Smart lease agreements leverage blockchain technology and IoT devices to automate rent payments, track property conditions, and enhance transparency, reducing disputes between landlords and tenants. Ground leases involve a tenant leasing land from the owner for long-term use, often spanning 30 to 99 years, allowing development without purchasing the land itself. Explore the benefits and key differences of these leasing options to optimize your real estate investments.
Why it is important
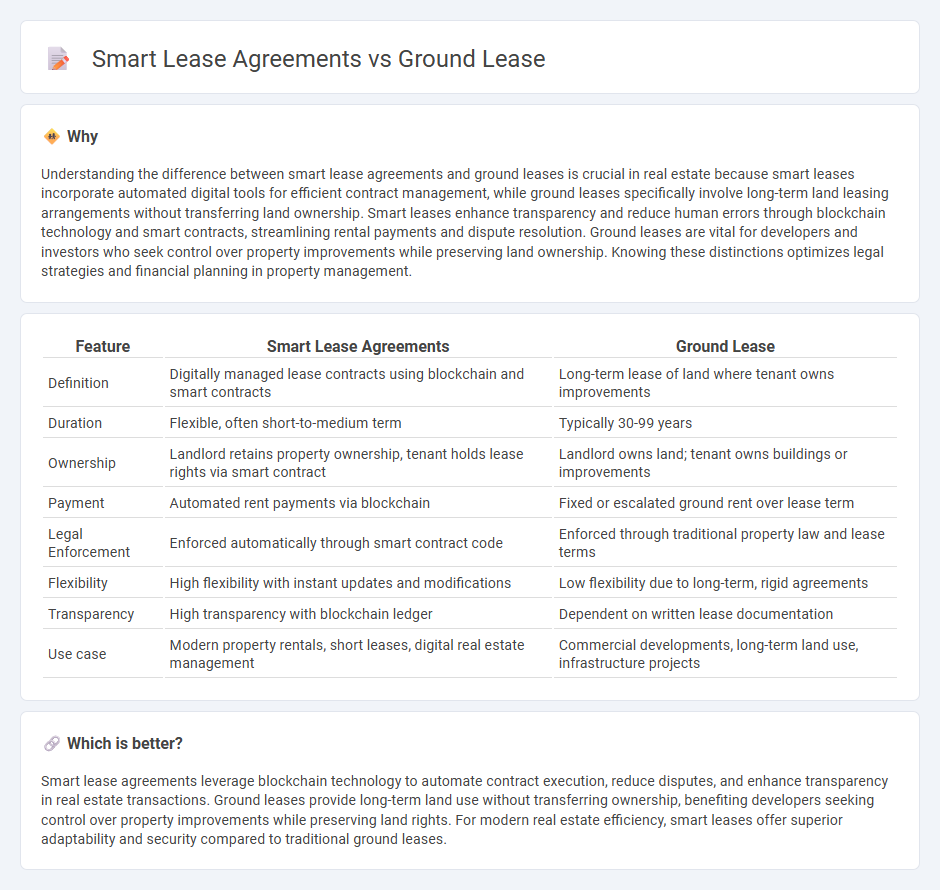
Understanding the difference between smart lease agreements and ground leases is crucial in real estate because smart leases incorporate automated digital tools for efficient contract management, while ground leases specifically involve long-term land leasing arrangements without transferring land ownership. Smart leases enhance transparency and reduce human errors through blockchain technology and smart contracts, streamlining rental payments and dispute resolution. Ground leases are vital for developers and investors who seek control over property improvements while preserving land ownership. Knowing these distinctions optimizes legal strategies and financial planning in property management.
Comparison Table
| Feature | Smart Lease Agreements | Ground Lease |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Digitally managed lease contracts using blockchain and smart contracts | Long-term lease of land where tenant owns improvements |
| Duration | Flexible, often short-to-medium term | Typically 30-99 years |
| Ownership | Landlord retains property ownership, tenant holds lease rights via smart contract | Landlord owns land; tenant owns buildings or improvements |
| Payment | Automated rent payments via blockchain | Fixed or escalated ground rent over lease term |
| Legal Enforcement | Enforced automatically through smart contract code | Enforced through traditional property law and lease terms |
| Flexibility | High flexibility with instant updates and modifications | Low flexibility due to long-term, rigid agreements |
| Transparency | High transparency with blockchain ledger | Dependent on written lease documentation |
| Use case | Modern property rentals, short leases, digital real estate management | Commercial developments, long-term land use, infrastructure projects |
Which is better?
Smart lease agreements leverage blockchain technology to automate contract execution, reduce disputes, and enhance transparency in real estate transactions. Ground leases provide long-term land use without transferring ownership, benefiting developers seeking control over property improvements while preserving land rights. For modern real estate efficiency, smart leases offer superior adaptability and security compared to traditional ground leases.
Connection
Smart lease agreements utilize blockchain technology to automate contract execution and ensure transparency in real estate transactions, enhancing the security and efficiency of ground leases. Ground leases, which involve long-term leasing of land rather than property ownership, benefit from smart lease agreements by reducing disputes and streamlining rent payments through programmable smart contracts. This integration supports landlords and tenants by providing verifiable terms and timely enforcement, revolutionizing traditional leasing models in real estate.
Key Terms
Lease Term
Ground leases typically span 50 to 99 years, granting long-term control over land while requiring tenants to develop and maintain improvements. Smart lease agreements often feature shorter, more flexible terms designed to adapt to evolving business needs and technology integration. Explore the benefits and implications of each lease type to determine the optimal term for your property strategy.
Rent Structure
Ground leases typically involve long-term agreements with fixed or periodically escalated rent based on land value, ensuring predictable income for lessors. Smart leases incorporate dynamic rent structures integrating real-time data, such as market trends and tenant performance metrics, to optimize rental income flexibly. Explore how these innovative rent structures impact financial outcomes and lease efficiency by learning more about their practical applications.
Maintenance Responsibility
Ground lease agreements often place maintenance responsibility for the land and any structures on the tenant, requiring them to handle repairs and upkeep throughout the lease term. Smart lease agreements typically integrate technology-driven clauses that clearly allocate maintenance duties, often incorporating automated systems for tracking and managing repairs efficiently. Explore how these differences impact cost and liability in lease management to optimize your property investment strategy.
Source and External Links
Key Considerations in a Ground Lease - A ground lease is a long-term lease (typically 50 to 99 years) of unimproved land where the tenant leases the land and constructs buildings or improvements, owning those improvements during the lease while paying expenses except the landlord's mortgage and income taxes.
Ground Lease vs Land Lease: Key Differences - Ground leases allow landowners to lease land for long periods (50-99 years) retaining land ownership while tenants can develop the land and own improvements, benefiting from development without upfront land purchase.
What Is A Ground Lease | Definition & Examples - A ground lease is a formal contract between a landowner and tenant detailing lease terms including duration, rights, financial conditions, default procedures, insurance, and end-of-lease arrangements for property development on leased land.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com