Resale arbitrage involves purchasing discounted or clearance products from physical or online retailers and reselling them at a higher price, leveraging price differences to generate profit. Dropshipping operates on a model where sellers list products without holding inventory, fulfilling orders by directly shipping from suppliers to customers, reducing upfront investment and storage costs. Explore the advantages and challenges of resale arbitrage and dropshipping to determine the best strategy for your retail business.
Why it is important
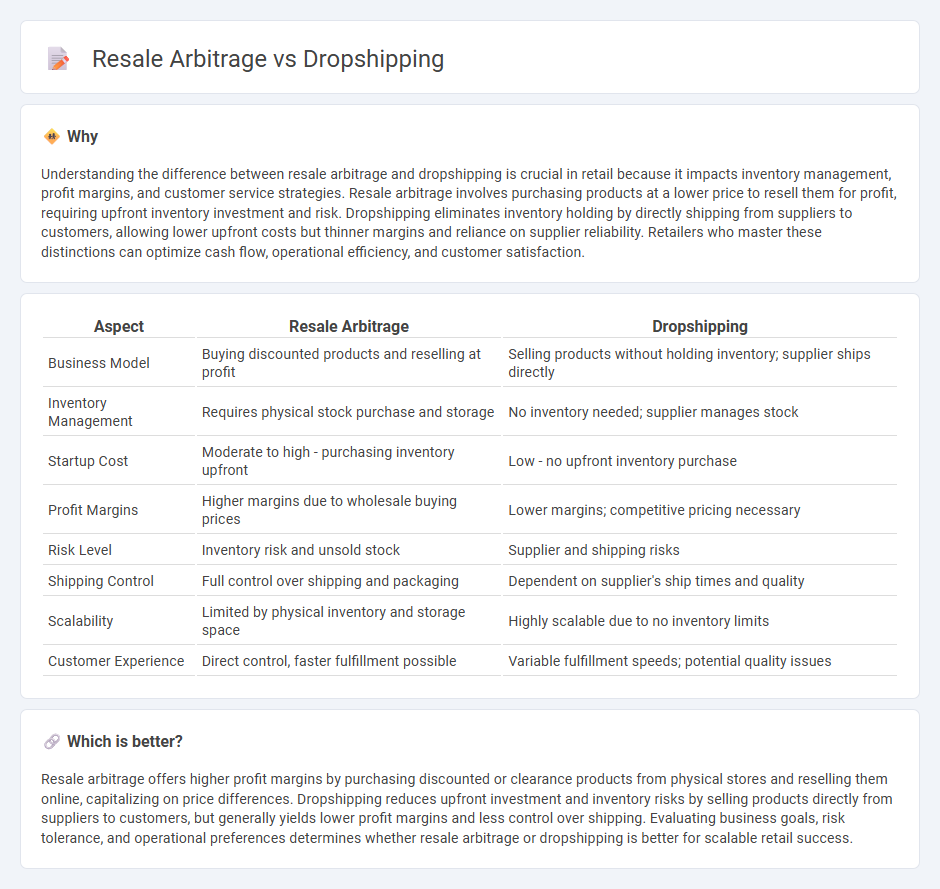
Understanding the difference between resale arbitrage and dropshipping is crucial in retail because it impacts inventory management, profit margins, and customer service strategies. Resale arbitrage involves purchasing products at a lower price to resell them for profit, requiring upfront inventory investment and risk. Dropshipping eliminates inventory holding by directly shipping from suppliers to customers, allowing lower upfront costs but thinner margins and reliance on supplier reliability. Retailers who master these distinctions can optimize cash flow, operational efficiency, and customer satisfaction.
Comparison Table
| Aspect | Resale Arbitrage | Dropshipping |
|---|---|---|
| Business Model | Buying discounted products and reselling at profit | Selling products without holding inventory; supplier ships directly |
| Inventory Management | Requires physical stock purchase and storage | No inventory needed; supplier manages stock |
| Startup Cost | Moderate to high - purchasing inventory upfront | Low - no upfront inventory purchase |
| Profit Margins | Higher margins due to wholesale buying prices | Lower margins; competitive pricing necessary |
| Risk Level | Inventory risk and unsold stock | Supplier and shipping risks |
| Shipping Control | Full control over shipping and packaging | Dependent on supplier's ship times and quality |
| Scalability | Limited by physical inventory and storage space | Highly scalable due to no inventory limits |
| Customer Experience | Direct control, faster fulfillment possible | Variable fulfillment speeds; potential quality issues |
Which is better?
Resale arbitrage offers higher profit margins by purchasing discounted or clearance products from physical stores and reselling them online, capitalizing on price differences. Dropshipping reduces upfront investment and inventory risks by selling products directly from suppliers to customers, but generally yields lower profit margins and less control over shipping. Evaluating business goals, risk tolerance, and operational preferences determines whether resale arbitrage or dropshipping is better for scalable retail success.
Connection
Resale arbitrage and dropshipping both capitalize on sourcing products at lower costs for profit through online retail platforms. Resale arbitrage involves purchasing discounted inventory from retail stores to resell at higher prices, while dropshipping relies on suppliers to fulfill orders directly without holding stock. Both strategies reduce upfront investment and inventory risk, enabling entrepreneurs to test market demand with minimal capital.
Key Terms
Inventory Management
Dropshipping eliminates the need for inventory management by transferring order fulfillment directly to suppliers, reducing holding costs and risks associated with unsold stock. In resale arbitrage, entrepreneurs purchase products upfront, requiring storage solutions, stock tracking, and potential markdowns for excess inventory. Explore detailed inventory strategies and how they impact cash flow and operational efficiency in both models.
Supplier Relationships
Dropshipping relies heavily on establishing strong supplier relationships as products ship directly from vendors to customers, making supplier reliability critical for timely delivery and product quality. Resale arbitrage involves purchasing inventory upfront from various retail sources, reducing dependence on suppliers but requiring effective inventory management and competitive sourcing strategies. Explore in-depth insights on optimizing supplier partnerships and sourcing methods by learning more.
Profit Margins
Dropshipping offers lower profit margins, typically ranging from 10% to 30%, due to higher competition and supplier fees, while resale arbitrage can yield margins between 30% and 60% by sourcing discounted or clearance items for resale at a premium. Profit margin differences are influenced by factors such as inventory costs, shipping expenses, and pricing flexibility, with resale arbitrage allowing more control over product selection and markups. Explore detailed strategies and insights to maximize profitability in both dropshipping and resale arbitrage models.
Source and External Links
What Is Dropshipping and How Does It Work? (2025) - Dropshipping is a business model where the seller partners with a supplier who stores, packages, and ships products directly to customers, allowing the seller to operate without holding inventory.
What Is Dropshipping and How Does It Work? - In dropshipping, the retailer creates an online store and sells products they do not stock, purchasing items from a supplier only after making a sale and having the supplier ship directly to the customer.
Drop shipping - Dropshipping is a retail method where sellers take customer orders without inventory, forwarding these to a supplier who ships the goods directly, enabling low startup costs but reducing control over quality and shipping.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com