Ethical supply chains prioritize transparency, labor rights, and environmental impact to ensure responsible sourcing and fair treatment throughout the production process. Circular supply chains focus on resource efficiency by designing products for reuse, recycling, and reduction of waste, promoting sustainability through closed-loop systems. Explore how integrating both approaches can optimize your business's social responsibility and environmental performance.
Why it is important
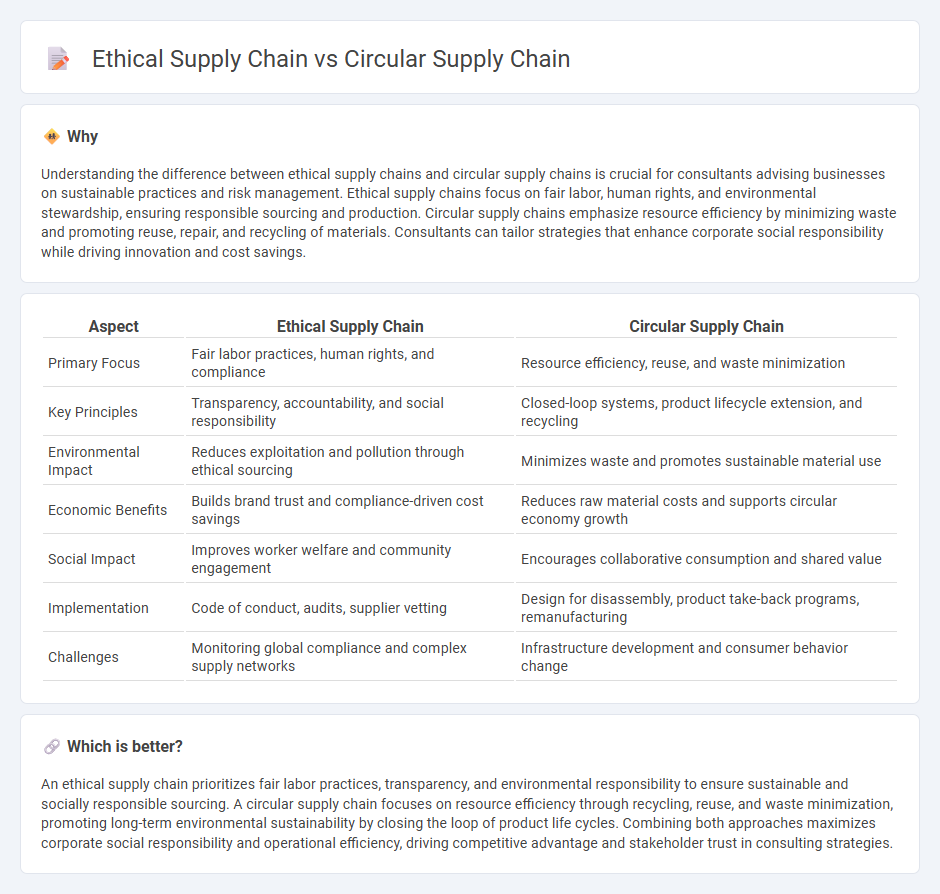
Understanding the difference between ethical supply chains and circular supply chains is crucial for consultants advising businesses on sustainable practices and risk management. Ethical supply chains focus on fair labor, human rights, and environmental stewardship, ensuring responsible sourcing and production. Circular supply chains emphasize resource efficiency by minimizing waste and promoting reuse, repair, and recycling of materials. Consultants can tailor strategies that enhance corporate social responsibility while driving innovation and cost savings.
Comparison Table
| Aspect | Ethical Supply Chain | Circular Supply Chain |
|---|---|---|
| Primary Focus | Fair labor practices, human rights, and compliance | Resource efficiency, reuse, and waste minimization |
| Key Principles | Transparency, accountability, and social responsibility | Closed-loop systems, product lifecycle extension, and recycling |
| Environmental Impact | Reduces exploitation and pollution through ethical sourcing | Minimizes waste and promotes sustainable material use |
| Economic Benefits | Builds brand trust and compliance-driven cost savings | Reduces raw material costs and supports circular economy growth |
| Social Impact | Improves worker welfare and community engagement | Encourages collaborative consumption and shared value |
| Implementation | Code of conduct, audits, supplier vetting | Design for disassembly, product take-back programs, remanufacturing |
| Challenges | Monitoring global compliance and complex supply networks | Infrastructure development and consumer behavior change |
Which is better?
An ethical supply chain prioritizes fair labor practices, transparency, and environmental responsibility to ensure sustainable and socially responsible sourcing. A circular supply chain focuses on resource efficiency through recycling, reuse, and waste minimization, promoting long-term environmental sustainability by closing the loop of product life cycles. Combining both approaches maximizes corporate social responsibility and operational efficiency, driving competitive advantage and stakeholder trust in consulting strategies.
Connection
Ethical supply chains prioritize transparency, fair labor practices, and environmental responsibility, which are core principles also embraced by circular supply chains that focus on resource efficiency and waste minimization through recycling and reuse. Both frameworks promote sustainability by reducing environmental impact and ensuring social accountability across the supply network. Integrating ethical and circular supply chain practices enhances corporate reputation, regulatory compliance, and long-term operational resilience.
Key Terms
Resource Efficiency (Circular Supply Chain)
A circular supply chain prioritizes resource efficiency by minimizing waste through recycling, reuse, and the continuous circulation of materials, ensuring input materials are kept within the production cycle for as long as possible. This contrasts with traditional supply chains that often rely on linear consumption and disposal, leading to resource depletion and environmental strain. Explore how adopting a circular model can enhance sustainability and operational efficiency in your supply chain strategies.
Fair Labor Practices (Ethical Supply Chain)
Fair labor practices in ethical supply chains prioritize worker rights, fair wages, safe working conditions, and prohibiting child or forced labor, ensuring social responsibility throughout production. Circular supply chains emphasize resource efficiency and waste reduction through recycling and reuse but do not inherently guarantee ethical labor standards. Explore how integrating fair labor practices within circular supply chains enhances both sustainability and social equity.
Traceability
Circular supply chains emphasize resource recovery and reuse, enhancing traceability through closed-loop systems that monitor product life cycles from production to recycling. Ethical supply chains prioritize transparent sourcing and fair labor practices, with traceability ensuring accountability and compliance with social and environmental standards. Discover how integrating traceability can improve both circularity and ethics in supply chain management.
Source and External Links
Designing supply chains for the circular economy - Circular supply chains are distributed, interconnected networks that keep products and materials in use through multidirectional flows of information, goods, and money, helping businesses reduce costs, emissions, and resource dependency while increasing resilience.
What Is a Circular Supply Chain? - Oracle - A circular supply chain extends the life of materials and goods by reusing, refurbishing, renting, and recycling, minimizing waste and protecting ecosystems by keeping resources in circulation as long as possible.
What is a circular supply chain? - Institute of Sustainability Studies - Circular supply chains prioritize continuous resource use by designing for durability, implementing reverse logistics, using recycled materials, and collaborating with partners to minimize waste and maximize product life cycles.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com