Dark pattern compliance focuses on designing user interfaces that obscure or manipulate consent to maximize data collection, often conflicting with ethical standards. Data minimization emphasizes collecting only essential user information, aligning with regulations like GDPR to protect privacy and enhance trust. Explore the balance between ethical consulting practices and regulatory compliance to optimize user data strategies.
Why it is important
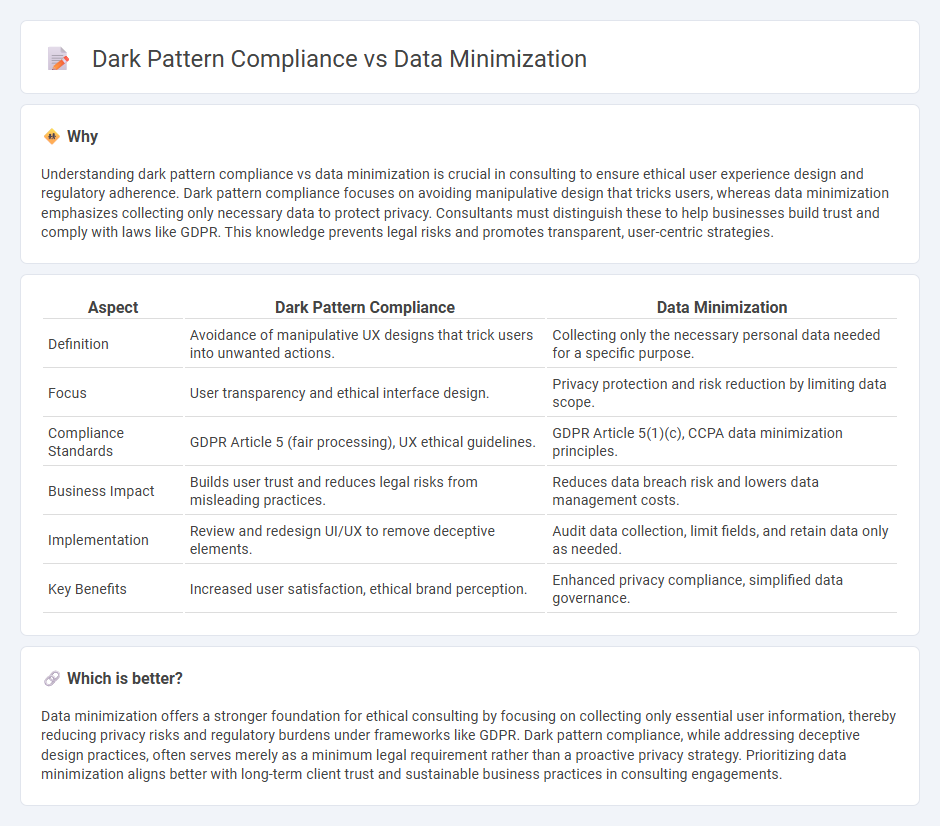
Understanding dark pattern compliance vs data minimization is crucial in consulting to ensure ethical user experience design and regulatory adherence. Dark pattern compliance focuses on avoiding manipulative design that tricks users, whereas data minimization emphasizes collecting only necessary data to protect privacy. Consultants must distinguish these to help businesses build trust and comply with laws like GDPR. This knowledge prevents legal risks and promotes transparent, user-centric strategies.
Comparison Table
| Aspect | Dark Pattern Compliance | Data Minimization |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Avoidance of manipulative UX designs that trick users into unwanted actions. | Collecting only the necessary personal data needed for a specific purpose. |
| Focus | User transparency and ethical interface design. | Privacy protection and risk reduction by limiting data scope. |
| Compliance Standards | GDPR Article 5 (fair processing), UX ethical guidelines. | GDPR Article 5(1)(c), CCPA data minimization principles. |
| Business Impact | Builds user trust and reduces legal risks from misleading practices. | Reduces data breach risk and lowers data management costs. |
| Implementation | Review and redesign UI/UX to remove deceptive elements. | Audit data collection, limit fields, and retain data only as needed. |
| Key Benefits | Increased user satisfaction, ethical brand perception. | Enhanced privacy compliance, simplified data governance. |
Which is better?
Data minimization offers a stronger foundation for ethical consulting by focusing on collecting only essential user information, thereby reducing privacy risks and regulatory burdens under frameworks like GDPR. Dark pattern compliance, while addressing deceptive design practices, often serves merely as a minimum legal requirement rather than a proactive privacy strategy. Prioritizing data minimization aligns better with long-term client trust and sustainable business practices in consulting engagements.
Connection
Dark pattern compliance directly impacts data minimization by enforcing user-friendly interfaces that avoid deceptive tactics designed to collect excessive personal data. Effective data minimization strategies reduce the risk of non-compliance with regulations such as GDPR by limiting data collection to only what is necessary, thereby mitigating potential privacy violations associated with dark patterns. Consulting services help organizations align dark pattern compliance with data minimization principles to enhance ethical data practices and regulatory adherence.
Key Terms
Informed Consent
Data minimization enhances informed consent by limiting personal data collection to what is necessary, reducing user exposure and ensuring transparency. In contrast, dark pattern compliance can manipulate consent dialogs to obscure true data use, undermining genuine user understanding and control. Explore effective strategies to balance user privacy and ethical design practices for informed consent.
Purpose Limitation
Data minimization ensures that only necessary personal information is collected, aligning with the principle of Purpose Limitation by restricting data use to specific, explicit objectives. Dark pattern compliance requires avoiding deceptive design techniques that coerce users into oversharing data, thereby reinforcing transparency and clear purpose communication. Explore more insights into balancing ethical data practices with regulatory compliance.
User Autonomy
Data minimization ensures that only essential user information is collected, reducing privacy risks and enhancing user control over personal data. Dark pattern compliance involves eliminating deceptive design practices that manipulate users into sharing more data than intended, thereby supporting ethical standards and maintaining trust. Explore how prioritizing user autonomy can transform data privacy strategies while fostering transparent digital experiences.
Source and External Links
What is Data Minimization? Main Principles & Techniques - Data minimization is a key privacy principle involving collecting and retaining only the minimal necessary personal information, with techniques such as data masking and strict data retention policies to protect sensitive data and ensure timely deletion when no longer needed.
What is Data Minimization and Why is it Important? - Data minimization limits data collection and retention to only what is necessary, which reduces storage costs, enhances security by shrinking the attack surface, improves data quality, streamlines data management, and helps comply with regulations like GDPR.
Data minimization - Wikipedia - Data minimization is the principle of collecting, processing, and storing only the necessary amount of personal data for a specific purpose, reducing risks like identity theft, and is embedded in major regulations worldwide including the GDPR, UK GDPR, and several frameworks in the US, Canada, and the Asia-Pacific region.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com