Lease-to-own models offer tenants the opportunity to rent a property with a portion of their payments contributing toward eventual ownership, providing a pathway to homeownership without immediate mortgage qualification. Leaseback arrangements involve selling a property and then leasing it back from the new owner, enabling sellers to free capital while retaining occupancy. Explore the differences and benefits of these innovative real estate financing options to determine which aligns best with your financial goals.
Why it is important
Understanding the difference between lease-to-own and leaseback models is crucial for investors and homeowners to make informed financial decisions and optimize property value. Lease-to-own agreements allow tenants to build equity and eventually purchase the property, providing a pathway to ownership. Leaseback arrangements enable sellers to maintain occupancy by leasing the property after sale, improving liquidity without relocating. Accurate knowledge of these models impacts investment strategy, cash flow management, and long-term asset planning in real estate.
Comparison Table
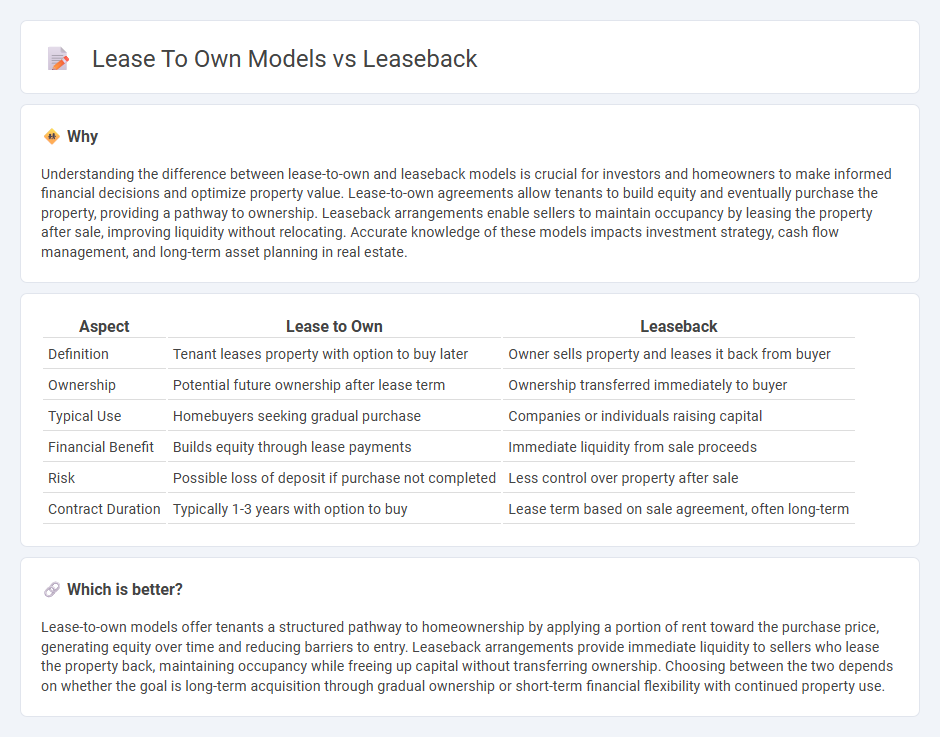
| Aspect | Lease to Own | Leaseback |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Tenant leases property with option to buy later | Owner sells property and leases it back from buyer |
| Ownership | Potential future ownership after lease term | Ownership transferred immediately to buyer |
| Typical Use | Homebuyers seeking gradual purchase | Companies or individuals raising capital |
| Financial Benefit | Builds equity through lease payments | Immediate liquidity from sale proceeds |
| Risk | Possible loss of deposit if purchase not completed | Less control over property after sale |
| Contract Duration | Typically 1-3 years with option to buy | Lease term based on sale agreement, often long-term |
Which is better?
Lease-to-own models offer tenants a structured pathway to homeownership by applying a portion of rent toward the purchase price, generating equity over time and reducing barriers to entry. Leaseback arrangements provide immediate liquidity to sellers who lease the property back, maintaining occupancy while freeing up capital without transferring ownership. Choosing between the two depends on whether the goal is long-term acquisition through gradual ownership or short-term financial flexibility with continued property use.
Connection
Lease-to-own models and leaseback arrangements both involve leasing property with future ownership or financial benefits, creating flexible real estate investment strategies. Lease-to-own allows tenants to apply rent payments toward purchasing the property, while leaseback enables owners to sell the property and lease it back to maintain operational control. These models connect through enabling asset liquidity and long-term property acquisition or usage options.
Key Terms
Ownership Transfer
Leaseback models allow current owners to sell their asset and immediately lease it back, maintaining operational control without transferring ownership, while lease to own models gradually transfer ownership to the lessee through payments over time. In lease to own agreements, lessees build equity with each payment until full ownership is achieved, contrasting with leaseback where ownership remains with the original seller. Explore further to understand which model fits your strategic goals for asset management and investment.
Rent Payments
Leaseback models involve a company selling an asset and leasing it back, allowing for consistent rent payments that improve cash flow without ownership transfer. Lease-to-own agreements require tenants to make rent payments with a portion applied toward eventual ownership, blending rental expenses with purchase savings. Explore the detailed financial impacts of rent payments in both models to determine the best fit for your business goals.
Purchase Option
Leaseback models allow property owners to sell their asset and lease it back, retaining operational control while freeing up capital; purchase options are typically absent or limited. Lease-to-own models incorporate a predetermined purchase option enabling tenants to apply lease payments toward ownership, facilitating eventual acquisition. Explore detailed comparisons to understand which model aligns best with your financial strategy and long-term goals.
Source and External Links
What Is A Leaseback Definition? - Marketplace Homes - This webpage explains that a leaseback allows property owners to sell their assets and continue using them as tenants through a rental agreement.
What to consider with a leaseback agreement Rate - Provides insights into how leaseback agreements can help sellers by giving them more time to find a new home after selling their property.
Sale-leasebacks | W. P. Carey - Describes how companies use sale-leasebacks to convert real estate into working capital while maintaining operational control through a long-term lease.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com