Generative audio technology creates soundscapes and music through AI algorithms, enabling dynamic and customizable audio experiences. In contrast, audio watermarking embeds imperceptible signals within sound files to protect copyrights and verify authenticity. Explore the distinctions and applications of these innovative audio technologies to understand their impact on media security and creativity.
Why it is important
Understanding the difference between generative audio and audio watermarking is crucial for protecting intellectual property and enhancing media authenticity. Generative audio refers to AI-produced sounds created from algorithms, while audio watermarking embeds imperceptible data into audio files for copyright tracking. Accurate recognition of these technologies supports effective content creation, security, and rights management in digital audio industries. This knowledge helps differentiate creative synthesis from protective encoding, optimizing both innovation and legal safeguards.
Comparison Table
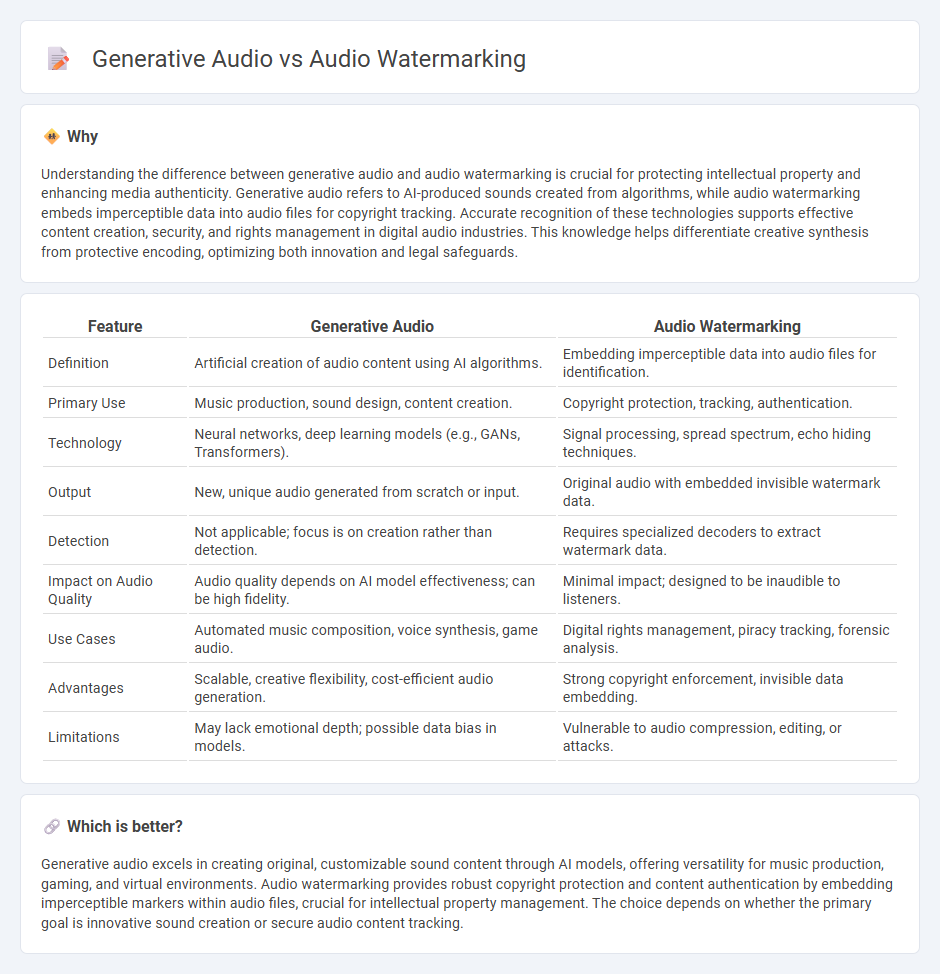
| Feature | Generative Audio | Audio Watermarking |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Artificial creation of audio content using AI algorithms. | Embedding imperceptible data into audio files for identification. |
| Primary Use | Music production, sound design, content creation. | Copyright protection, tracking, authentication. |
| Technology | Neural networks, deep learning models (e.g., GANs, Transformers). | Signal processing, spread spectrum, echo hiding techniques. |
| Output | New, unique audio generated from scratch or input. | Original audio with embedded invisible watermark data. |
| Detection | Not applicable; focus is on creation rather than detection. | Requires specialized decoders to extract watermark data. |
| Impact on Audio Quality | Audio quality depends on AI model effectiveness; can be high fidelity. | Minimal impact; designed to be inaudible to listeners. |
| Use Cases | Automated music composition, voice synthesis, game audio. | Digital rights management, piracy tracking, forensic analysis. |
| Advantages | Scalable, creative flexibility, cost-efficient audio generation. | Strong copyright enforcement, invisible data embedding. |
| Limitations | May lack emotional depth; possible data bias in models. | Vulnerable to audio compression, editing, or attacks. |
Which is better?
Generative audio excels in creating original, customizable sound content through AI models, offering versatility for music production, gaming, and virtual environments. Audio watermarking provides robust copyright protection and content authentication by embedding imperceptible markers within audio files, crucial for intellectual property management. The choice depends on whether the primary goal is innovative sound creation or secure audio content tracking.
Connection
Generative audio leverages AI algorithms to create original soundscapes, while audio watermarking embeds imperceptible data within these sounds to verify authenticity and ownership. This connection ensures that generative audio content can be securely tracked and protected against unauthorized use or piracy. Combining these technologies enhances digital rights management in the evolving landscape of AI-generated media.
Key Terms
Audio Watermarking:
Audio watermarking embeds imperceptible codes within sound files to protect intellectual property and verify authenticity, ensuring content remains secure from unauthorized use. This technique maintains audio quality while enabling traceability and copyright enforcement in digital media distribution. Explore deeper into audio watermarking to discover its critical role in digital rights management and forensic audio analysis.
Robustness
Audio watermarking offers high robustness by embedding imperceptible, tamper-resistant signals within audio files to ensure copyright protection and content authentication even after compression or noise interference. Generative audio models excel in creating realistic soundscapes but generally lack inherent mechanisms to resist manipulation or unauthorized replication, making robustness a critical challenge. Explore more about the comparative strengths and applications of audio watermarking and generative audio in securing digital sound content.
Imperceptibility
Audio watermarking ensures imperceptibility by embedding data within the audio signal without affecting sound quality, leveraging techniques like spread spectrum and echo hiding to maintain listener experience. Generative audio, however, creates new sounds where imperceptibility relates to seamless integration of synthetic elements without noticeable artifacts, relying on advanced AI models to mimic natural audio textures. Explore the latest advancements in imperceptible audio watermarking and generative audio to understand how these technologies enhance audio fidelity and security.
Source and External Links
Benchmarking Robustness of Audio Watermarking - Presents AudioMarkBench, the first systematic benchmark for evaluating the robustness of audio watermarking against removal and forgery, analyzing modern techniques like AudioSeal, Timbre, and WavMark.
Audio watermarking algorithm is first to solve "second-screen problem" in real time - Introduces an algorithm from Amazon that detects watermarked audio in real time even after it has been played and recorded in noisy environments--solving the "second-screen problem".
Audio Watermarking: A Comprehensive Review - Surveys three decades of digital audio watermarking methods, including time-domain techniques like least significant bit (LSB) insertion and echo-based approaches, highlighting their pros, cons, and security considerations.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com