Phantom inventory occurs when a retail system shows stock available despite items being physically missing, often due to theft, misplacement, or data entry errors. Cycle count errors arise from inaccuracies during periodic manual inventory checks, leading to discrepancies between recorded and actual stock levels. Discover how understanding these issues can improve inventory accuracy and streamline retail operations.
Why it is important
Understanding the difference between phantom inventory and cycle count error is crucial for retail accuracy because phantom inventory refers to stock that appears in records but does not physically exist, while cycle count errors stem from mistakes during physical inventory checks. Identifying phantom inventory helps prevent lost sales and improves demand forecasting by addressing discrepancies caused by theft, misplacement, or system errors. Recognizing cycle count errors ensures inventory records are reliable and operational processes are optimized by refining counting procedures and staff training. Accurate distinction enhances inventory management efficiency, reduces shrinkage, and increases overall retail profitability.
Comparison Table
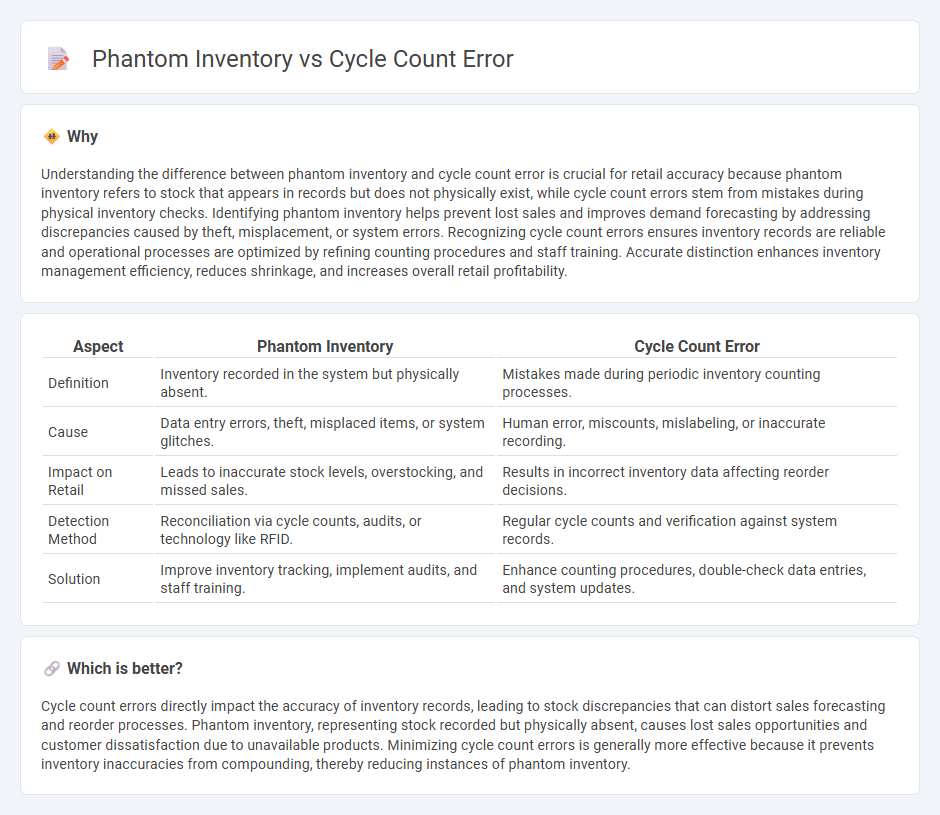
| Aspect | Phantom Inventory | Cycle Count Error |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Inventory recorded in the system but physically absent. | Mistakes made during periodic inventory counting processes. |
| Cause | Data entry errors, theft, misplaced items, or system glitches. | Human error, miscounts, mislabeling, or inaccurate recording. |
| Impact on Retail | Leads to inaccurate stock levels, overstocking, and missed sales. | Results in incorrect inventory data affecting reorder decisions. |
| Detection Method | Reconciliation via cycle counts, audits, or technology like RFID. | Regular cycle counts and verification against system records. |
| Solution | Improve inventory tracking, implement audits, and staff training. | Enhance counting procedures, double-check data entries, and system updates. |
Which is better?
Cycle count errors directly impact the accuracy of inventory records, leading to stock discrepancies that can distort sales forecasting and reorder processes. Phantom inventory, representing stock recorded but physically absent, causes lost sales opportunities and customer dissatisfaction due to unavailable products. Minimizing cycle count errors is generally more effective because it prevents inventory inaccuracies from compounding, thereby reducing instances of phantom inventory.
Connection
Phantom inventory occurs when retail systems show stock availability that physically doesn't exist, often caused by cycle count errors during inventory audits. These cycle count errors misrecord actual stock levels, leading to discrepancies between recorded and real inventory. Such inaccuracies disrupt inventory management, resulting in lost sales, overstocks, and inefficient supply chain operations.
Key Terms
Stock Discrepancies
Cycle count errors occur when physical counts of inventory during routine checks differ from recorded quantities, often caused by miscounts or data entry mistakes. Phantom inventory refers to stock recorded in the system that does not actually exist on shelves, typically due to theft, misplaced items, or unreported damage. Understanding these stock discrepancies is crucial for accurate inventory management; explore detailed strategies to address them effectively.
Inventory Accuracy
Cycle count errors occur when discrepancies arise between recorded inventory and actual stock during regular physical counts, often caused by data entry mistakes or misplaced items. Phantom inventory refers to stock records indicating inventory exists when items are actually missing or never received, leading to inaccurate demand planning and potential stockouts. Explore more strategies to enhance inventory accuracy and eliminate costly errors.
Shrinkage
Cycle count error occurs when discrepancies arise between recorded and actual stock during inventory checks, often due to data entry mistakes or misplacement. Phantom inventory refers to stock appearing in the system but missing physically, significantly contributing to shrinkage by inflating available inventory figures. Understanding these distinctions is essential to reducing shrinkage losses and improving inventory accuracy--explore more insights on effective shrinkage control strategies.
Source and External Links
Why did I get a cycle count sequence purge error? - This error occurs when purging a cycle count sequence if there are pending transactions against the cycle count, ensuring that these transactions are processed before purging.
How do I fix an error in a Cycle Count? - To fix a cycle count error, create a new cycle count for the items with errors, count them again, and submit the new cycle count to correct the inventory records.
Cycle Counting & Inventory Accuracy - Strategos, Inc - Cycle counting helps find and correct inventory record errors by auditing a random sample regularly and immediately fixing errors to maintain accuracy.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com