Phantom inventory refers to discrepancies where stock records show available products that are actually missing, causing false inventory levels in retail management systems. Replenishment error occurs when the process of restocking shelves is inaccurate, leading to either overstocking or stockouts that disrupt sales and customer satisfaction. Explore more to understand how these issues impact retail efficiency and strategies to minimize their effects.
Why it is important
Understanding the difference between phantom inventory and replenishment error is crucial for optimizing retail operations and minimizing financial losses. Phantom inventory occurs when the system shows items in stock that are physically absent, leading to inaccurate sales forecasting and stockouts. Replenishment error involves mistakes during restocking, causing either overstocking or stock shortages that disrupt customer satisfaction. Accurate identification of these issues enables retailers to implement targeted solutions, improving inventory accuracy and operational efficiency.
Comparison Table
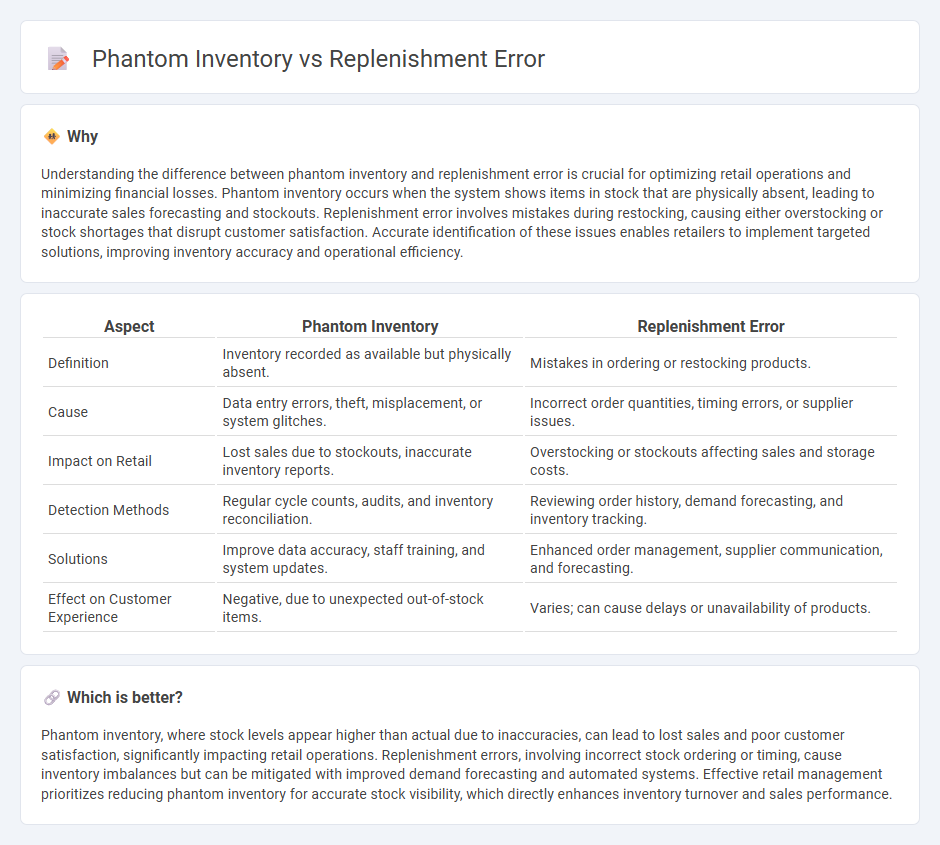
| Aspect | Phantom Inventory | Replenishment Error |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Inventory recorded as available but physically absent. | Mistakes in ordering or restocking products. |
| Cause | Data entry errors, theft, misplacement, or system glitches. | Incorrect order quantities, timing errors, or supplier issues. |
| Impact on Retail | Lost sales due to stockouts, inaccurate inventory reports. | Overstocking or stockouts affecting sales and storage costs. |
| Detection Methods | Regular cycle counts, audits, and inventory reconciliation. | Reviewing order history, demand forecasting, and inventory tracking. |
| Solutions | Improve data accuracy, staff training, and system updates. | Enhanced order management, supplier communication, and forecasting. |
| Effect on Customer Experience | Negative, due to unexpected out-of-stock items. | Varies; can cause delays or unavailability of products. |
Which is better?
Phantom inventory, where stock levels appear higher than actual due to inaccuracies, can lead to lost sales and poor customer satisfaction, significantly impacting retail operations. Replenishment errors, involving incorrect stock ordering or timing, cause inventory imbalances but can be mitigated with improved demand forecasting and automated systems. Effective retail management prioritizes reducing phantom inventory for accurate stock visibility, which directly enhances inventory turnover and sales performance.
Connection
Phantom inventory occurs when a retail system shows available stock that doesn't physically exist, often due to data inaccuracies or theft. Replenishment errors arise when these false stock levels trigger incorrect restocking decisions, leading to overstocking or stockouts. Accurate inventory tracking and integrated replenishment systems are essential to minimize these interconnected challenges and optimize supply chain efficiency.
Key Terms
Stockouts
Replenishment errors occur when inventory orders do not match actual demand, causing discrepancies that lead to stockouts and decreased sales. Phantom inventory refers to inaccurate stock records showing items as available when they are physically out-of-stock, disrupting order fulfillment and inventory planning. Explore detailed strategies to minimize stockouts caused by replenishment errors and phantom inventory for optimized supply chain management.
Inventory accuracy
Replenishment errors occur when stock quantities are incorrectly updated during resupply, leading to discrepancies between physical inventory and recorded levels. Phantom inventory arises when the system shows stock availability despite the product being out of stock, often due to untracked sales or theft, impacting inventory accuracy critical for supply chain efficiency. Explore further strategies to improve inventory accuracy and minimize these costly errors.
Point-of-Sale (POS) data
Replenishment errors occur when inaccurate Point-of-Sale (POS) data leads to incorrect stock orders, causing overstock or stockouts. Phantom inventory arises when POS systems fail to capture real-time sales, reflecting non-existent stock levels that disrupt supply chain accuracy. Explore advanced POS analytics to minimize these issues and improve inventory management.
Source and External Links
Calculate Replenishment Parameters failed with error - A replenishment error in inventory management can occur due to incorrect settings or sorting order issues in replenishment processes, such as an internal error stating "Sequence's sorting order is wrong or it's not sorted" during parameter calculation in systems like Acumatica.
FBA replenishment, internal Amazon error - In Amazon FBA, a replenishment error might arise from barcode conflicts, such as a manufacturer barcode being linked to more than one ASIN, causing issues in inventory replenishment despite correct SKU and UPC data.
10.01.90 cyan replenishment error - In HP printers, a replenishment error like code 10.01.90 indicates toner replenishment malfunction where toner fails to flow correctly into the imaging drum, often caused by toner gate misalignment or toner seal failure.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com