Leasing ghost kitchens offers flexible, lower-cost options for food entrepreneurs compared to traditional retail pad leasing, which involves higher expenses and longer commitments tied to customer foot traffic. Ghost kitchens maximize urban space efficiency by catering exclusively to delivery services, while retail pads demand prime locations with substantial visibility to drive in-store sales. Explore the advantages and challenges of both leasing models to make informed real estate decisions in the evolving food service industry.
Why it is important
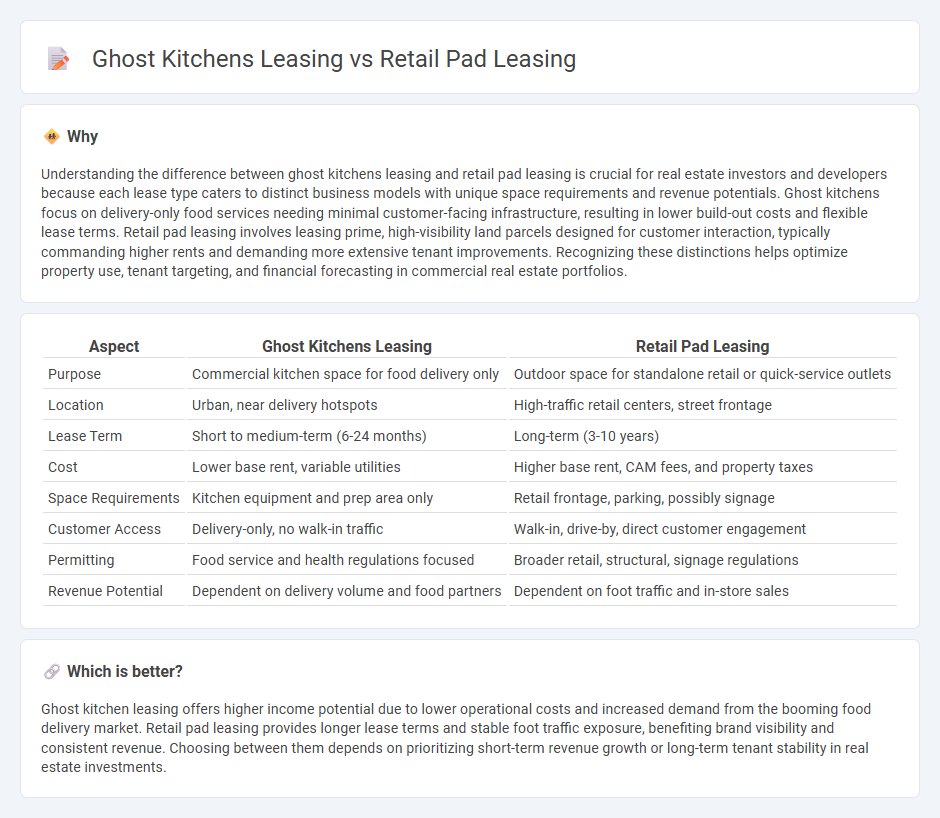
Understanding the difference between ghost kitchens leasing and retail pad leasing is crucial for real estate investors and developers because each lease type caters to distinct business models with unique space requirements and revenue potentials. Ghost kitchens focus on delivery-only food services needing minimal customer-facing infrastructure, resulting in lower build-out costs and flexible lease terms. Retail pad leasing involves leasing prime, high-visibility land parcels designed for customer interaction, typically commanding higher rents and demanding more extensive tenant improvements. Recognizing these distinctions helps optimize property use, tenant targeting, and financial forecasting in commercial real estate portfolios.
Comparison Table
| Aspect | Ghost Kitchens Leasing | Retail Pad Leasing |
|---|---|---|
| Purpose | Commercial kitchen space for food delivery only | Outdoor space for standalone retail or quick-service outlets |
| Location | Urban, near delivery hotspots | High-traffic retail centers, street frontage |
| Lease Term | Short to medium-term (6-24 months) | Long-term (3-10 years) |
| Cost | Lower base rent, variable utilities | Higher base rent, CAM fees, and property taxes |
| Space Requirements | Kitchen equipment and prep area only | Retail frontage, parking, possibly signage |
| Customer Access | Delivery-only, no walk-in traffic | Walk-in, drive-by, direct customer engagement |
| Permitting | Food service and health regulations focused | Broader retail, structural, signage regulations |
| Revenue Potential | Dependent on delivery volume and food partners | Dependent on foot traffic and in-store sales |
Which is better?
Ghost kitchen leasing offers higher income potential due to lower operational costs and increased demand from the booming food delivery market. Retail pad leasing provides longer lease terms and stable foot traffic exposure, benefiting brand visibility and consistent revenue. Choosing between them depends on prioritizing short-term revenue growth or long-term tenant stability in real estate investments.
Connection
Ghost kitchens leasing and retail pad leasing intersect through their shared reliance on flexible commercial real estate spaces designed to accommodate evolving consumer demands and delivery-focused food services. Both leasing types capitalize on high-visibility locations with strategic accessibility, driving foot traffic for retail pads and delivery efficiency for ghost kitchens. Market trends reveal increased investment in mixed-use developments where retail pads support ghost kitchen operations, optimizing property value and tenant synergy.
Key Terms
Triple Net Lease (NNN)
Triple Net Lease (NNN) agreements in retail pad leasing require tenants to cover property taxes, insurance, and maintenance, making it attractive for landlords seeking predictable income and minimal management responsibilities. Ghost kitchens leasing under NNN terms often involves lower initial costs and flexible space utilization but may present higher utility and operational expenses due to intensive kitchen equipment use. Explore detailed comparisons and financial implications to optimize your leasing strategy.
Zoning Regulations
Retail pad leasing typically requires compliance with commercial zoning laws allowing customer-facing businesses in high-traffic areas, while ghost kitchens often fall under industrial or mixed-use zoning due to their delivery-only model. Zoning regulations impact factors such as parking requirements, signage, and operating hours, which vary significantly between retail spaces and ghost kitchen facilities. Explore detailed zoning guidelines to determine the optimal leasing strategy for your business.
Build-Out Requirements
Retail pad leasing demands significant build-out investments including storefront construction, HVAC installation, and compliance with zoning laws to create a customer-facing environment. Ghost kitchens leasing requires specialized build-out for commercial-grade kitchens with heavy-duty ventilation, plumbing for food prep, and delivery-access design, often resulting in lower upfront costs but higher operational efficiency. Explore further to understand how these build-out requirements impact your leasing strategy and budget allocation.
Source and External Links
What Are the Key Features of a Successful Pad Site? - A retail pad site is a freestanding parcel within a larger commercial development, prized for its visibility and accessibility, often hosting businesses like banks, restaurants, and retail stores.
What Is a Pad Site? - Matthews Real Estate Investment Services - Retail pad leases are typically triple net leases with annual rent increases, favored by investment-grade tenants such as banks and quick-service restaurants due to their prime locations and customer traffic.
Understanding Pad Sites: The Hidden Gems of Real Estate - Pad sites are standalone, commercially zoned parcels near major roads with dedicated parking, often leased to single users like fast-food restaurants or convenience stores, providing strategic retail opportunities.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com