Green leases integrate environmental sustainability clauses into property agreements to promote energy efficiency and reduce carbon footprints, benefiting both landlords and tenants through shared eco-friendly responsibilities. Ground leases involve a tenant leasing land typically for long terms, constructing buildings on it while the landowner retains ownership, often used in commercial real estate developments. Explore the distinctions and advantages of green leases versus ground leases to optimize property management strategies.
Why it is important
Understanding the difference between green leases and ground leases is crucial in real estate as green leases focus on sustainability practices and energy efficiency obligations, while ground leases pertain to long-term land use agreements without property ownership transfer. Green leases can significantly reduce operating costs and environmental impact, affecting tenant and landlord responsibilities for building improvements. Ground leases often impact property valuation, financing options, and development potential due to their unique land tenure structure. Recognizing these differences aids investors, developers, and tenants in making informed decisions aligned with their financial and environmental goals.
Comparison Table
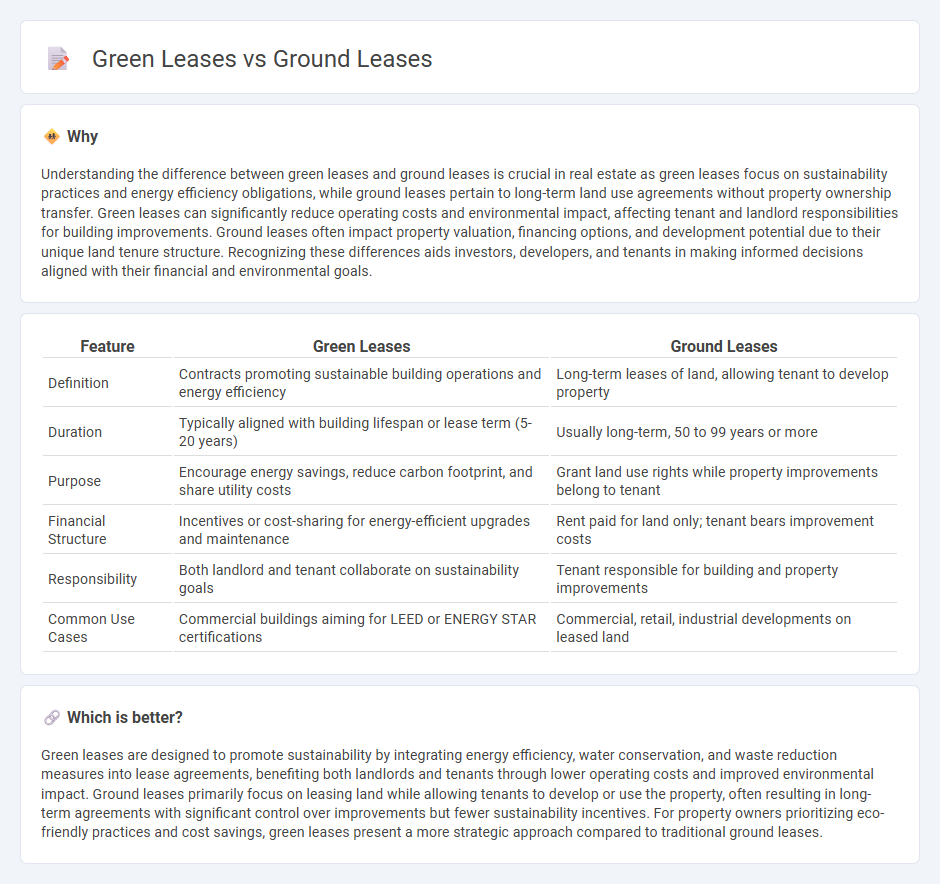
| Feature | Green Leases | Ground Leases |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Contracts promoting sustainable building operations and energy efficiency | Long-term leases of land, allowing tenant to develop property |
| Duration | Typically aligned with building lifespan or lease term (5-20 years) | Usually long-term, 50 to 99 years or more |
| Purpose | Encourage energy savings, reduce carbon footprint, and share utility costs | Grant land use rights while property improvements belong to tenant |
| Financial Structure | Incentives or cost-sharing for energy-efficient upgrades and maintenance | Rent paid for land only; tenant bears improvement costs |
| Responsibility | Both landlord and tenant collaborate on sustainability goals | Tenant responsible for building and property improvements |
| Common Use Cases | Commercial buildings aiming for LEED or ENERGY STAR certifications | Commercial, retail, industrial developments on leased land |
Which is better?
Green leases are designed to promote sustainability by integrating energy efficiency, water conservation, and waste reduction measures into lease agreements, benefiting both landlords and tenants through lower operating costs and improved environmental impact. Ground leases primarily focus on leasing land while allowing tenants to develop or use the property, often resulting in long-term agreements with significant control over improvements but fewer sustainability incentives. For property owners prioritizing eco-friendly practices and cost savings, green leases present a more strategic approach compared to traditional ground leases.
Connection
Green leases and ground leases intersect in promoting sustainable property management and long-term land use. Green leases integrate environmental performance clauses into lease agreements, encouraging energy efficiency and reduced carbon footprints, while ground leases typically involve long-term land rental agreements that can incorporate sustainable development requirements. Combining these lease types supports eco-friendly real estate projects by aligning tenant and landlord incentives toward environmental responsibility and optimized land utilization.
Key Terms
Landlord-Tenant Rights (Ground Lease)
Ground leases establish long-term tenant rights to use and develop land owned by the landlord, often spanning decades, with the tenant responsible for improvements and property maintenance. Green leases integrate sustainability clauses, requiring both landlord and tenant to share obligations for energy efficiency, waste reduction, and environmental compliance within the leased property. Explore the distinct landlord-tenant rights and responsibilities embedded in ground and green leases to optimize your leasing strategy.
Sustainability Clauses (Green Lease)
Ground leases typically involve long-term land agreements allowing tenants to develop property while the owner retains land ownership, with limited emphasis on sustainability clauses. Green leases integrate sustainability requirements directly into the lease terms, promoting energy efficiency, waste reduction, and environmental responsibility through specific clauses on resource management and carbon reduction. Discover how incorporating sustainability clauses in green leases drives eco-friendly property management and long-term environmental benefits.
Triple Net Lease (Ground Lease)
Ground leases, a type of Triple Net Lease, require tenants to pay property taxes, insurance, and maintenance, transferring significant financial responsibilities away from the landlord. In contrast, green leases integrate sustainability clauses promoting energy efficiency, waste reduction, and environmentally friendly operations, aligning landlord and tenant goals toward ecological impact reduction. Discover how ground leases and green leases differ in risk allocation and environmental benefits by exploring their impacts on real estate investment strategies.
Source and External Links
What is a Ground Lease? A Breakdown for Commercial Real Estate - This article explains the basics of ground leases, including their long-term nature and how they allow tenants to develop land without owning it.
Key Considerations in a Ground Lease - This article discusses the complexities and benefits of ground leases for both landlords and tenants, highlighting their advantages and key considerations.
Ground Lease vs Land Lease: Key Differences - This webpage provides insights into the differences between ground leases and land leases, focusing on ownership and development rights.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com