Upzoning increases allowable building density or height within a zoning district to accommodate growth and intensify land use. Rezoning involves changing the designated land use category, such as converting residential zones to commercial or industrial purposes, impacting property values and development opportunities. Explore the key differences and implications of upzoning versus rezoning to better navigate real estate regulations.
Why it is important
Understanding the difference between upzoning and rezoning is crucial for real estate investors and developers to accurately assess property value and permissible land use. Upzoning typically increases the density or height limits, allowing for more intensive development, while rezoning changes the property's land use category altogether. This distinction impacts project feasibility, regulatory compliance, and potential return on investment. Knowing these terms helps stakeholders navigate zoning laws to optimize development opportunities.
Comparison Table
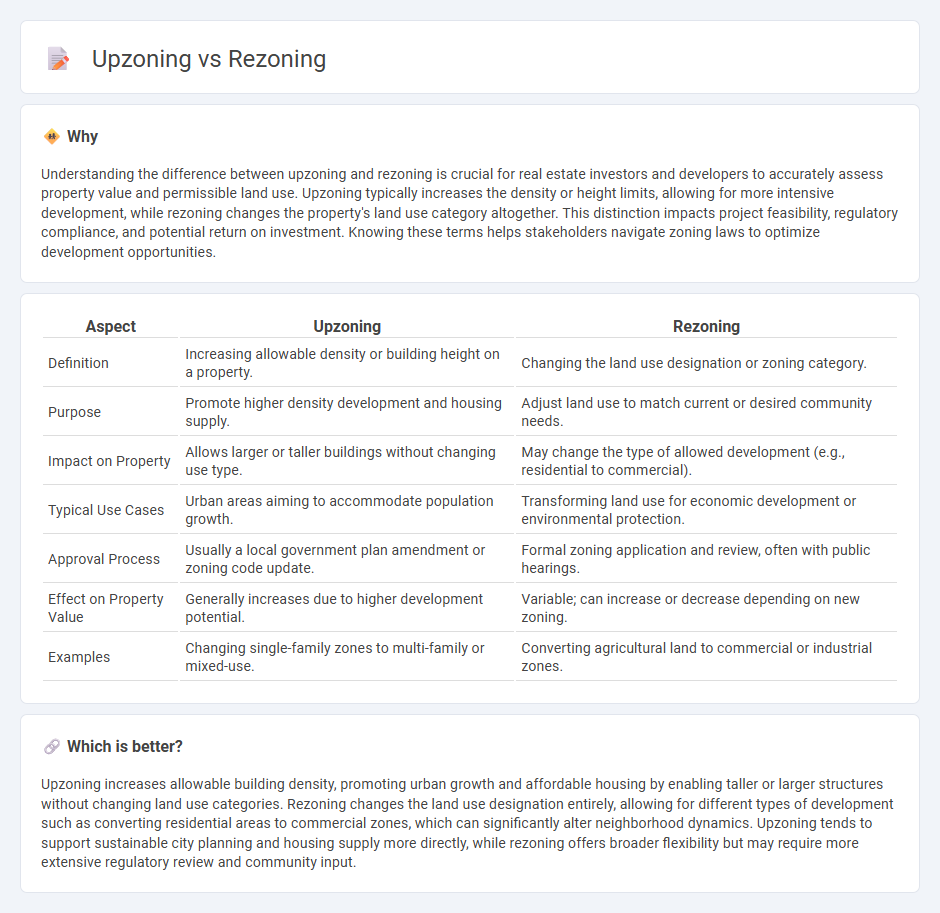
| Aspect | Upzoning | Rezoning |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Increasing allowable density or building height on a property. | Changing the land use designation or zoning category. |
| Purpose | Promote higher density development and housing supply. | Adjust land use to match current or desired community needs. |
| Impact on Property | Allows larger or taller buildings without changing use type. | May change the type of allowed development (e.g., residential to commercial). |
| Typical Use Cases | Urban areas aiming to accommodate population growth. | Transforming land use for economic development or environmental protection. |
| Approval Process | Usually a local government plan amendment or zoning code update. | Formal zoning application and review, often with public hearings. |
| Effect on Property Value | Generally increases due to higher development potential. | Variable; can increase or decrease depending on new zoning. |
| Examples | Changing single-family zones to multi-family or mixed-use. | Converting agricultural land to commercial or industrial zones. |
Which is better?
Upzoning increases allowable building density, promoting urban growth and affordable housing by enabling taller or larger structures without changing land use categories. Rezoning changes the land use designation entirely, allowing for different types of development such as converting residential areas to commercial zones, which can significantly alter neighborhood dynamics. Upzoning tends to support sustainable city planning and housing supply more directly, while rezoning offers broader flexibility but may require more extensive regulatory review and community input.
Connection
Upzoning and rezoning both involve changes to land-use regulations that alter property development potential, with upzoning specifically increasing allowable density or building height within a zoning district. Rezoning refers to the process of changing the land use classification from one zone category to another, often to accommodate new growth or urban planning goals. Together, these regulatory tools enable cities to manage urban density, encourage affordable housing development, and guide sustainable community expansion.
Key Terms
Land Use
Rezoning involves changing the designated land use category, such as converting residential zones to commercial or industrial, impacting permissible activities and development standards. Upzoning specifically increases the allowable density or building height within an existing zone, enabling more intensive land use like taller buildings or more units per acre. Explore detailed differences and implications of rezoning and upzoning for strategic land use planning.
Zoning Classification
Rezoning involves changing the zoning classification of a specific land parcel, altering permitted uses such as residential, commercial, or industrial designations. Upzoning specifically increases the density or intensity allowed, for example, shifting from single-family residential to multi-family or high-rise commercial use. Explore how these distinct zoning adjustments impact urban development and property values further.
Density
Rezoning involves changing land use regulations to alter permitted uses, impacting overall density by potentially allowing denser or more varied developments. Upzoning specifically increases allowable density by raising limits on building size, height, or units per acre to promote urban growth and housing supply. Explore our comprehensive guide to understand how these zoning strategies influence urban density and development opportunities.
Source and External Links
Rezoning - Prince George's County Council - Rezoning involves changing existing zoning either by zoning map amendments requested by property owners or through comprehensive rezonings applying to entire geographic areas, aiming for orderly land use planning and limiting piecemeal changes.
Rezoning Land - Dane County Planning and Development - Rezoning is a formal petition process to change zoning designations or boundaries for a property, with review and approval by local committees and boards after public hearings, typically requiring several months.
The Property Rezoning Process: What Land Developers Need to Know - Property rezoning is a critical and complex permitting step for developers to change land uses or development standards that don't fit existing zoning, often requiring familiarity with local classifications and possible alternatives like variances.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com