Microfulfillment centers leverage advanced automation and AI-driven inventory management to accelerate order fulfillment, significantly reducing delivery times compared to traditional brick-and-mortar stores. Brick-and-mortar stores provide immediate in-person shopping experiences and product examination but often face challenges in inventory turnover and space limitations. Explore the evolving retail landscape by understanding the distinct advantages of microfulfillment centers versus physical stores.
Why it is important
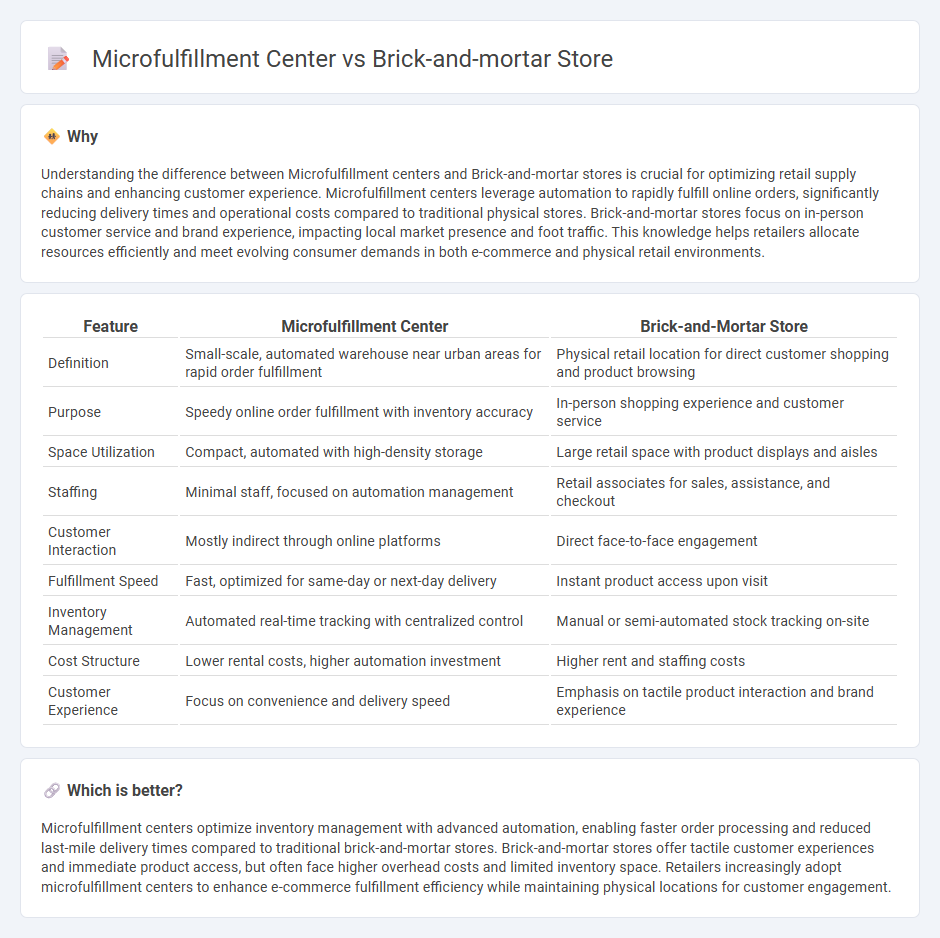
Understanding the difference between Microfulfillment centers and Brick-and-mortar stores is crucial for optimizing retail supply chains and enhancing customer experience. Microfulfillment centers leverage automation to rapidly fulfill online orders, significantly reducing delivery times and operational costs compared to traditional physical stores. Brick-and-mortar stores focus on in-person customer service and brand experience, impacting local market presence and foot traffic. This knowledge helps retailers allocate resources efficiently and meet evolving consumer demands in both e-commerce and physical retail environments.
Comparison Table
| Feature | Microfulfillment Center | Brick-and-Mortar Store |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Small-scale, automated warehouse near urban areas for rapid order fulfillment | Physical retail location for direct customer shopping and product browsing |
| Purpose | Speedy online order fulfillment with inventory accuracy | In-person shopping experience and customer service |
| Space Utilization | Compact, automated with high-density storage | Large retail space with product displays and aisles |
| Staffing | Minimal staff, focused on automation management | Retail associates for sales, assistance, and checkout |
| Customer Interaction | Mostly indirect through online platforms | Direct face-to-face engagement |
| Fulfillment Speed | Fast, optimized for same-day or next-day delivery | Instant product access upon visit |
| Inventory Management | Automated real-time tracking with centralized control | Manual or semi-automated stock tracking on-site |
| Cost Structure | Lower rental costs, higher automation investment | Higher rent and staffing costs |
| Customer Experience | Focus on convenience and delivery speed | Emphasis on tactile product interaction and brand experience |
Which is better?
Microfulfillment centers optimize inventory management with advanced automation, enabling faster order processing and reduced last-mile delivery times compared to traditional brick-and-mortar stores. Brick-and-mortar stores offer tactile customer experiences and immediate product access, but often face higher overhead costs and limited inventory space. Retailers increasingly adopt microfulfillment centers to enhance e-commerce fulfillment efficiency while maintaining physical locations for customer engagement.
Connection
Microfulfillment centers enhance brick-and-mortar stores by enabling rapid inventory replenishment and facilitating efficient order fulfillment near physical retail locations. Integration of these centers with traditional stores supports omnichannel retail strategies, improving customer experience through faster delivery and convenient in-store pickups. Retailers leverage real-time data from microfulfillment centers to optimize stock levels and reduce out-of-stock situations in brick-and-mortar environments.
Key Terms
Physical Footprint
Brick-and-mortar stores require extensive physical footprints to accommodate inventory, customer browsing, and checkout areas, often resulting in high real estate costs and limited flexibility in urban locations. Microfulfillment centers utilize compact, automated spaces to efficiently process online orders, significantly reducing the space needed compared to traditional stores while maintaining proximity to end consumers for faster delivery. Explore how microfulfillment centers can transform retail logistics and optimize space usage in your business.
Inventory Management
Brick-and-mortar stores require extensive on-site inventory to meet immediate customer demand, often leading to higher storage costs and potential stockouts. Microfulfillment centers leverage automation and real-time data to optimize inventory turnover, reduce holding costs, and enhance order accuracy within urban areas. Discover how this shift in inventory management can transform retail efficiency and customer satisfaction.
Last-Mile Delivery
Brick-and-mortar stores traditionally rely on in-store inventory and local foot traffic to fulfill orders, often leading to slower last-mile delivery due to limited storage and operational flexibility. Microfulfillment centers leverage automation and compact urban locations, enabling faster, more efficient last-mile delivery by optimizing inventory management and proximity to consumers. Explore the latest strategies and technologies driving last-mile delivery improvements in both models to enhance customer satisfaction.
Source and External Links
Brick and Mortar Stores: Types, Benefits, Examples (2024) - Shopify - A brick-and-mortar store is a physical retail location where customers can visit in person to view, try, and buy products, traditionally featuring a storefront, sales staff, and direct shopping experiences.
Brick-and-Mortar Stores: Key Definition, Pros, and Cons - Metrobi - Brick-and-mortar stores refer to physical shops where customers can see, touch, and purchase goods face-to-face, including department stores, specialty shops, supermarkets, and convenience stores.
Brick and mortar - Wikipedia - Brick-and-mortar businesses have a physical presence such as retail shops or warehouses, contrasting with online-only businesses, enabling face-to-face customer interaction and requiring considerations like storefront visibility and foot traffic.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com