Vertical farming real estate maximizes urban space by integrating multi-level agricultural facilities within buildings, offering sustainable solutions for local food production and reducing transportation costs. Industrial real estate focuses on large-scale warehouses, factories, and distribution centers designed for manufacturing and logistics, often requiring expansive land and infrastructure. Explore the benefits and challenges of both to understand how real estate innovation drives future city development.
Why it is important
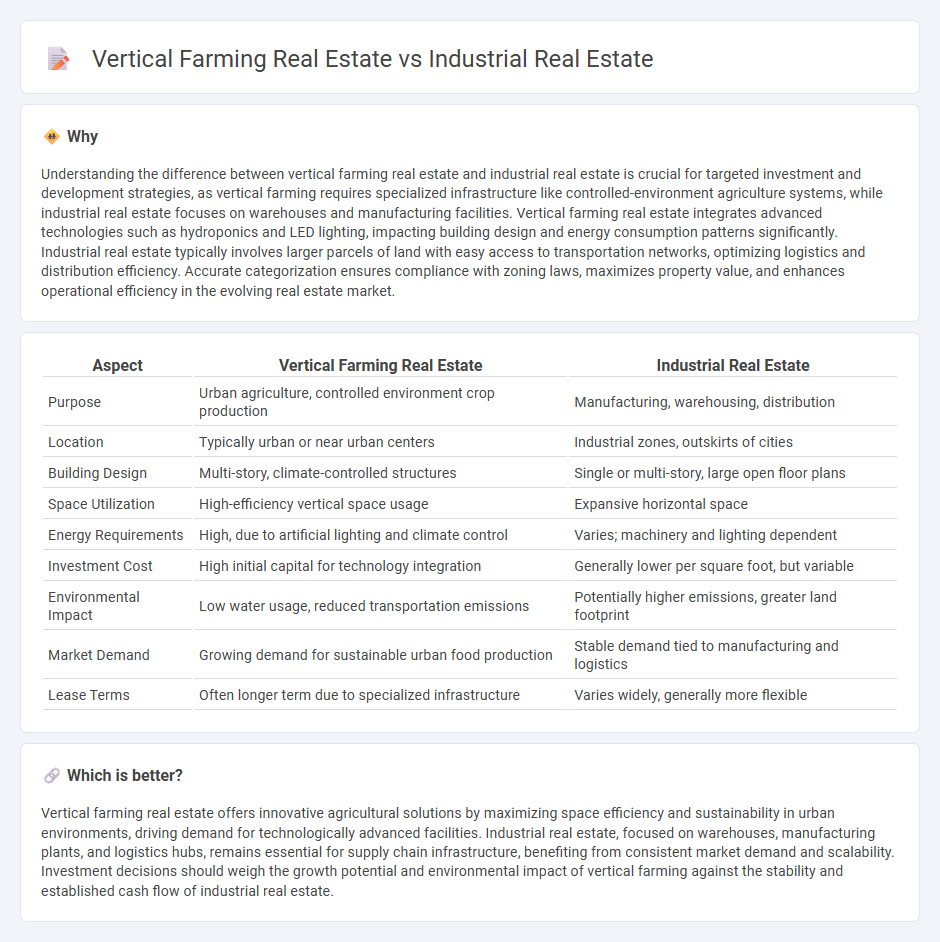
Understanding the difference between vertical farming real estate and industrial real estate is crucial for targeted investment and development strategies, as vertical farming requires specialized infrastructure like controlled-environment agriculture systems, while industrial real estate focuses on warehouses and manufacturing facilities. Vertical farming real estate integrates advanced technologies such as hydroponics and LED lighting, impacting building design and energy consumption patterns significantly. Industrial real estate typically involves larger parcels of land with easy access to transportation networks, optimizing logistics and distribution efficiency. Accurate categorization ensures compliance with zoning laws, maximizes property value, and enhances operational efficiency in the evolving real estate market.
Comparison Table
| Aspect | Vertical Farming Real Estate | Industrial Real Estate |
|---|---|---|
| Purpose | Urban agriculture, controlled environment crop production | Manufacturing, warehousing, distribution |
| Location | Typically urban or near urban centers | Industrial zones, outskirts of cities |
| Building Design | Multi-story, climate-controlled structures | Single or multi-story, large open floor plans |
| Space Utilization | High-efficiency vertical space usage | Expansive horizontal space |
| Energy Requirements | High, due to artificial lighting and climate control | Varies; machinery and lighting dependent |
| Investment Cost | High initial capital for technology integration | Generally lower per square foot, but variable |
| Environmental Impact | Low water usage, reduced transportation emissions | Potentially higher emissions, greater land footprint |
| Market Demand | Growing demand for sustainable urban food production | Stable demand tied to manufacturing and logistics |
| Lease Terms | Often longer term due to specialized infrastructure | Varies widely, generally more flexible |
Which is better?
Vertical farming real estate offers innovative agricultural solutions by maximizing space efficiency and sustainability in urban environments, driving demand for technologically advanced facilities. Industrial real estate, focused on warehouses, manufacturing plants, and logistics hubs, remains essential for supply chain infrastructure, benefiting from consistent market demand and scalability. Investment decisions should weigh the growth potential and environmental impact of vertical farming against the stability and established cash flow of industrial real estate.
Connection
Vertical farming real estate leverages industrial real estate spaces for urban agriculture, optimizing underutilized warehouses and factories to cultivate crops vertically. This integration enhances land use efficiency and supports sustainable food production within industrial zones. Industrial real estate's infrastructure and location provide ideal conditions for implementing vertical farming technologies, promoting innovative urban development.
Key Terms
Zoning
Industrial real estate zoning typically supports manufacturing, warehousing, and logistics activities, often allowing for high-capacity infrastructure and heavy vehicle access. Vertical farming real estate requires specialized zoning that permits agricultural activities within urban or industrial zones, highlighting the need for water access, environmental controls, and minimal chemical exposure. Explore zoning regulations and their impact on investment potential in vertical farming versus traditional industrial real estate.
Infrastructure
Industrial real estate prioritizes robust infrastructure such as heavy-duty power supply, large loading docks, and extensive warehousing space to support logistics and manufacturing operations. Vertical farming real estate demands advanced HVAC systems, specialized lighting, and precise climate control to optimize plant growth within multi-story facilities. Discover how infrastructure requirements shape the future of these divergent real estate sectors.
Controlled Environment
Industrial real estate tailored for controlled environments often includes warehouses and factories designed for precise climate control but generally lacks the specialized infrastructure crucial for vertical farming, such as adjustable LED lighting and hydroponic systems. Vertical farming real estate prioritizes multi-story, energy-efficient structures equipped with innovative technology to optimize plant growth, water recycling, and nutrient delivery within a controlled environment agriculture (CEA) framework. Explore the unique features and benefits of both real estate types to understand how they cater to the specific demands of controlled environment agriculture.
Source and External Links
What Is Industrial Real Estate | Definition & Examples - DoorLoop - Industrial real estate encompasses properties used for non-public commercial activities like manufacturing, warehousing, and parcel delivery, often involving large spaces tailored to heavy or light manufacturing needs.
The Ultimate Guide to Industrial Real Estate - The Cauble Group - Industrial real estate broadly includes land and buildings that accommodate industrial activities such as production, assembly, warehousing, research, storage, and distribution, typically located in zoned industrial areas to minimize disruption to other businesses or residences.
Top industrial real estate trends - J.P. Morgan - Driven by e-commerce growth and demand for last-mile delivery, industrial real estate is maturing with trends showing market stabilization, slower rent growth, steady vacancies above pre-pandemic averages, and emerging opportunities in cold storage and AI-related facilities.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com