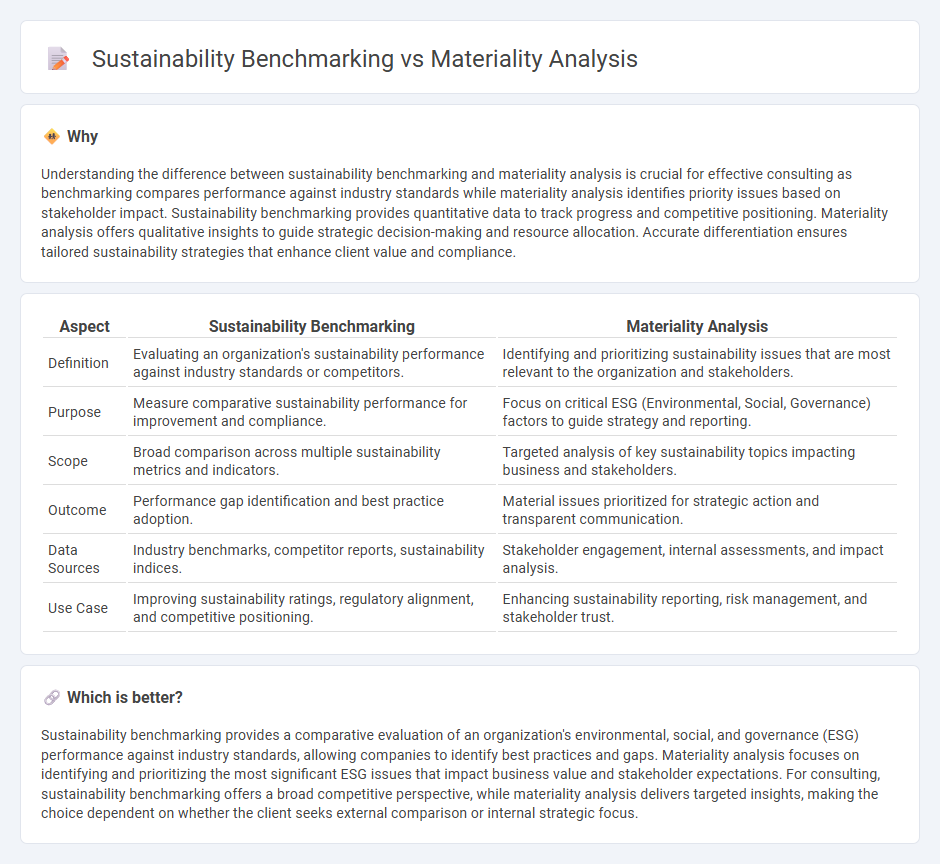
Understanding the difference between sustainability benchmarking and materiality analysis is crucial for effective consulting as benchmarking compares performance against industry standards while materiality analysis identifies priority issues based on stakeholder impact. Sustainability benchmarking provides quantitative data to track progress and competitive positioning. Materiality analysis offers qualitative insights to guide strategic decision-making and resource allocation. Accurate differentiation ensures tailored sustainability strategies that enhance client value and compliance.
Comparison Table
| Aspect | Sustainability Benchmarking | Materiality Analysis |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Evaluating an organization's sustainability performance against industry standards or competitors. | Identifying and prioritizing sustainability issues that are most relevant to the organization and stakeholders. |
| Purpose | Measure comparative sustainability performance for improvement and compliance. | Focus on critical ESG (Environmental, Social, Governance) factors to guide strategy and reporting. |
| Scope | Broad comparison across multiple sustainability metrics and indicators. | Targeted analysis of key sustainability topics impacting business and stakeholders. |
| Outcome | Performance gap identification and best practice adoption. | Material issues prioritized for strategic action and transparent communication. |
| Data Sources | Industry benchmarks, competitor reports, sustainability indices. | Stakeholder engagement, internal assessments, and impact analysis. |
| Use Case | Improving sustainability ratings, regulatory alignment, and competitive positioning. | Enhancing sustainability reporting, risk management, and stakeholder trust. |
Which is better?
Sustainability benchmarking provides a comparative evaluation of an organization's environmental, social, and governance (ESG) performance against industry standards, allowing companies to identify best practices and gaps. Materiality analysis focuses on identifying and prioritizing the most significant ESG issues that impact business value and stakeholder expectations. For consulting, sustainability benchmarking offers a broad competitive perspective, while materiality analysis delivers targeted insights, making the choice dependent on whether the client seeks external comparison or internal strategic focus.
Connection
Sustainability benchmarking and materiality analysis are connected through their focus on identifying and prioritizing environmental, social, and governance (ESG) issues that impact business performance and stakeholder value. Materiality analysis determines the most relevant sustainability topics for a company, while benchmarking compares these factors against industry standards and competitors to assess performance gaps. Together, they enable organizations to develop strategic sustainability initiatives aligned with material ESG priorities and best practices.
Key Terms
Stakeholder Engagement
Materiality analysis identifies and prioritizes environmental, social, and governance (ESG) issues based on stakeholder input to align corporate strategy with stakeholder concerns. Sustainability benchmarking compares a company's ESG performance against industry peers, highlighting areas for improvement by analyzing metrics such as carbon emissions, diversity rates, and governance practices. Explore how effective stakeholder engagement drives both processes for deeper insights and strategic sustainability.
Key Performance Indicators (KPIs)
Materiality analysis identifies the most significant environmental, social, and governance (ESG) issues that impact a company's long-term value and stakeholder interests, guiding strategic focus towards relevant Key Performance Indicators (KPIs). Sustainability benchmarking compares a company's ESG performance against industry peers and standards, highlighting strengths and gaps through quantifiable KPIs to drive continuous improvement. Explore how integrating materiality analysis with sustainability benchmarking can optimize your KPI-driven sustainability strategy.
Industry Standards
Materiality analysis identifies and prioritizes environmental, social, and governance (ESG) issues most relevant to a company's business impact and stakeholder concerns, aligning strategies with key industry risks and opportunities. Sustainability benchmarking measures a company's performance against established industry standards, regulatory frameworks, and peer organizations to gauge competitive positioning and compliance. Explore how integrating materiality analysis with sustainability benchmarking can enhance strategic decision-making and drive industry leadership.
Source and External Links
Materiality Analysis Definition - Youmatter - A materiality analysis is a method used by organizations to identify and prioritize the most important environmental, social, and governance (ESG) issues that impact both business success and stakeholder expectations, typically visualized in a materiality matrix.
Materiality Assessment: definition, guidelines, and examples - Materiality assessment systematically identifies relevant ESG topics for a company, forms the foundation for sustainability management and nonfinancial reporting, and is increasingly required for compliance with regulations like the CSRD, which mandates independent audits of sustainability reports based on materiality analysis.
How is a materiality analysis prepared? - APLANET - Preparing a materiality analysis involves defining stakeholder groups, benchmarking against industry peers, and prioritizing sustainability issues to guide informed decision-making and risk management.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com