Agrihood communities integrate residential living with active farming, promoting sustainability through locally grown produce and shared green spaces. Eco-villages focus on holistic environmental practices, emphasizing renewable energy, low-impact construction, and communal living to minimize ecological footprints. Explore the unique benefits and lifestyles offered by agrihoods and eco-villages to find your ideal sustainable community.
Why it is important
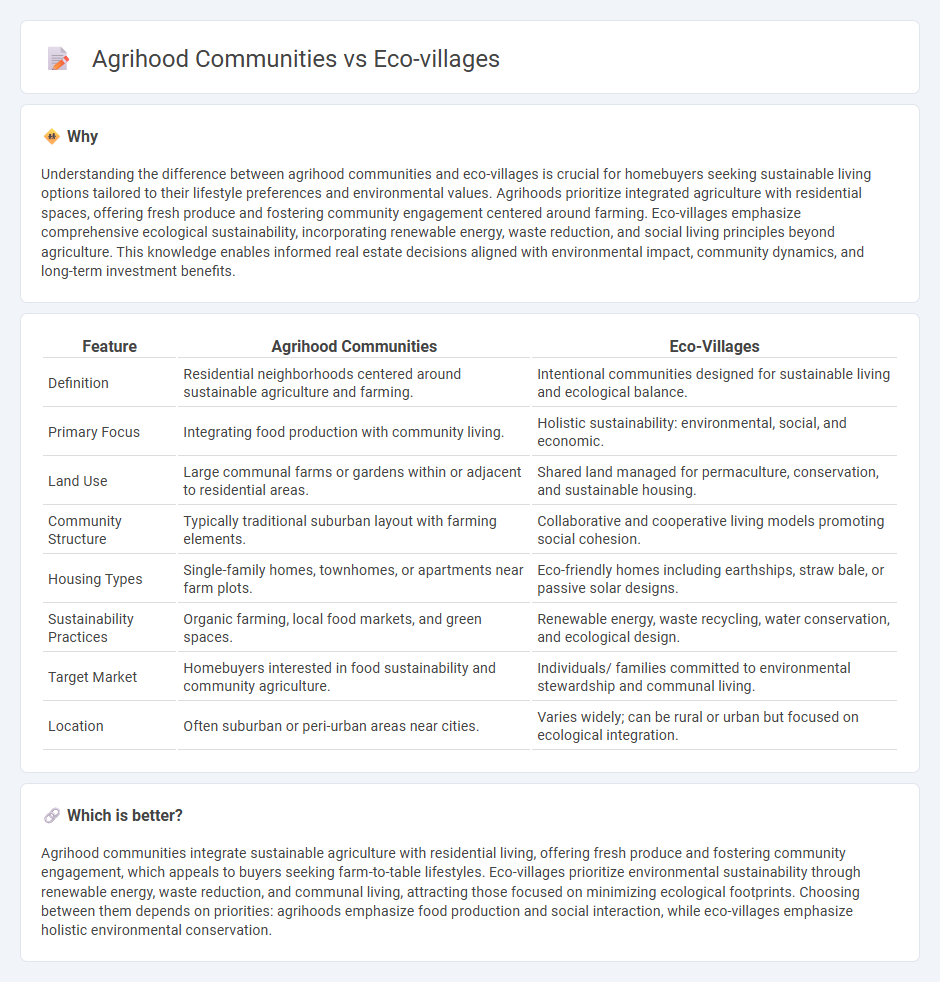
Understanding the difference between agrihood communities and eco-villages is crucial for homebuyers seeking sustainable living options tailored to their lifestyle preferences and environmental values. Agrihoods prioritize integrated agriculture with residential spaces, offering fresh produce and fostering community engagement centered around farming. Eco-villages emphasize comprehensive ecological sustainability, incorporating renewable energy, waste reduction, and social living principles beyond agriculture. This knowledge enables informed real estate decisions aligned with environmental impact, community dynamics, and long-term investment benefits.
Comparison Table
| Feature | Agrihood Communities | Eco-Villages |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Residential neighborhoods centered around sustainable agriculture and farming. | Intentional communities designed for sustainable living and ecological balance. |
| Primary Focus | Integrating food production with community living. | Holistic sustainability: environmental, social, and economic. |
| Land Use | Large communal farms or gardens within or adjacent to residential areas. | Shared land managed for permaculture, conservation, and sustainable housing. |
| Community Structure | Typically traditional suburban layout with farming elements. | Collaborative and cooperative living models promoting social cohesion. |
| Housing Types | Single-family homes, townhomes, or apartments near farm plots. | Eco-friendly homes including earthships, straw bale, or passive solar designs. |
| Sustainability Practices | Organic farming, local food markets, and green spaces. | Renewable energy, waste recycling, water conservation, and ecological design. |
| Target Market | Homebuyers interested in food sustainability and community agriculture. | Individuals/ families committed to environmental stewardship and communal living. |
| Location | Often suburban or peri-urban areas near cities. | Varies widely; can be rural or urban but focused on ecological integration. |
Which is better?
Agrihood communities integrate sustainable agriculture with residential living, offering fresh produce and fostering community engagement, which appeals to buyers seeking farm-to-table lifestyles. Eco-villages prioritize environmental sustainability through renewable energy, waste reduction, and communal living, attracting those focused on minimizing ecological footprints. Choosing between them depends on priorities: agrihoods emphasize food production and social interaction, while eco-villages emphasize holistic environmental conservation.
Connection
Agrihood communities and eco-villages are connected through their shared focus on sustainable living and integrated green spaces that promote ecological balance. Both prioritize local food production, with agrihoods centered around community farms and eco-villages incorporating permaculture principles to minimize environmental impact. These real estate models attract environmentally conscious buyers seeking residential areas that support healthy lifestyles and reduce carbon footprints.
Key Terms
Sustainability
Eco-villages prioritize holistic sustainability by integrating renewable energy, waste reduction, and community-driven resource management, creating self-sufficient living environments. Agrihood communities emphasize sustainable agriculture, local food production, and green space preservation, fostering strong connections between residents and their environment through shared farming practices. Explore how these innovative models are transforming sustainable living to enhance environmental and social wellbeing.
Community Farming
Eco-villages prioritize sustainable living with community farming tasks deeply integrated into daily life, promoting ecological balance and social cohesion. Agrihood communities center around modern agricultural practices, offering residents access to shared farm-to-table resources and fostering urban-rural connection. Explore how these models transform community farming and sustainable lifestyles.
Green Infrastructure
Eco-villages prioritize resilient green infrastructure by integrating renewable energy systems, rainwater harvesting, and permaculture designs to create self-sustaining environments. Agrihood communities emphasize sustainable agriculture with green infrastructure featuring community gardens, stormwater management through bioswales, and farm-to-table initiatives that enhance local food systems. Explore the distinct approaches both models use to foster sustainability and environmental stewardship.
Source and External Links
Ecovillages From Around the World for Sustainable Living - Earth.Org - Ecovillages are intentional or traditional communities aiming to be socially, culturally, ecologically, and economically sustainable, with over 1,100 worldwide, combining traditional wisdom and new innovations to minimize environmental and social impacts.
5 of the World's Coolest EcoVillages - The World Economic Forum - Findhorn EcoVillage in Scotland is a leading example of an ecovillage, using sustainable architecture, renewable energy, and a low ecological footprint to promote a holistic approach connecting social, spiritual, economic, and ecological life.
Ecovillage - Wikipedia - Ecovillages focus on sustainability through renewable energy, waste minimization, organic farming, green building techniques, and fostering a strong sense of community and participation to support resilience and sustainable living.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com