Consulting on dark pattern compliance involves identifying and mitigating manipulative design tactics that deceive users and violate regulations such as GDPR and CCPA. Ethical design prioritizes transparency, user autonomy, and informed consent, promoting trust and long-term customer loyalty. Explore how expert consulting can guide your business towards responsible and compliant design strategies.
Why it is important
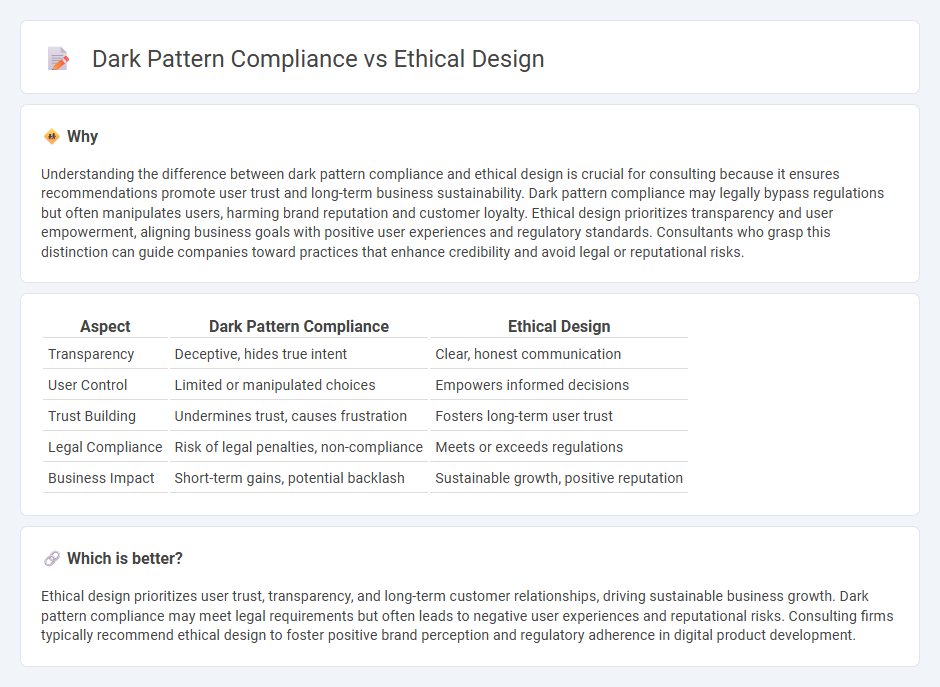
Understanding the difference between dark pattern compliance and ethical design is crucial for consulting because it ensures recommendations promote user trust and long-term business sustainability. Dark pattern compliance may legally bypass regulations but often manipulates users, harming brand reputation and customer loyalty. Ethical design prioritizes transparency and user empowerment, aligning business goals with positive user experiences and regulatory standards. Consultants who grasp this distinction can guide companies toward practices that enhance credibility and avoid legal or reputational risks.
Comparison Table
| Aspect | Dark Pattern Compliance | Ethical Design |
|---|---|---|
| Transparency | Deceptive, hides true intent | Clear, honest communication |
| User Control | Limited or manipulated choices | Empowers informed decisions |
| Trust Building | Undermines trust, causes frustration | Fosters long-term user trust |
| Legal Compliance | Risk of legal penalties, non-compliance | Meets or exceeds regulations |
| Business Impact | Short-term gains, potential backlash | Sustainable growth, positive reputation |
Which is better?
Ethical design prioritizes user trust, transparency, and long-term customer relationships, driving sustainable business growth. Dark pattern compliance may meet legal requirements but often leads to negative user experiences and reputational risks. Consulting firms typically recommend ethical design to foster positive brand perception and regulatory adherence in digital product development.
Connection
Dark pattern compliance and ethical design intersect in prioritizing user autonomy and transparency within digital interfaces. Adhering to regulations against manipulative dark patterns ensures ethical design practices that foster trust, enhance user experience, and prevent legal repercussions. Organizations integrating ethical design principles reduce the risk of deceptive tactics while promoting long-term customer loyalty and brand integrity.
Key Terms
Informed Consent
Ethical design prioritizes transparency and user autonomy by ensuring informed consent is obtained without manipulation, clearly communicating the purpose and implications of data collection. Dark pattern compliance exploits cognitive biases to obscure consent options, often leading users to unknowingly agree to terms they might reject if fully aware. Explore effective strategies to distinguish ethical informed consent from deceptive practices and enhance user trust.
Transparency
Ethical design prioritizes transparency by ensuring users fully understand how their data is collected, used, and shared, fostering informed consent and trust. In contrast, dark pattern compliance often involves obscuring information or manipulating interfaces to mislead users, compromising transparency and user autonomy. Explore strategies to enhance transparency and promote ethical design practices in digital environments.
User Autonomy
Ethical design prioritizes user autonomy by ensuring transparency, informed consent, and respect for user choices, while dark pattern compliance manipulates users into actions that benefit businesses at the expense of genuine consent. Emphasizing user autonomy fosters trust and preserves long-term customer relationships, contrasting sharply with dark patterns that erode user confidence and may lead to legal repercussions. Explore how balancing ethical design and regulatory compliance can protect user rights and enhance digital experiences.
Source and External Links
Ethical Design Guide: Principles, Benefits, and Examples - This article covers the key principles of ethical design, including fairness, transparency, and inclusivity, and discusses its benefits for users and businesses.
The Principles of Ethical Design (And How to Use Them) - This resource explains the fundamentals of ethical design, emphasizing moral responsibility and the impact of design on society.
Ethical Design: What It Is & Why It's Important - This article highlights the importance of ethical design in resisting manipulative patterns, respecting data privacy, and promoting accessibility and co-design.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com