Infill development maximizes underutilized urban land by repurposing vacant lots within existing neighborhoods, promoting efficient infrastructure use and walkability. Brownfield development focuses on rehabilitating previously contaminated or abandoned industrial sites, addressing environmental challenges to create new commercial or residential spaces. Explore the benefits and challenges of these strategic urban growth methods to understand their impact on sustainable real estate development.
Why it is important
Understanding the difference between infill development, which focuses on developing vacant or underused parcels within existing urban areas, and brownfield development, involving the cleanup and reuse of previously contaminated industrial sites, is crucial for effective real estate planning. Infill development maximizes land efficiency and revitalizes neighborhoods, while brownfield development addresses environmental remediation and urban renewal challenges. Knowing these distinctions helps investors and planners make informed decisions about risk, cost, and community impact in real estate projects. This knowledge also supports sustainable urban growth and compliance with regulatory frameworks.
Comparison Table
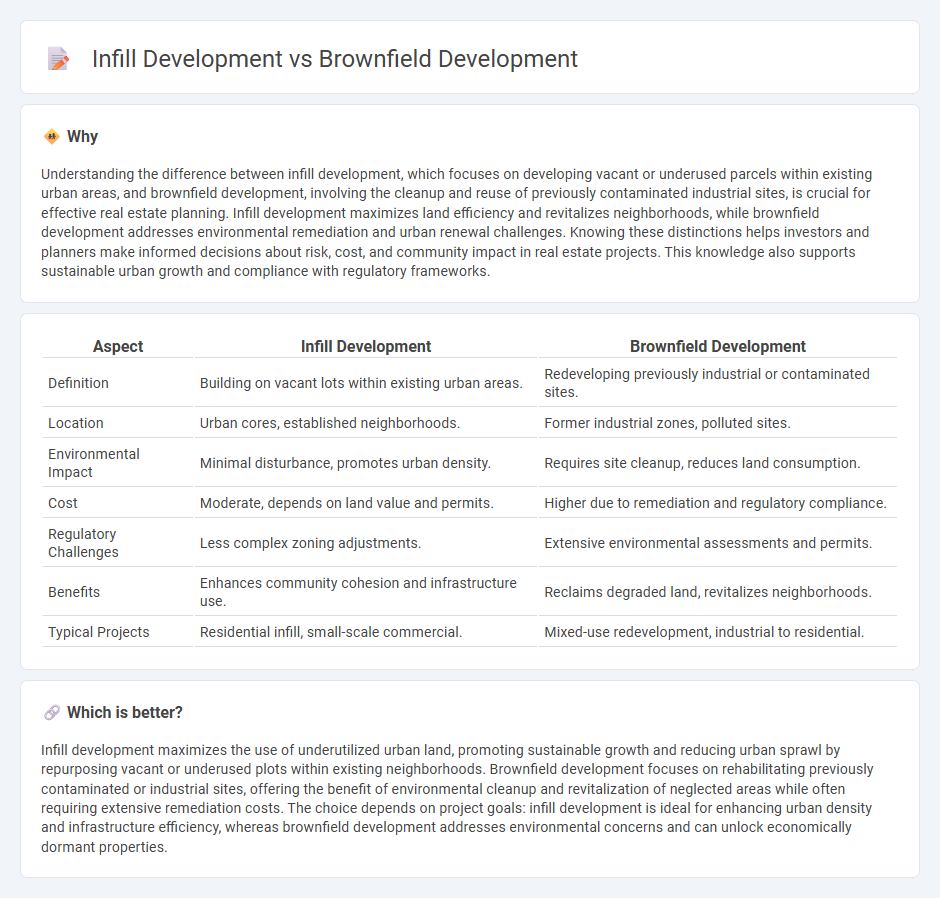
| Aspect | Infill Development | Brownfield Development |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Building on vacant lots within existing urban areas. | Redeveloping previously industrial or contaminated sites. |
| Location | Urban cores, established neighborhoods. | Former industrial zones, polluted sites. |
| Environmental Impact | Minimal disturbance, promotes urban density. | Requires site cleanup, reduces land consumption. |
| Cost | Moderate, depends on land value and permits. | Higher due to remediation and regulatory compliance. |
| Regulatory Challenges | Less complex zoning adjustments. | Extensive environmental assessments and permits. |
| Benefits | Enhances community cohesion and infrastructure use. | Reclaims degraded land, revitalizes neighborhoods. |
| Typical Projects | Residential infill, small-scale commercial. | Mixed-use redevelopment, industrial to residential. |
Which is better?
Infill development maximizes the use of underutilized urban land, promoting sustainable growth and reducing urban sprawl by repurposing vacant or underused plots within existing neighborhoods. Brownfield development focuses on rehabilitating previously contaminated or industrial sites, offering the benefit of environmental cleanup and revitalization of neglected areas while often requiring extensive remediation costs. The choice depends on project goals: infill development is ideal for enhancing urban density and infrastructure efficiency, whereas brownfield development addresses environmental concerns and can unlock economically dormant properties.
Connection
Infill development and brownfield development are closely connected as both focus on revitalizing underutilized urban areas to optimize land use and curb urban sprawl. Brownfield sites, often contaminated industrial or commercial properties, present unique challenges and opportunities for infill development by transforming neglected land into valuable residential or commercial spaces. This synergy promotes sustainable urban regeneration, enhances local economies, and improves environmental quality by reusing existing infrastructure and reducing the need for new land acquisition.
Key Terms
**Brownfield Development:**
Brownfield development involves the redevelopment of previously industrial or contaminated sites, transforming underutilized land into productive urban spaces while addressing environmental remediation. It optimizes land use in already developed areas, reducing urban sprawl and preserving greenfields by rehabilitating existing infrastructure. Explore the benefits and challenges of brownfield development to understand its role in sustainable urban growth.
Contamination
Brownfield development focuses on rehabilitating previously contaminated or industrial sites, requiring extensive environmental assessments and remediation to manage hazardous substances such as heavy metals, petroleum hydrocarbons, or asbestos. Infill development typically occurs on underutilized parcels within urban areas with minimal contamination, reducing the need for complex cleanup processes. Explore further to understand how contamination challenges influence project costs and urban planning strategies.
Remediation
Brownfield development involves the cleanup and repurposing of previously contaminated or underutilized lands, requiring extensive environmental remediation to ensure safety and suitability for new construction. Infill development optimizes the use of vacant or underused parcels within existing urban areas, often necessitating targeted remediation to address minor contamination or soil issues. Explore detailed strategies and benefits of remediation in both brownfield and infill developments to maximize sustainable urban growth.
Source and External Links
Brownfield Development and the Implications of Net-Land-Take Targets - Brownfield development involves repurposing previously developed urban land for new residential, commercial, or mixed-use projects, aligning with sustainable goals by reducing greenfield sprawl and unlocking significant real estate value.
Brownfield Overview and Definition - US EPA - A brownfield is property whose redevelopment is complicated by potential hazardous substances, requiring careful cleanup and management before reuse for new development purposes.
Brownfield Development - Stantec - Brownfield sites are transformed from perceived liabilities into valuable, economically viable assets through integrated planning, cleanup, and design, turning dormant lands into thriving community spaces.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com