Adaptive reuse properties transform existing buildings into functional spaces, preserving architectural heritage while meeting modern needs. Pop-up property installations offer temporary, flexible solutions designed for short-term commercial or community use in underutilized locations. Explore the benefits and challenges of both strategies to understand how they shape urban development.
Why it is important
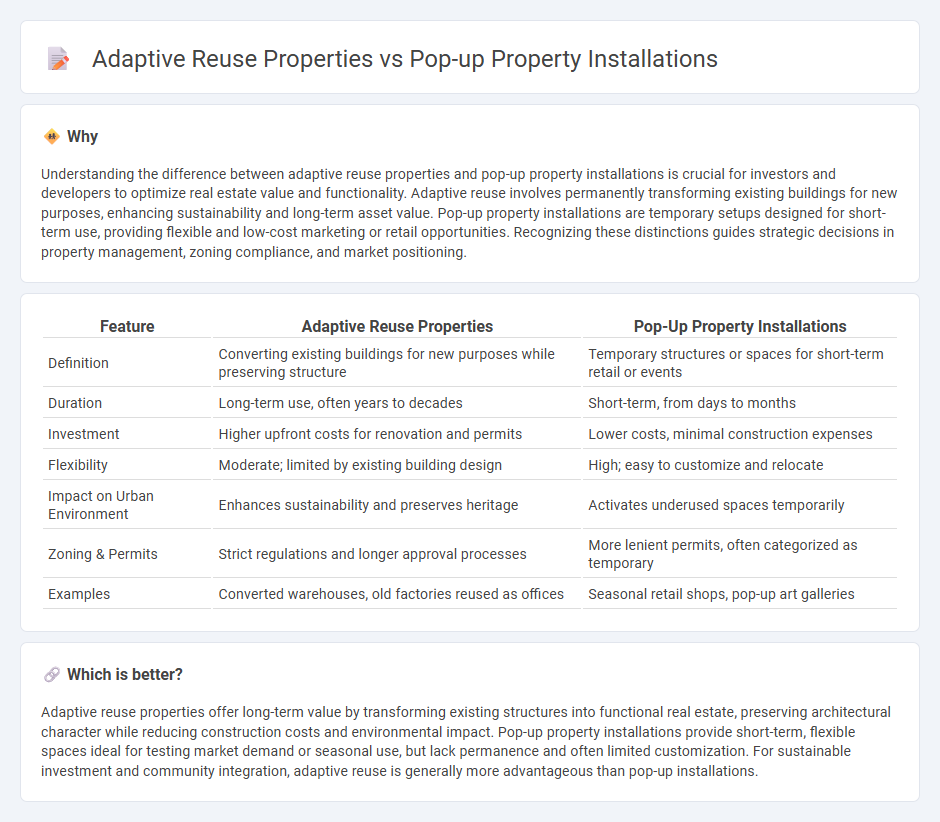
Understanding the difference between adaptive reuse properties and pop-up property installations is crucial for investors and developers to optimize real estate value and functionality. Adaptive reuse involves permanently transforming existing buildings for new purposes, enhancing sustainability and long-term asset value. Pop-up property installations are temporary setups designed for short-term use, providing flexible and low-cost marketing or retail opportunities. Recognizing these distinctions guides strategic decisions in property management, zoning compliance, and market positioning.
Comparison Table
| Feature | Adaptive Reuse Properties | Pop-Up Property Installations |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Converting existing buildings for new purposes while preserving structure | Temporary structures or spaces for short-term retail or events |
| Duration | Long-term use, often years to decades | Short-term, from days to months |
| Investment | Higher upfront costs for renovation and permits | Lower costs, minimal construction expenses |
| Flexibility | Moderate; limited by existing building design | High; easy to customize and relocate |
| Impact on Urban Environment | Enhances sustainability and preserves heritage | Activates underused spaces temporarily |
| Zoning & Permits | Strict regulations and longer approval processes | More lenient permits, often categorized as temporary |
| Examples | Converted warehouses, old factories reused as offices | Seasonal retail shops, pop-up art galleries |
Which is better?
Adaptive reuse properties offer long-term value by transforming existing structures into functional real estate, preserving architectural character while reducing construction costs and environmental impact. Pop-up property installations provide short-term, flexible spaces ideal for testing market demand or seasonal use, but lack permanence and often limited customization. For sustainable investment and community integration, adaptive reuse is generally more advantageous than pop-up installations.
Connection
Adaptive reuse properties and pop-up property installations both maximize the utility of existing urban spaces by transforming underutilized or vacant buildings into functional environments, often meeting temporary or evolving community needs. These strategies reduce the environmental impact of new constructions by repurposing structures, contributing to sustainable real estate development. The connection lies in their shared focus on flexibility, cost-efficiency, and revitalizing urban landscapes through innovative property utilization.
Key Terms
Temporary Structures
Pop-up property installations, designed as temporary structures, offer flexible, short-term solutions ideal for events, retail, or marketing purposes, leveraging modular designs for quick assembly and disassembly. Adaptive reuse properties transform existing buildings to serve new functions, extending their life cycle while preserving architectural heritage, but require more permanent modifications than pop-ups. Explore the distinct benefits and applications of these temporary and adaptive solutions to enhance your property strategy.
Repurposing
Repurposing in pop-up property installations involves temporary, flexible use of urban spaces to activate underutilized locations without extensive modifications. Adaptive reuse properties transform existing buildings through structural renovations to serve new, long-term functions while preserving architectural integrity. Explore more about how each strategy enhances urban revitalization and sustainable development.
Zoning Compliance
Pop-up property installations often benefit from temporary zoning permits designed for short-term use, allowing quick deployment without extensive regulatory hurdles. Adaptive reuse properties must adhere to permanent zoning regulations, requiring detailed compliance with building codes and land-use requirements for long-term occupancy. Explore in-depth zoning compliance strategies for both property types to optimize project feasibility and legal adherence.
Source and External Links
Pop-Up House: the affordable passive house | Multipod Studio - The Pop-Up House is a quick-install, low-cost, recyclable passive house made from lightweight insulating blocks and wooden panels, delivering excellent thermal insulation without the need for heating, assembled in just four days with no special tools.
A Passive Pop Up House - Rise - This Pop-Up House concept features energy-efficient construction using 12-inch insulated blocks separated by wooden boards, exceeding European passive house standards with a highly airtight and thermally insulated envelope to minimize energy use.
PopUpHut - Escape To Your Tiny House! - PopUpHuts are eco-friendly, pre-built tiny houses made from upcycled shipping containers, designed for mobility and versatile uses such as offices, studios, or pop-up retail spaces, with easy setup and year-round insulation.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com