Phantom inventory refers to stock that appears in the system but does not physically exist, often caused by data errors or theft, leading to discrepancies in inventory management. Obsolete inventory consists of products that are no longer sellable due to expiration, seasonality, or shifts in consumer demand, negatively impacting cash flow and storage efficiency. Explore more to understand how managing phantom and obsolete inventory optimizes retail operations and profitability.
Why it is important
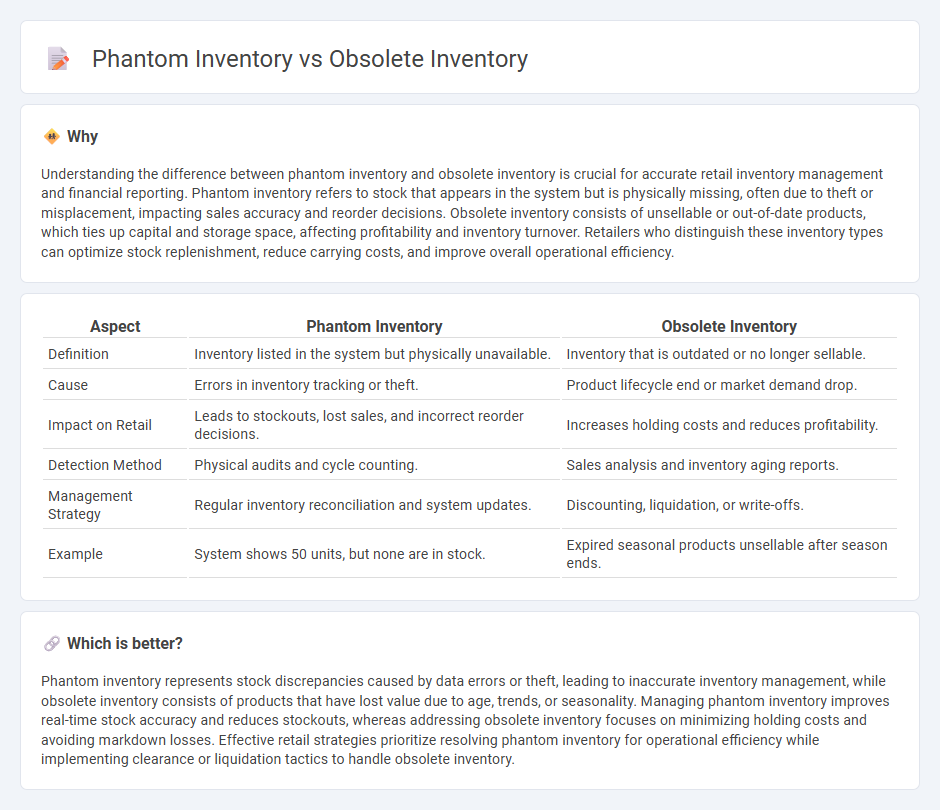
Understanding the difference between phantom inventory and obsolete inventory is crucial for accurate retail inventory management and financial reporting. Phantom inventory refers to stock that appears in the system but is physically missing, often due to theft or misplacement, impacting sales accuracy and reorder decisions. Obsolete inventory consists of unsellable or out-of-date products, which ties up capital and storage space, affecting profitability and inventory turnover. Retailers who distinguish these inventory types can optimize stock replenishment, reduce carrying costs, and improve overall operational efficiency.
Comparison Table
| Aspect | Phantom Inventory | Obsolete Inventory |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Inventory listed in the system but physically unavailable. | Inventory that is outdated or no longer sellable. |
| Cause | Errors in inventory tracking or theft. | Product lifecycle end or market demand drop. |
| Impact on Retail | Leads to stockouts, lost sales, and incorrect reorder decisions. | Increases holding costs and reduces profitability. |
| Detection Method | Physical audits and cycle counting. | Sales analysis and inventory aging reports. |
| Management Strategy | Regular inventory reconciliation and system updates. | Discounting, liquidation, or write-offs. |
| Example | System shows 50 units, but none are in stock. | Expired seasonal products unsellable after season ends. |
Which is better?
Phantom inventory represents stock discrepancies caused by data errors or theft, leading to inaccurate inventory management, while obsolete inventory consists of products that have lost value due to age, trends, or seasonality. Managing phantom inventory improves real-time stock accuracy and reduces stockouts, whereas addressing obsolete inventory focuses on minimizing holding costs and avoiding markdown losses. Effective retail strategies prioritize resolving phantom inventory for operational efficiency while implementing clearance or liquidation tactics to handle obsolete inventory.
Connection
Phantom inventory occurs when stock records indicate available products that are physically missing, often due to theft, misplacement, or data errors, leading to inaccuracies in inventory management. Obsolete inventory consists of unsellable or outdated products that occupy valuable warehouse space and tie up capital. The connection lies in phantom inventory masking the true quantity of stock, which contributes to overstocking and eventually results in obsolete inventory, increasing carrying costs and reducing retail profitability.
Key Terms
Stock Accuracy
Obsolete inventory refers to stock that is outdated or no longer sellable, causing inaccuracies in inventory valuation and storage costs. Phantom inventory consists of items recorded in the system but physically absent, leading to discrepancies between actual stock and inventory records. Explore effective strategies to improve stock accuracy and minimize these inventory challenges.
Inventory Turnover
Obsolete inventory consists of unsellable stock that no longer meets market demand, while phantom inventory refers to discrepancies between recorded and actual stock levels often caused by data errors or theft. Both types negatively impact inventory turnover by inflating stock counts and reducing sales velocity, leading to inaccurate performance metrics and inefficient capital use. Explore strategies to distinguish and manage obsolete versus phantom inventory for improved turnover rates and operational efficiency.
Shrinkage
Obsolete inventory consists of unsellable or outdated stock that no longer holds value, while phantom inventory refers to inventory records showing stock that does not physically exist, often due to shrinkage caused by theft, damage, or miscounting. Effective inventory management systems reduce shrinkage by accurately tracking physical stock and preventing phantom inventory discrepancies. Explore in-depth strategies to minimize inventory shrinkage and improve supply chain accuracy.
Source and External Links
How to Reduce Obsolete Inventory - Obsolete inventory refers to products no longer useful for sale due to reasons like outdated technology, expired items, or changes in consumer demand, which ties up capital and occupies warehouse space; strategies to manage it include selling at a discount, donating, writing off, or returning to suppliers to improve profitability and operational efficiency.
Obsolete Inventory: How to Prevent and Manage Excess Stock - Obsolete inventory, also called dead stock, creates financial burdens by tying up working capital and increasing storage costs, operational inefficiencies by occupying warehouse space needed for high-turnover products, and can harm company reputation if customers perceive poor management.
Obsolete Inventory Guide: How to Identify, Manage & Avoid It - Obsolete inventory occurs when products are no longer in demand due to factors like technological advances and poor forecasting, and using real-time inventory management systems can significantly reduce obsolete inventory costs and improve profitability through better tracking and purchasing decisions.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com