Opportunity Zone investing offers targeted tax incentives for property developments in designated low-income areas, creating potential for significant capital gains deferrals and exclusions. REIT investing provides liquidity and diversification through publicly traded real estate portfolios, facilitating access to commercial and residential property markets without direct ownership responsibilities. Explore more to understand which real estate investment strategy aligns with your financial goals.
Why it is important
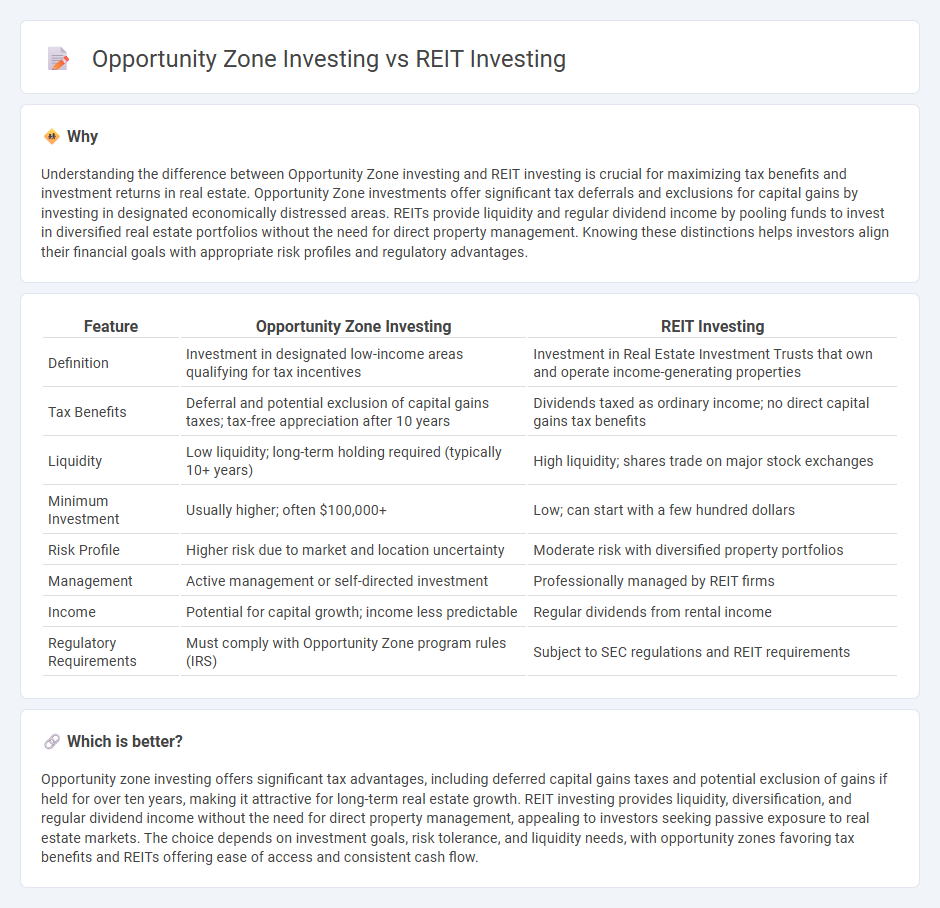
Understanding the difference between Opportunity Zone investing and REIT investing is crucial for maximizing tax benefits and investment returns in real estate. Opportunity Zone investments offer significant tax deferrals and exclusions for capital gains by investing in designated economically distressed areas. REITs provide liquidity and regular dividend income by pooling funds to invest in diversified real estate portfolios without the need for direct property management. Knowing these distinctions helps investors align their financial goals with appropriate risk profiles and regulatory advantages.
Comparison Table
| Feature | Opportunity Zone Investing | REIT Investing |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Investment in designated low-income areas qualifying for tax incentives | Investment in Real Estate Investment Trusts that own and operate income-generating properties |
| Tax Benefits | Deferral and potential exclusion of capital gains taxes; tax-free appreciation after 10 years | Dividends taxed as ordinary income; no direct capital gains tax benefits |
| Liquidity | Low liquidity; long-term holding required (typically 10+ years) | High liquidity; shares trade on major stock exchanges |
| Minimum Investment | Usually higher; often $100,000+ | Low; can start with a few hundred dollars |
| Risk Profile | Higher risk due to market and location uncertainty | Moderate risk with diversified property portfolios |
| Management | Active management or self-directed investment | Professionally managed by REIT firms |
| Income | Potential for capital growth; income less predictable | Regular dividends from rental income |
| Regulatory Requirements | Must comply with Opportunity Zone program rules (IRS) | Subject to SEC regulations and REIT requirements |
Which is better?
Opportunity zone investing offers significant tax advantages, including deferred capital gains taxes and potential exclusion of gains if held for over ten years, making it attractive for long-term real estate growth. REIT investing provides liquidity, diversification, and regular dividend income without the need for direct property management, appealing to investors seeking passive exposure to real estate markets. The choice depends on investment goals, risk tolerance, and liquidity needs, with opportunity zones favoring tax benefits and REITs offering ease of access and consistent cash flow.
Connection
Opportunity zone investing and REIT investing are connected through their shared focus on driving capital into real estate projects that promote economic development in designated low-income areas. Opportunity zones offer tax incentives for long-term investments, while real estate investment trusts (REITs) provide accessible platforms for pooling capital into diversified property portfolios within these zones. Combining opportunity zone benefits with REIT structures enhances investor access to tax-advantaged real estate opportunities and supports community revitalization.
Key Terms
Liquidity
REIT investing offers higher liquidity, with shares easily traded on public exchanges, allowing investors quick access to their capital. Opportunity zone investments, by contrast, require longer holding periods to maximize tax benefits, resulting in significantly reduced liquidity. Explore the detailed trade-offs between liquidity and tax incentives in these investment strategies to make informed decisions.
Tax Incentives
REIT investing offers significant tax benefits, including dividends taxed at favorable rates and deferral of capital gains through 1031 exchanges, while Opportunity Zone investing provides more substantial tax incentives such as deferral, reduction, and potential exclusion of capital gains on qualified investments held for specific periods. Opportunity Zone funds must invest in designated low-income areas, promoting economic development and offering investors tax-exempt appreciation after 10 years, a feature not available with standard REITs. Explore detailed comparisons of tax incentives between REIT and Opportunity Zone investing to optimize your portfolio strategies.
Diversification
REIT investing offers diversified exposure to income-generating real estate assets across various property types and geographic locations, reducing risk through portfolio variety. Opportunity zone investing focuses on capital gains tax incentives by investing in designated economically distressed areas, potentially leading to high growth but with concentrated market risks. Explore the benefits and risks of each strategy to determine the best fit for your investment goals.
Source and External Links
What is a REIT? - Explains how REITs offer a way for people to invest in real estate without having to directly manage properties.
What are REITs & how do they work? - Discusses the benefits of REITs, including income generation and portfolio diversification.
Best-Performing REITs of July 2025, How to Invest - Provides information on top-performing REITs and how to invest in them, including through ETFs.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com