Upzoning increases allowable building density or height within a zone, facilitating higher development potential and promoting urban growth. A variance grants an exception to specific zoning regulations, allowing property owners to deviate from rules for unique circumstances without changing the zone's designation. Explore the distinctions between upzoning and variances to understand their impacts on property development and urban planning.
Why it is important
Understanding the difference between upzoning and variance is crucial in real estate as upzoning permanently changes land use regulations allowing higher density development, while a variance grants a temporary or case-specific exception to existing zoning rules. Real estate investors and developers must know these distinctions to evaluate property potential accurately and navigate legal requirements efficiently. Zoning impacts property value, development possibilities, and community planning outcomes significantly. This knowledge helps in making informed decisions that align with investment goals and regulatory compliance.
Comparison Table
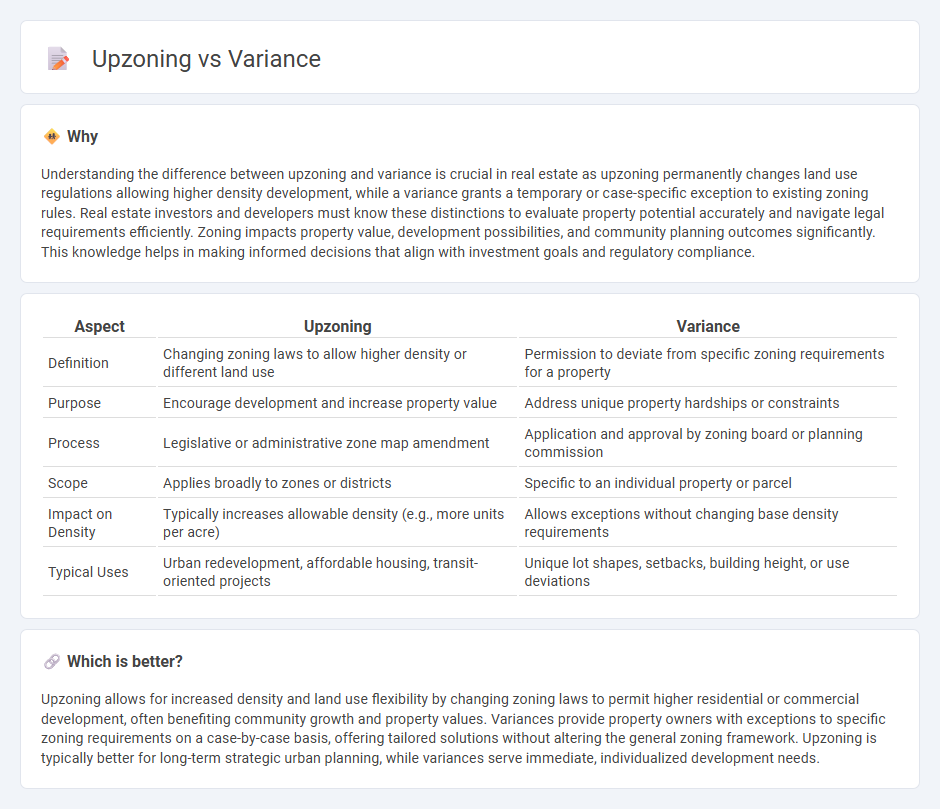
| Aspect | Upzoning | Variance |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Changing zoning laws to allow higher density or different land use | Permission to deviate from specific zoning requirements for a property |
| Purpose | Encourage development and increase property value | Address unique property hardships or constraints |
| Process | Legislative or administrative zone map amendment | Application and approval by zoning board or planning commission |
| Scope | Applies broadly to zones or districts | Specific to an individual property or parcel |
| Impact on Density | Typically increases allowable density (e.g., more units per acre) | Allows exceptions without changing base density requirements |
| Typical Uses | Urban redevelopment, affordable housing, transit-oriented projects | Unique lot shapes, setbacks, building height, or use deviations |
Which is better?
Upzoning allows for increased density and land use flexibility by changing zoning laws to permit higher residential or commercial development, often benefiting community growth and property values. Variances provide property owners with exceptions to specific zoning requirements on a case-by-case basis, offering tailored solutions without altering the general zoning framework. Upzoning is typically better for long-term strategic urban planning, while variances serve immediate, individualized development needs.
Connection
Upzoning increases allowable building density and height, altering zoning regulations to promote higher development potential. Variance grants exceptions to specific zoning rules when strict compliance causes undue hardship, often enabling builds that align with upzoning goals. Both tools facilitate increased land use flexibility and support real estate development by accommodating growth beyond original zoning limits.
Key Terms
Zoning Regulations
Variance allows property owners to deviate from existing zoning requirements due to unique circumstances, offering flexibility within strict zoning rules. Upzoning changes zoning classifications to permit higher density or different land uses, enabling increased development potential and efficient land use. Explore detailed comparisons of variance and upzoning to understand their impact on urban planning and property development.
Land Use
Variance allows property owners to deviate from existing zoning regulations for specific land use exceptions, typically when strict rules cause undue hardship. Upzoning involves changing zoning ordinances to permit higher-density land use, promoting greater development and increased urban density. Explore the impacts of variance and upzoning on land use planning and community development to understand their roles better.
Permitted Uses
Variance and upzoning both modify land use regulations but differ fundamentally in scope and application; variance grants individual property exceptions to zoning rules, often for unique hardship cases, while upzoning changes zoning classifications to allow broader or more intensive permitted uses across larger areas. Variance requests typically involve deviations from use, setback, or dimensional standards, whereas upzoning permits higher densities, mixed uses, or commercial activities not previously allowed. Explore detailed comparisons on how permitted uses evolve under each process to understand their impact on urban development.
Source and External Links
Variance and Standard Deviation - This webpage provides a detailed explanation of variance and how it measures the spread of data from the mean value.
Variance - GeeksforGeeks - This article explains variance as a measure of how spread out values in a data set are from the mean, with examples and formulas.
Variance: Definition, Step by Step Examples - Statistics How To - This webpage offers a comprehensive overview of variance, including step-by-step examples and discussions on its advantages and disadvantages.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com