Agritourism properties offer unique opportunities for agricultural activities combined with tourism, attracting visitors seeking rural experiences and farm stays, whereas residential properties primarily serve as living spaces designed for personal and family use. These agritourism estates often include farmland, vineyards, and farmhouses, generating income through guest accommodations and local product sales, contrasting with the conventional housing focus of residential real estate. Explore the distinct advantages and investment potential of agritourism versus residential properties to make informed real estate decisions.
Why it is important
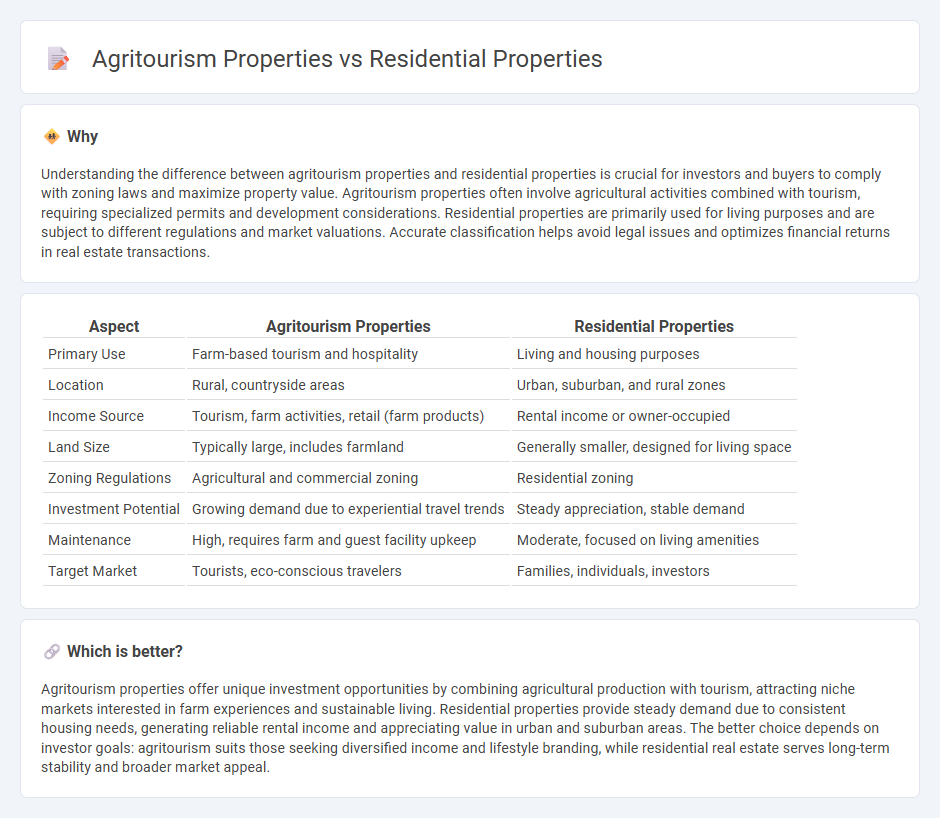
Understanding the difference between agritourism properties and residential properties is crucial for investors and buyers to comply with zoning laws and maximize property value. Agritourism properties often involve agricultural activities combined with tourism, requiring specialized permits and development considerations. Residential properties are primarily used for living purposes and are subject to different regulations and market valuations. Accurate classification helps avoid legal issues and optimizes financial returns in real estate transactions.
Comparison Table
| Aspect | Agritourism Properties | Residential Properties |
|---|---|---|
| Primary Use | Farm-based tourism and hospitality | Living and housing purposes |
| Location | Rural, countryside areas | Urban, suburban, and rural zones |
| Income Source | Tourism, farm activities, retail (farm products) | Rental income or owner-occupied |
| Land Size | Typically large, includes farmland | Generally smaller, designed for living space |
| Zoning Regulations | Agricultural and commercial zoning | Residential zoning |
| Investment Potential | Growing demand due to experiential travel trends | Steady appreciation, stable demand |
| Maintenance | High, requires farm and guest facility upkeep | Moderate, focused on living amenities |
| Target Market | Tourists, eco-conscious travelers | Families, individuals, investors |
Which is better?
Agritourism properties offer unique investment opportunities by combining agricultural production with tourism, attracting niche markets interested in farm experiences and sustainable living. Residential properties provide steady demand due to consistent housing needs, generating reliable rental income and appreciating value in urban and suburban areas. The better choice depends on investor goals: agritourism suits those seeking diversified income and lifestyle branding, while residential real estate serves long-term stability and broader market appeal.
Connection
Agritourism properties and residential properties are interconnected through the growing demand for rural living experiences that blend lifestyle with agricultural activities. Many residential buyers seek homes on agritourism sites to enjoy farm-to-table lifestyles, sustainable living, and recreational opportunities offered by working farms. This trend increases property values and encourages mixed-use developments that combine residential comfort with agricultural tourism.
Key Terms
Zoning
Residential properties are primarily zoned for housing, with regulations targeting building height, lot size, and residential use to maintain neighborhood character. Agritourism properties fall under agricultural zoning, which permits farming activities combined with tourism services like farm stays and events, often requiring special permits to balance commercial use and land preservation. Explore zoning details further to understand how these regulations shape property use and development opportunities.
Land use
Residential properties primarily emphasize land use for housing development, community infrastructure, and recreational spaces, optimizing for comfort and accessibility. Agritourism properties blend agricultural activities with tourism functions, utilizing land not only for crop production or livestock but also for experiential tourism services like farm stays, tours, and workshops. Explore more on how strategic land use shapes the value and functionality of both residential and agritourism properties.
Property valuation
Residential properties are primarily valued based on location, market demand, and comparable sales, with factors like neighborhood amenities and school districts significantly influencing prices. Agritourism properties require valuation methods that consider both land productivity and potential income from tourism activities, such as farm stays, recreational facilities, and event hosting, making their assessment more complex and multifaceted. Explore detailed valuation strategies to understand how these unique characteristics impact the market value of residential and agritourism properties.
Source and External Links
Residential Property - Residential property includes any building or unit zoned and used as living space, such as single-family homes and multi-family homes.
How Residential Property Is Valued - In Cook County, residential property value is assessed at 10% of its fair market value, using recent sales data of similar homes in the area.
Residential Properties - Residential Properties Ltd. is a prominent real estate company in Rhode Island, serving with around 250 agents and multiple offices.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com