Upzoning increases the allowed density of properties, enabling taller buildings and more units to address housing shortages in urban areas. Inclusionary zoning mandates that developers include a percentage of affordable housing within new projects to promote economic diversity. Explore the differences between upzoning and inclusionary zoning to understand their impact on urban development.
Why it is important
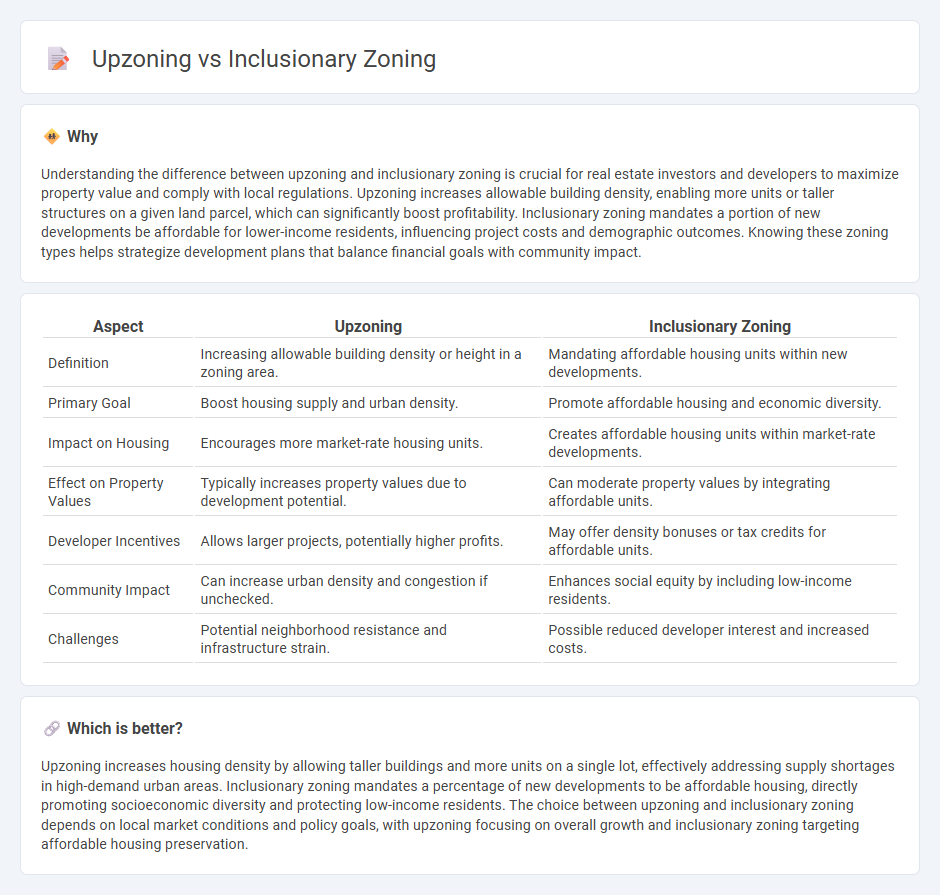
Understanding the difference between upzoning and inclusionary zoning is crucial for real estate investors and developers to maximize property value and comply with local regulations. Upzoning increases allowable building density, enabling more units or taller structures on a given land parcel, which can significantly boost profitability. Inclusionary zoning mandates a portion of new developments be affordable for lower-income residents, influencing project costs and demographic outcomes. Knowing these zoning types helps strategize development plans that balance financial goals with community impact.
Comparison Table
| Aspect | Upzoning | Inclusionary Zoning |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Increasing allowable building density or height in a zoning area. | Mandating affordable housing units within new developments. |
| Primary Goal | Boost housing supply and urban density. | Promote affordable housing and economic diversity. |
| Impact on Housing | Encourages more market-rate housing units. | Creates affordable housing units within market-rate developments. |
| Effect on Property Values | Typically increases property values due to development potential. | Can moderate property values by integrating affordable units. |
| Developer Incentives | Allows larger projects, potentially higher profits. | May offer density bonuses or tax credits for affordable units. |
| Community Impact | Can increase urban density and congestion if unchecked. | Enhances social equity by including low-income residents. |
| Challenges | Potential neighborhood resistance and infrastructure strain. | Possible reduced developer interest and increased costs. |
Which is better?
Upzoning increases housing density by allowing taller buildings and more units on a single lot, effectively addressing supply shortages in high-demand urban areas. Inclusionary zoning mandates a percentage of new developments to be affordable housing, directly promoting socioeconomic diversity and protecting low-income residents. The choice between upzoning and inclusionary zoning depends on local market conditions and policy goals, with upzoning focusing on overall growth and inclusionary zoning targeting affordable housing preservation.
Connection
Upzoning increases allowable building density, enabling the development of more housing units within a given area. Inclusionary zoning mandates a percentage of those units be affordable, integrating affordable housing requirements with higher density allowances. This connection promotes diverse, mixed-income communities while addressing housing shortages in urban real estate markets.
Key Terms
Affordable Housing
Inclusionary zoning mandates developers to allocate a percentage of new residential units as affordable housing, ensuring long-term affordability within mixed-income communities. Upzoning increases allowable building density and height, potentially boosting housing supply and affordability indirectly by enabling more units, though it lacks explicit affordable housing requirements. Explore the distinct impacts of inclusionary zoning and upzoning on affordable housing strategies to better understand their roles in urban development.
Density
Inclusionary zoning requires developers to allocate a percentage of new construction as affordable housing, often limiting overall density to maintain community character. Upzoning increases allowable building density and height, encouraging higher population density and more diverse housing types without specific affordability mandates. Explore the impacts of both strategies on urban growth and housing affordability to understand their roles in sustainable development.
Housing Supply
Inclusionary zoning mandates a percentage of new housing developments be affordable, directly increasing affordable housing supply while integrating diverse income groups. Upzoning permits higher density or taller buildings in specific areas, significantly boosting overall housing supply by enabling more units on existing land parcels. Explore how these strategies affect urban housing availability and community dynamics in detail.
Source and External Links
Housing Innovations Program: Inclusionary Zoning - Inclusionary zoning helps create affordable housing by requiring new developments to include a proportion of affordable units, often tied to the area median income.
What Is Inclusionary Zoning? | Planopedia - Inclusionary zoning is a policy tool that mandates or incentivizes the inclusion of affordable housing units in new developments to promote economic diversity and counteract exclusionary zoning.
Inclusionary Zoning - Boston's Inclusionary Zoning policy requires market-rate developments with seven or more units to include income-restricted housing, aiming to increase affordable housing supply.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com