Smart lease agreements leverage technology to streamline rent collection, maintenance tracking, and tenant communication, offering enhanced transparency and efficiency for both landlords and tenants. Triple Net Lease (NNN) structures shift property expenses such as taxes, insurance, and maintenance directly to tenants, providing predictable income for property owners while placing operational responsibilities on lessees. Discover the key differences and choose the optimal lease model for your real estate investment needs.
Why it is important
Understanding the difference between Smart lease agreements and Triple Net (NNN) leases is crucial for real estate investors to optimize cost allocation and risk management. A Smart lease integrates advanced technology and flexible terms tailored to tenant usage patterns, enhancing operational efficiency and tenant satisfaction. Triple Net leases shift property expenses such as taxes, insurance, and maintenance to tenants, ensuring predictable income for landlords but higher responsibility for tenants. Choosing the right lease type impacts financial forecasting, property management strategies, and long-term investment returns.
Comparison Table
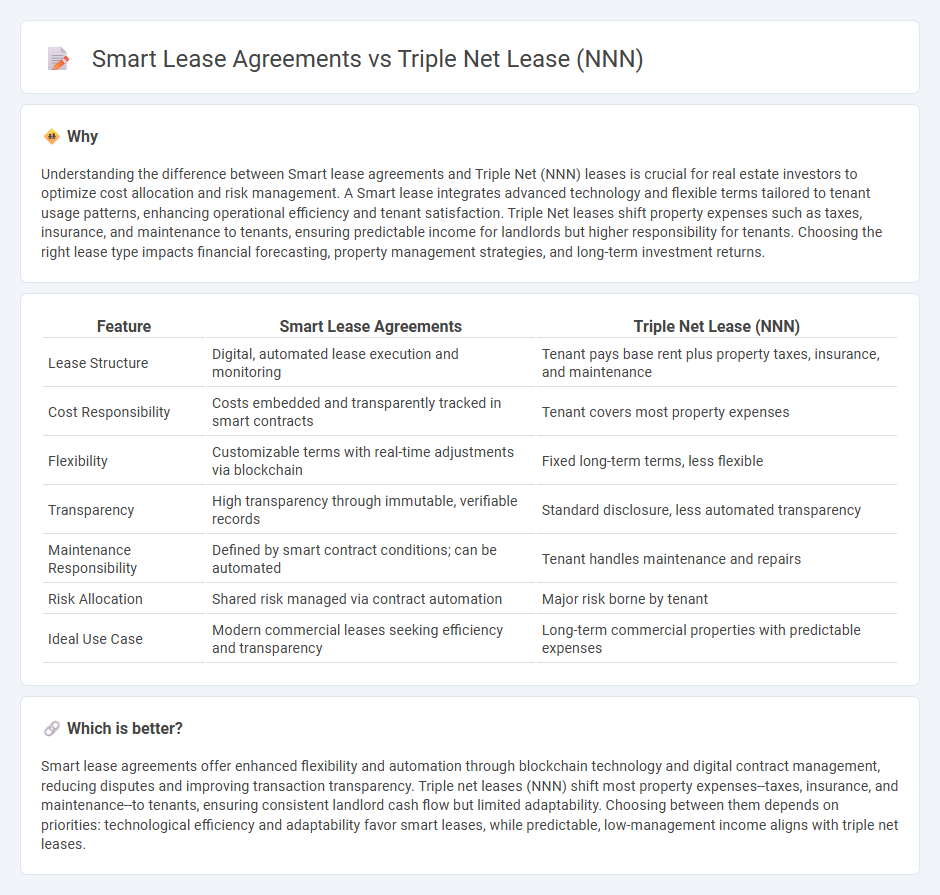
| Feature | Smart Lease Agreements | Triple Net Lease (NNN) |
|---|---|---|
| Lease Structure | Digital, automated lease execution and monitoring | Tenant pays base rent plus property taxes, insurance, and maintenance |
| Cost Responsibility | Costs embedded and transparently tracked in smart contracts | Tenant covers most property expenses |
| Flexibility | Customizable terms with real-time adjustments via blockchain | Fixed long-term terms, less flexible |
| Transparency | High transparency through immutable, verifiable records | Standard disclosure, less automated transparency |
| Maintenance Responsibility | Defined by smart contract conditions; can be automated | Tenant handles maintenance and repairs |
| Risk Allocation | Shared risk managed via contract automation | Major risk borne by tenant |
| Ideal Use Case | Modern commercial leases seeking efficiency and transparency | Long-term commercial properties with predictable expenses |
Which is better?
Smart lease agreements offer enhanced flexibility and automation through blockchain technology and digital contract management, reducing disputes and improving transaction transparency. Triple net leases (NNN) shift most property expenses--taxes, insurance, and maintenance--to tenants, ensuring consistent landlord cash flow but limited adaptability. Choosing between them depends on priorities: technological efficiency and adaptability favor smart leases, while predictable, low-management income aligns with triple net leases.
Connection
Smart lease agreements integrate advanced technology and automation to enhance the management of Triple Net Lease (NNN) contracts by streamlining rent payments, maintenance responsibilities, and expense tracking. Triple Net Lease requires tenants to cover property taxes, insurance, and maintenance, making precise data monitoring and transparent communication critical for both landlords and tenants. Implementing smart lease solutions improves efficiency, reduces disputes, and ensures compliance with NNN lease terms through real-time updates and digital record keeping.
Key Terms
Operating Expenses
Triple net lease (NNN) agreements transfer operating expenses--property taxes, insurance, and maintenance costs--directly to tenants, making their financial responsibilities clear and predictable. Smart lease agreements leverage technology and data analytics to optimize operating expense allocations, enhancing transparency and enabling dynamic adjustments based on real-time usage and market conditions. Explore how these lease structures impact your financial planning and tenant relationships for a smarter property strategy.
Maintenance Responsibility
Triple net lease (NNN) agreements place the burden of maintenance responsibility primarily on the tenant, covering property taxes, insurance, and repairs to the building structure and common areas. Smart lease agreements often incorporate technology-driven clauses that allow for dynamic maintenance scheduling, transparent cost-sharing, and real-time reporting to optimize property upkeep. Discover how these distinct lease structures impact property management and tenant obligations in greater detail.
Rent Structure
Triple net lease (NNN) agreements require tenants to pay base rent plus property taxes, insurance, and maintenance costs, transferring most financial obligations to the tenant. Smart lease agreements incorporate flexible rent structures utilizing data analytics, allowing dynamic rent adjustments based on usage, market trends, or operational performance. Explore how these rent structures can impact your leasing strategy and financial planning.
Source and External Links
triple net lease | Wex | US Law | LII / Legal Information Institute - A triple net lease (NNN) is a commercial lease where the tenant pays rent, utilities, and three major property expenses: insurance, maintenance, and taxes, shifting most financial responsibility and risk from landlord to tenant, commonly used in long-term leases of 10 to 15 years or more.
What is a Triple Net Lease (NNN): The Definitive Guide 2024 - The triple net lease requires the tenant to pay a prorated share of property expenses including insurance, real estate taxes, and common area maintenance (CAM) in addition to rent and utilities, generally lowering base rent while tenants cover most property costs except for major structural repairs often retained by landlords.
Benefits and Drawbacks of a Triple Net Lease (NNN) in Commercial Real Estate - A triple net lease makes tenants responsible for taxes, property insurance, and operating expenses on top of rent and utilities, offering tenants more freedom to customize and landlords stable income with less management, though tenants assume the risk of cost fluctuations and maintenance.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com