Consulting services navigate the complex balance between dark pattern compliance, which involves ethical design practices avoiding manipulative user interfaces, and stakeholder accountability, emphasizing transparent decision-making and trust-building. Emphasizing compliance with regulatory standards like GDPR and ensuring stakeholder interests fosters sustainable business growth and reputational integrity. Discover how expert consultants can guide your organization to uphold ethical standards while meeting stakeholder expectations.
Why it is important
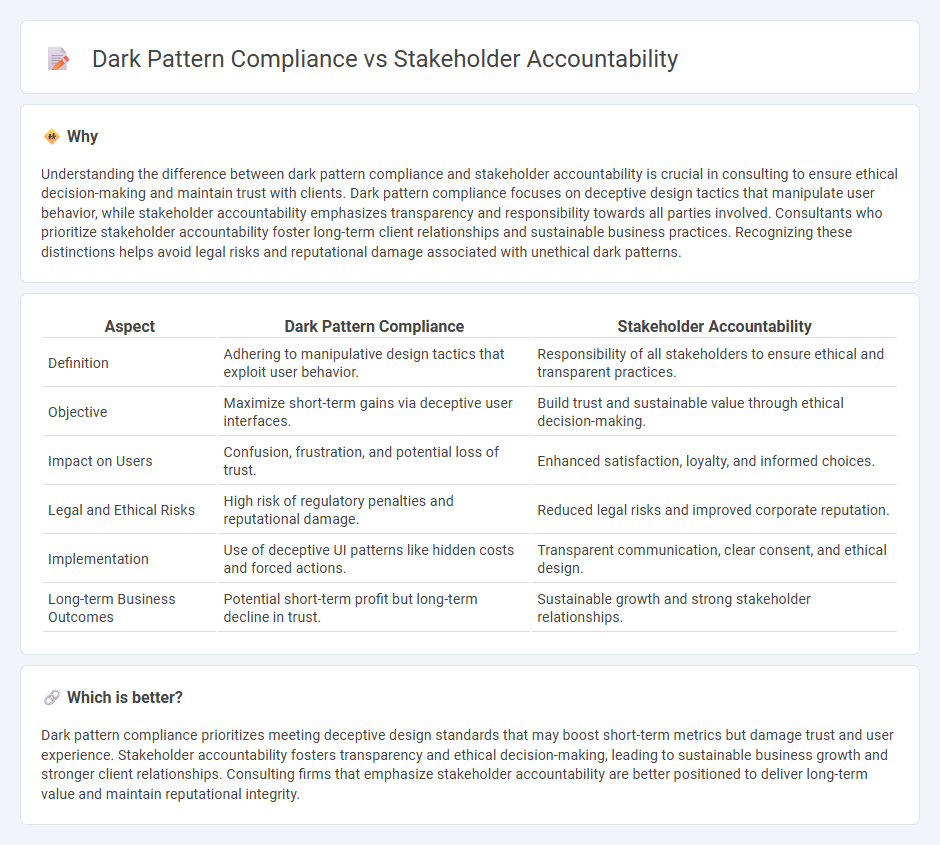
Understanding the difference between dark pattern compliance and stakeholder accountability is crucial in consulting to ensure ethical decision-making and maintain trust with clients. Dark pattern compliance focuses on deceptive design tactics that manipulate user behavior, while stakeholder accountability emphasizes transparency and responsibility towards all parties involved. Consultants who prioritize stakeholder accountability foster long-term client relationships and sustainable business practices. Recognizing these distinctions helps avoid legal risks and reputational damage associated with unethical dark patterns.
Comparison Table
| Aspect | Dark Pattern Compliance | Stakeholder Accountability |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Adhering to manipulative design tactics that exploit user behavior. | Responsibility of all stakeholders to ensure ethical and transparent practices. |
| Objective | Maximize short-term gains via deceptive user interfaces. | Build trust and sustainable value through ethical decision-making. |
| Impact on Users | Confusion, frustration, and potential loss of trust. | Enhanced satisfaction, loyalty, and informed choices. |
| Legal and Ethical Risks | High risk of regulatory penalties and reputational damage. | Reduced legal risks and improved corporate reputation. |
| Implementation | Use of deceptive UI patterns like hidden costs and forced actions. | Transparent communication, clear consent, and ethical design. |
| Long-term Business Outcomes | Potential short-term profit but long-term decline in trust. | Sustainable growth and strong stakeholder relationships. |
Which is better?
Dark pattern compliance prioritizes meeting deceptive design standards that may boost short-term metrics but damage trust and user experience. Stakeholder accountability fosters transparency and ethical decision-making, leading to sustainable business growth and stronger client relationships. Consulting firms that emphasize stakeholder accountability are better positioned to deliver long-term value and maintain reputational integrity.
Connection
Dark pattern compliance directly impacts stakeholder accountability by mandating transparent design practices that prevent user manipulation, ensuring ethical standards are upheld. Consulting firms play a crucial role in educating organizations about legal requirements and ethical design principles to mitigate risks associated with deceptive interfaces. Effective stakeholder accountability frameworks rely on dark pattern audits and compliance checks to maintain trust and regulatory adherence.
Key Terms
Transparency
Stakeholder accountability in digital design emphasizes clear communication, ethical data use, and user empowerment to prevent deceptive practices. Dark pattern compliance exploits design tactics to manipulate users, undermining transparency and trust. Explore how robust transparency standards can balance stakeholder responsibility with ethical user experiences.
Informed Consent
Informed consent is a crucial aspect of stakeholder accountability, ensuring users understand and voluntarily agree to data practices without manipulation. Dark pattern compliance often undermines informed consent by employing deceptive design techniques that mislead users into unintended agreements. Explore how transparent interfaces and ethical design can enhance true informed consent and strengthen stakeholder trust.
Ethical Guidelines
Ethical guidelines emphasize stakeholder accountability by ensuring transparency, fairness, and user consent to prevent manipulative design tactics known as dark patterns. Regulatory frameworks like GDPR and CCPA enforce compliance by promoting user rights and penalizing deceptive practices. Explore ethical design practices to enhance stakeholder trust and regulatory adherence.
Source and External Links
Stakeholder Accountability: Importance & Definition - Vaia - Stakeholder accountability is the responsibility of organizations to transparently and ethically meet the needs and expectations of all stakeholders involved or affected by their activities, enhancing trust, reputation, and sustainable growth through open communication and aligning business practices with stakeholder values.
Stakeholder involvement as a form of accountability - In public agencies, stakeholder accountability involves a moral and managerial obligation to be responsive and collaborate with stakeholders, who hold legitimate authority to hold agencies accountable, thus improving policy implementation and organizational effectiveness.
To Build Trust, Businesses Must Reimagine Stakeholder Engagement - Leading businesses are institutionalizing stakeholder engagement as a key governance function by expanding feedback channels, regularly assessing engagement effectiveness, and disclosing efforts, all to strengthen accountability and maintain their social license to operate.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com