Green leases focus on sustainability by integrating energy efficiency and environmental responsibility into commercial property agreements, encouraging tenants to reduce carbon footprints and utility costs. Net-net leases, also known as double net leases, require tenants to cover property taxes and insurance premiums on top of base rent, shifting operational expenses away from landlords. Discover the key differences and benefits of green leases versus net-net leases to make informed real estate decisions.
Why it is important
Understanding the difference between green leases and net-net leases is crucial for real estate investors and tenants to optimize cost management and sustainability goals. Green leases integrate environmental performance standards, promoting energy efficiency and reducing utility expenses. Net-net leases pass property taxes and insurance costs to tenants, affecting overall financial liabilities. Distinguishing these lease types enables informed decision-making that balances economic benefits with environmental impact.
Comparison Table
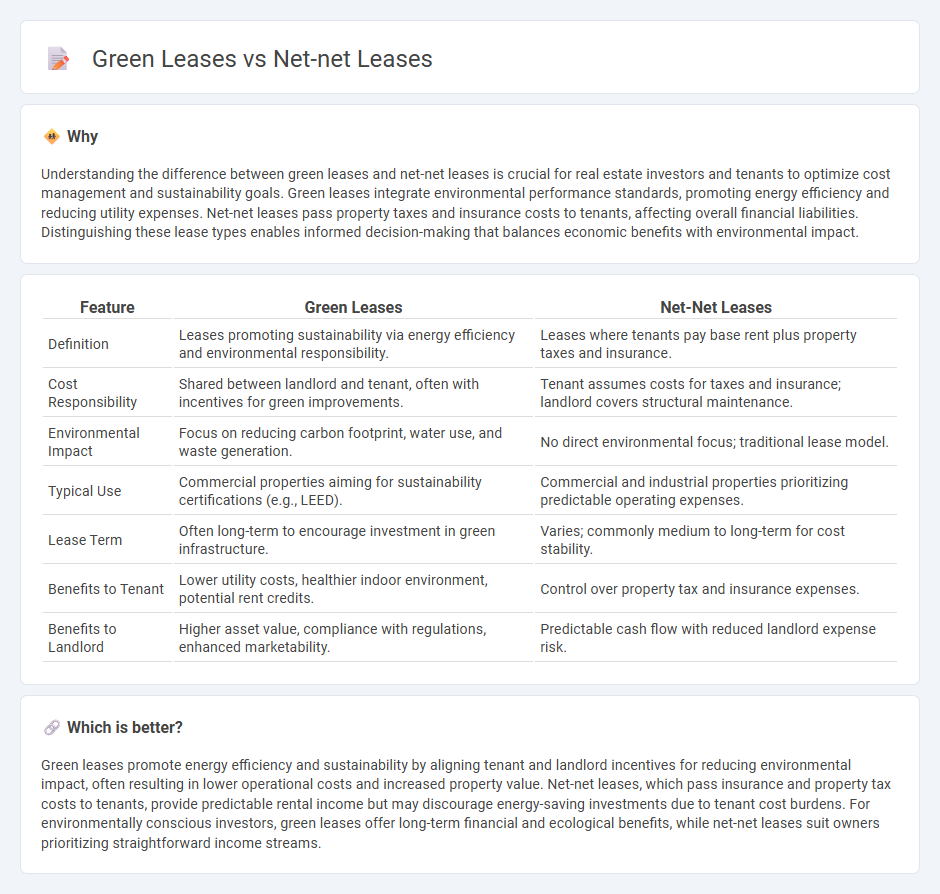
| Feature | Green Leases | Net-Net Leases |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Leases promoting sustainability via energy efficiency and environmental responsibility. | Leases where tenants pay base rent plus property taxes and insurance. |
| Cost Responsibility | Shared between landlord and tenant, often with incentives for green improvements. | Tenant assumes costs for taxes and insurance; landlord covers structural maintenance. |
| Environmental Impact | Focus on reducing carbon footprint, water use, and waste generation. | No direct environmental focus; traditional lease model. |
| Typical Use | Commercial properties aiming for sustainability certifications (e.g., LEED). | Commercial and industrial properties prioritizing predictable operating expenses. |
| Lease Term | Often long-term to encourage investment in green infrastructure. | Varies; commonly medium to long-term for cost stability. |
| Benefits to Tenant | Lower utility costs, healthier indoor environment, potential rent credits. | Control over property tax and insurance expenses. |
| Benefits to Landlord | Higher asset value, compliance with regulations, enhanced marketability. | Predictable cash flow with reduced landlord expense risk. |
Which is better?
Green leases promote energy efficiency and sustainability by aligning tenant and landlord incentives for reducing environmental impact, often resulting in lower operational costs and increased property value. Net-net leases, which pass insurance and property tax costs to tenants, provide predictable rental income but may discourage energy-saving investments due to tenant cost burdens. For environmentally conscious investors, green leases offer long-term financial and ecological benefits, while net-net leases suit owners prioritizing straightforward income streams.
Connection
Green leases and net-net leases intersect through their shared focus on operational costs and sustainability in real estate. Green leases incorporate environmental performance standards that can influence net-net lease expenses, where tenants are responsible for property taxes, insurance, and maintenance. Aligning these lease types promotes energy efficiency and cost transparency, benefiting landlords and tenants alike.
Key Terms
Operating Expenses
Net-net leases require tenants to cover property taxes and insurance while landlords handle operating expenses, creating a predictable expense framework. Green leases integrate sustainability clauses that allocate operating expense responsibilities based on energy efficiency targets and environmental performance metrics, promoting cost savings and eco-friendly management. Discover how these lease structures impact financial planning and sustainability goals in commercial real estate.
Sustainability Clauses
Net-net leases typically require tenants to pay property taxes and insurance in addition to rent, while green leases incorporate sustainability clauses that promote energy efficiency, waste reduction, and environmentally responsible building operations. Green leases align landlord and tenant interests by encouraging shared investments in eco-friendly upgrades and ongoing sustainable practices, leading to reduced environmental impact and operational costs. Explore the benefits and implementation strategies of these leases to enhance sustainability in commercial property management.
Tenant Responsibilities
Net-net leases require tenants to cover property taxes and insurance, increasing their financial obligations beyond base rent. Green leases emphasize sustainable practices, obligating tenants to adopt energy-efficient measures and collaborate on environmental goals. Explore the distinct tenant responsibilities across both lease types to optimize lease negotiations and property management.
Source and External Links
What Is a Net Lease in Commercial Real Estate? - A double net lease, or "net-net" lease, requires the tenant to pay rent plus property taxes and insurance premiums, with the landlord typically responsible for maintenance.
Net Lease - A double net lease means the tenant pays rent plus property taxes and insurance premiums, with the landlord handling maintenance costs.
Understanding Gross, Double Net, and Triple Net Leases - A double net lease involves tenants paying property taxes and insurance premiums alongside rent, while the landlord covers maintenance.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com