Tiny home communities offer compact, energy-efficient living with a focus on sustainability and minimalist design, appealing to eco-conscious buyers seeking affordable housing solutions. Mobile home communities provide larger, typically more affordable residences with greater flexibility in location and customization options for families or retirees. Explore the unique benefits and challenges of each community type to find the ideal living environment for your lifestyle.
Why it is important
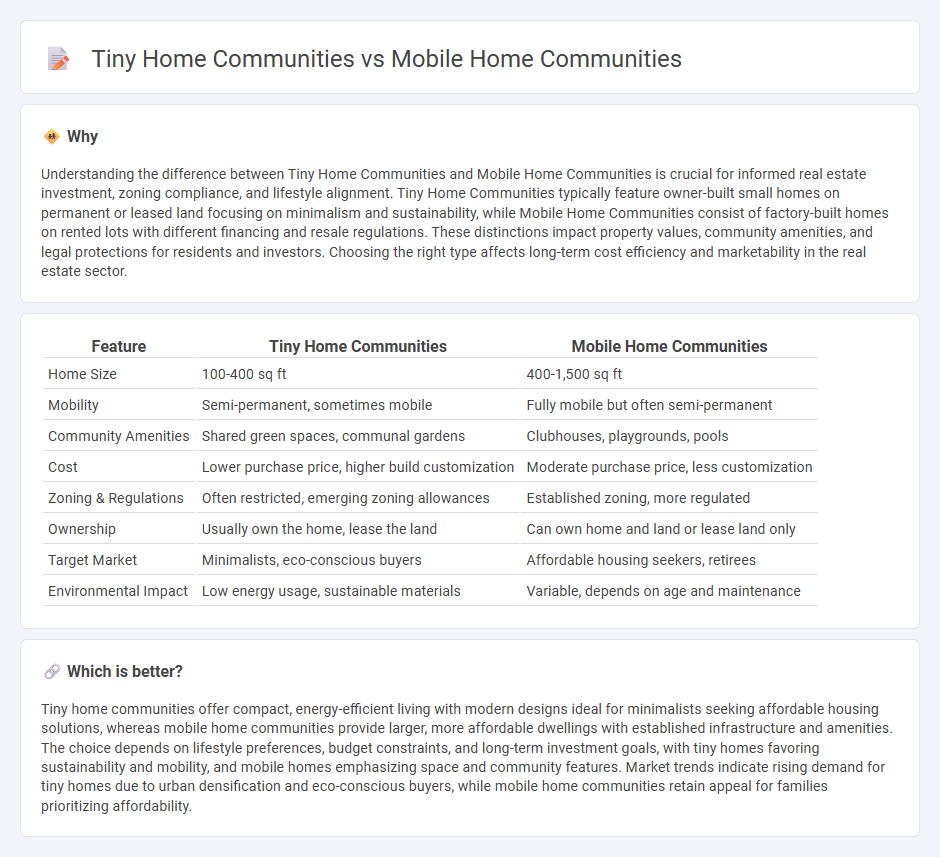
Understanding the difference between Tiny Home Communities and Mobile Home Communities is crucial for informed real estate investment, zoning compliance, and lifestyle alignment. Tiny Home Communities typically feature owner-built small homes on permanent or leased land focusing on minimalism and sustainability, while Mobile Home Communities consist of factory-built homes on rented lots with different financing and resale regulations. These distinctions impact property values, community amenities, and legal protections for residents and investors. Choosing the right type affects long-term cost efficiency and marketability in the real estate sector.
Comparison Table
| Feature | Tiny Home Communities | Mobile Home Communities |
|---|---|---|
| Home Size | 100-400 sq ft | 400-1,500 sq ft |
| Mobility | Semi-permanent, sometimes mobile | Fully mobile but often semi-permanent |
| Community Amenities | Shared green spaces, communal gardens | Clubhouses, playgrounds, pools |
| Cost | Lower purchase price, higher build customization | Moderate purchase price, less customization |
| Zoning & Regulations | Often restricted, emerging zoning allowances | Established zoning, more regulated |
| Ownership | Usually own the home, lease the land | Can own home and land or lease land only |
| Target Market | Minimalists, eco-conscious buyers | Affordable housing seekers, retirees |
| Environmental Impact | Low energy usage, sustainable materials | Variable, depends on age and maintenance |
Which is better?
Tiny home communities offer compact, energy-efficient living with modern designs ideal for minimalists seeking affordable housing solutions, whereas mobile home communities provide larger, more affordable dwellings with established infrastructure and amenities. The choice depends on lifestyle preferences, budget constraints, and long-term investment goals, with tiny homes favoring sustainability and mobility, and mobile homes emphasizing space and community features. Market trends indicate rising demand for tiny homes due to urban densification and eco-conscious buyers, while mobile home communities retain appeal for families prioritizing affordability.
Connection
Tiny home communities and mobile home communities both provide affordable, space-efficient living options that address housing shortages in urban and rural areas. These communities share infrastructure elements such as communal spaces, utility hookups, and zoning regulations that support compact residential designs. Their popularity is driven by the demand for minimalist lifestyles, lower maintenance costs, and increased mobility compared to traditional housing.
Key Terms
Zoning Regulations
Mobile home communities often benefit from established zoning regulations that designate specific land for manufactured housing, allowing for easier development and integration into residential areas. Tiny home communities face more complex zoning challenges, as many municipalities lack clear regulations for homes under traditional minimum size requirements, often classifying them as accessory structures or requiring variances. Explore local zoning policies further to understand the distinctions and opportunities for both community types.
Land Lease Agreements
Land lease agreements in mobile home communities typically involve long-term leases with fixed monthly fees, covering common area maintenance and amenities, ensuring stable housing costs. Tiny home communities often offer more flexible lease terms, sometimes incorporating shared ownership models or shorter lease durations tailored to minimalist lifestyles. Explore the differences in land lease agreements to determine which community type aligns best with your housing preferences and financial goals.
Infrastructure Requirements
Mobile home communities require extensive infrastructure including paved roads, utility hookups (water, electricity, sewage), and designated parking spaces tailored for larger, transportable units. Tiny home communities often emphasize sustainable infrastructure with shared utilities, compact roadways, and efficient waste management systems designed for smaller footprints. Explore how infrastructure shapes the development and livability of these unique housing solutions.
Source and External Links
Continental Communities: Home - One of the largest owner-operators of manufactured housing communities offering affordable, safe living with quality amenities, flexible home rental and purchase programs, and professional on-site management.
MHVillage: Mobile Homes - A comprehensive platform to find mobile home communities, including homes for sale and rent, with extensive search filters and detailed listing information across the U.S.
Manufactured Home Communities by Westland - Owner and operator of 17 manufactured home communities primarily in Southern California, featuring amenities like clubhouses, dog parks, and pools with a strong focus on community and affordability.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com