Dynamic pricing in real estate adjusts property prices based on market demand, competition, and buyer behavior, allowing sellers to maximize revenue in fluctuating markets. Fixed pricing sets a constant price regardless of market changes, providing stability and predictability for both buyers and sellers. Explore the advantages and challenges of dynamic versus fixed pricing strategies to optimize your real estate investments.
Why it is important
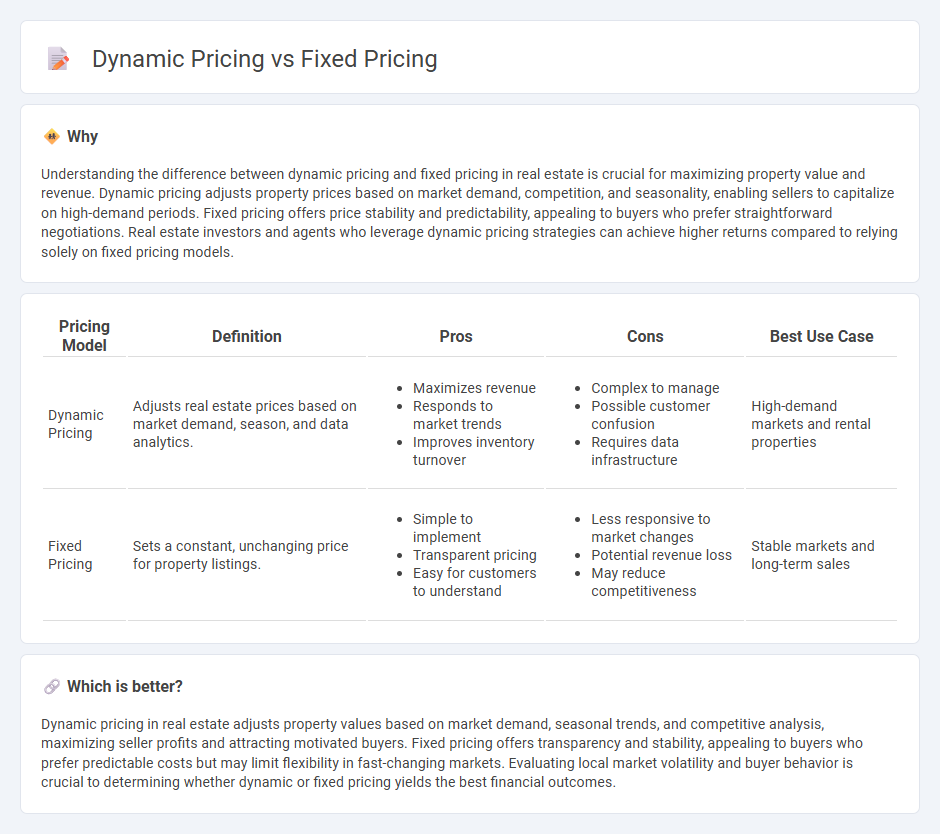
Understanding the difference between dynamic pricing and fixed pricing in real estate is crucial for maximizing property value and revenue. Dynamic pricing adjusts property prices based on market demand, competition, and seasonality, enabling sellers to capitalize on high-demand periods. Fixed pricing offers price stability and predictability, appealing to buyers who prefer straightforward negotiations. Real estate investors and agents who leverage dynamic pricing strategies can achieve higher returns compared to relying solely on fixed pricing models.
Comparison Table
| Pricing Model | Definition | Pros | Cons | Best Use Case |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Dynamic Pricing | Adjusts real estate prices based on market demand, season, and data analytics. |
|
|
High-demand markets and rental properties |
| Fixed Pricing | Sets a constant, unchanging price for property listings. |
|
|
Stable markets and long-term sales |
Which is better?
Dynamic pricing in real estate adjusts property values based on market demand, seasonal trends, and competitive analysis, maximizing seller profits and attracting motivated buyers. Fixed pricing offers transparency and stability, appealing to buyers who prefer predictable costs but may limit flexibility in fast-changing markets. Evaluating local market volatility and buyer behavior is crucial to determining whether dynamic or fixed pricing yields the best financial outcomes.
Connection
Dynamic pricing and fixed pricing in real estate are connected through their influence on property valuation and market responsiveness. Dynamic pricing adjusts property prices based on real-time factors like demand, inventory, and market trends, enhancing competitiveness. Fixed pricing offers stability and predictability, appealing to buyers seeking transparency, while dynamic pricing maximizes revenue by aligning prices with current market conditions.
Key Terms
Market Demand
Fixed pricing maintains consistent product rates regardless of market fluctuations, offering stability for consumers and businesses. Dynamic pricing adjusts costs in real-time based on demand, competitor pricing, and inventory levels, maximizing revenue during peak periods. Explore how market demand influences pricing strategies to optimize your business outcomes.
Price Adjustment
Fixed pricing maintains consistent costs regardless of market fluctuations, ensuring predictable revenue and straightforward budgeting for businesses. Dynamic pricing adjusts prices in real-time based on demand, competitor pricing, and other market conditions, maximizing profitability and market responsiveness. Explore deeper insights on how price adjustment strategies impact revenue optimization to enhance your pricing model.
Inventory Turnover
Fixed pricing maintains consistent prices, providing stability but potentially slowing inventory turnover when market demand fluctuates. Dynamic pricing adjusts prices based on real-time factors such as demand, competitor pricing, and inventory levels, accelerating inventory turnover by aligning prices with consumer behavior. Explore the advantages and challenges of both strategies to optimize inventory management effectively.
Source and External Links
Fixed Price Explained: What Is It? How Does It Work? - NetSuite - A fixed price is a set price that does not vary in response to external factors or bargaining and can be fixed for a period before becoming variable, providing cash flow certainty and ease of accounting but also exposing the seller to potential cost risks.
Fixed price - Wikipedia - Fixed price is a price for a good or service that is not subject to negotiation or bargaining, sometimes set by sellers or regulated by authorities, commonly used in retail stores in many regions and in fixed-price contracts.
Fixed Pricing Strategy--Definition, Examples & Best Use Cases - Fixed pricing models include subscription-based fees, fixed fee-for-service, bundled pricing, and government-regulated prices offering predictable and stable pricing regardless of usage or time spent.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com