Outside-in benchmarking compares an organization's performance against industry leaders outside its direct market to uncover innovative practices and competitive advantages. Generic benchmarking evaluates processes and performance metrics against best practices irrespective of the industry, aiming to identify universal improvements. Explore how these benchmarking approaches can transform your consulting strategy and drive superior results.
Why it is important
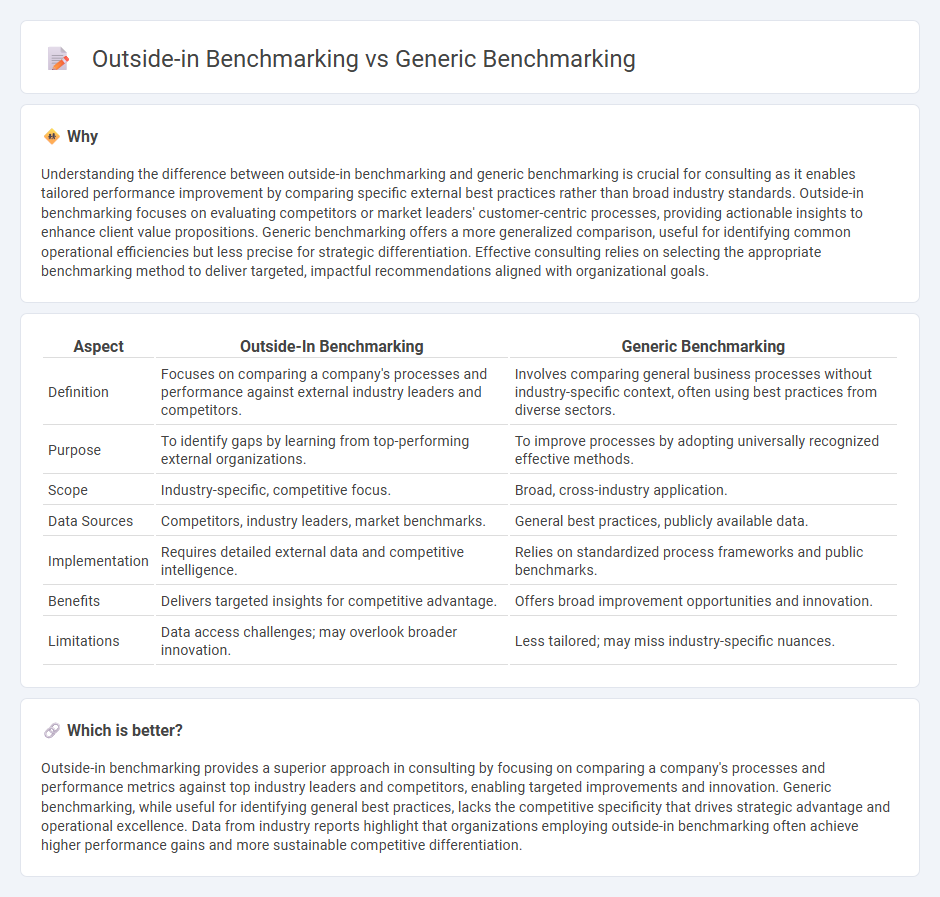
Understanding the difference between outside-in benchmarking and generic benchmarking is crucial for consulting as it enables tailored performance improvement by comparing specific external best practices rather than broad industry standards. Outside-in benchmarking focuses on evaluating competitors or market leaders' customer-centric processes, providing actionable insights to enhance client value propositions. Generic benchmarking offers a more generalized comparison, useful for identifying common operational efficiencies but less precise for strategic differentiation. Effective consulting relies on selecting the appropriate benchmarking method to deliver targeted, impactful recommendations aligned with organizational goals.
Comparison Table
| Aspect | Outside-In Benchmarking | Generic Benchmarking |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Focuses on comparing a company's processes and performance against external industry leaders and competitors. | Involves comparing general business processes without industry-specific context, often using best practices from diverse sectors. |
| Purpose | To identify gaps by learning from top-performing external organizations. | To improve processes by adopting universally recognized effective methods. |
| Scope | Industry-specific, competitive focus. | Broad, cross-industry application. |
| Data Sources | Competitors, industry leaders, market benchmarks. | General best practices, publicly available data. |
| Implementation | Requires detailed external data and competitive intelligence. | Relies on standardized process frameworks and public benchmarks. |
| Benefits | Delivers targeted insights for competitive advantage. | Offers broad improvement opportunities and innovation. |
| Limitations | Data access challenges; may overlook broader innovation. | Less tailored; may miss industry-specific nuances. |
Which is better?
Outside-in benchmarking provides a superior approach in consulting by focusing on comparing a company's processes and performance metrics against top industry leaders and competitors, enabling targeted improvements and innovation. Generic benchmarking, while useful for identifying general best practices, lacks the competitive specificity that drives strategic advantage and operational excellence. Data from industry reports highlight that organizations employing outside-in benchmarking often achieve higher performance gains and more sustainable competitive differentiation.
Connection
Outside-in benchmarking involves comparing an organization's processes and performance metrics against external industry leaders, providing a holistic perspective on best practices. Generic benchmarking focuses on evaluating common processes across different industries to identify universal operational improvements. By integrating outside-in benchmarking with generic benchmarking, companies gain a comprehensive understanding of both external competitive standards and cross-industry efficiencies, driving strategic and operational excellence.
Key Terms
Best Practices
Generic benchmarking involves comparing business processes and performance metrics against industry standards or competitors to identify areas for improvement. Outside-in benchmarking specifically focuses on adopting best practices from leading companies outside the immediate industry to drive innovation and enhance competitive advantage. Explore how leveraging these benchmarking strategies can optimize your organization's performance and strategic growth.
Industry Standards
Generic benchmarking compares processes and performance metrics across diverse industries to identify best practices and foster innovation beyond sector boundaries. Outside-in benchmarking specifically evaluates a company's performance against industry standards and top competitors to align strategies with market leaders and customer expectations. Explore detailed methodologies and impact analyses to enhance your benchmarking approach effectively.
External Comparison
Generic benchmarking involves comparing internal processes and performance metrics against industry best practices broadly, whereas outside-in benchmarking specifically emphasizes external comparison by analyzing competitors and market leaders to gain strategic insights. This method leverages data from outside the organization to identify performance gaps and innovation opportunities relative to market trends and customer expectations. Explore further to understand how outside-in benchmarking can transform your competitive strategy.
Source and External Links
Generic Benchmarking - Generic benchmarking is the process of comparing a company or product's performance against another in the same industry, focusing on metrics like market share, profitability, or customer satisfaction to identify improvement areas.
What Is Generic Benchmarking? (Plus Other Benchmarking Types) - Generic benchmarking compares general business functions such as administrative processes or hiring practices across companies in different industries to gain broad perspectives and innovative ideas beyond industry boundaries.
Manufacturing Benchmarking Guide: Benefits, Types, and More - Generic benchmarking involves comparing high-level work processes or conceptual outcomes across companies and industries, emphasizing broad marketplace standards like cultural competence or environmental sustainability rather than industry-specific measures.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com