Green leases promote energy efficiency and sustainable practices by aligning landlord and tenant responsibilities for environmental performance in commercial real estate. Ground leases, typically long-term agreements, grant tenants the right to develop and use land owned by the landlord, often separating land ownership from building ownership. Explore the distinct benefits and legal nuances of green leases versus ground leases to make informed real estate decisions.
Why it is important
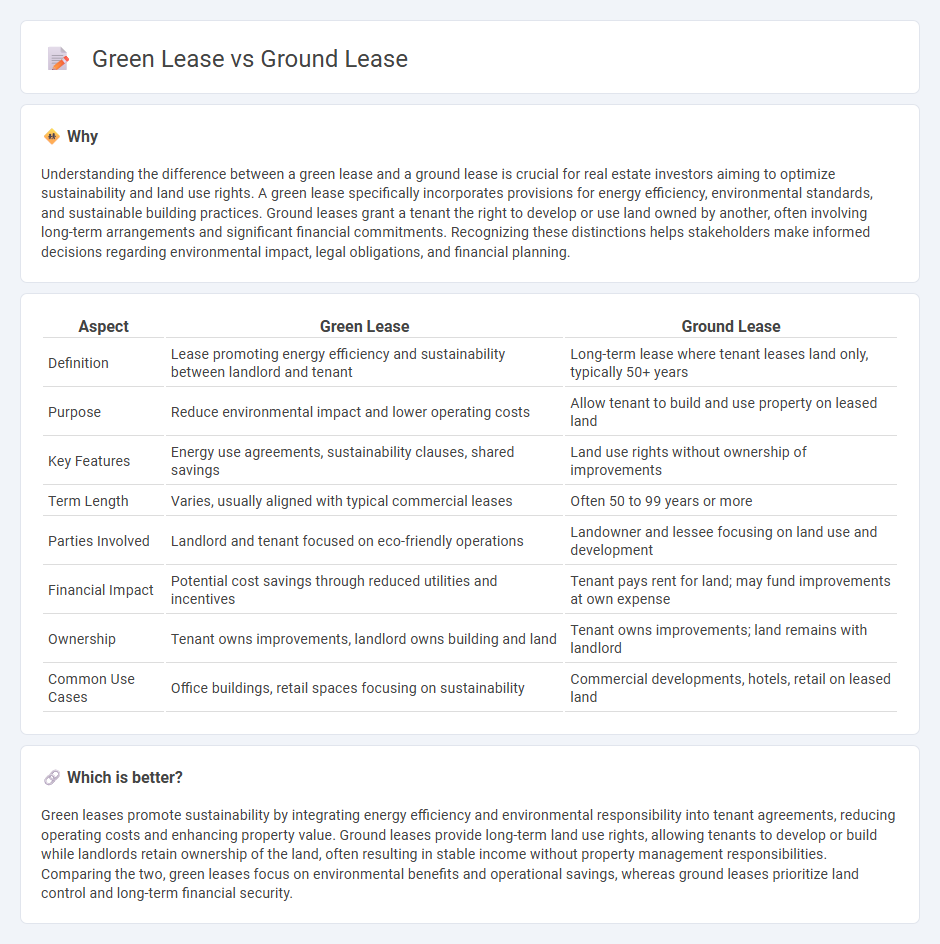
Understanding the difference between a green lease and a ground lease is crucial for real estate investors aiming to optimize sustainability and land use rights. A green lease specifically incorporates provisions for energy efficiency, environmental standards, and sustainable building practices. Ground leases grant a tenant the right to develop or use land owned by another, often involving long-term arrangements and significant financial commitments. Recognizing these distinctions helps stakeholders make informed decisions regarding environmental impact, legal obligations, and financial planning.
Comparison Table
| Aspect | Green Lease | Ground Lease |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Lease promoting energy efficiency and sustainability between landlord and tenant | Long-term lease where tenant leases land only, typically 50+ years |
| Purpose | Reduce environmental impact and lower operating costs | Allow tenant to build and use property on leased land |
| Key Features | Energy use agreements, sustainability clauses, shared savings | Land use rights without ownership of improvements |
| Term Length | Varies, usually aligned with typical commercial leases | Often 50 to 99 years or more |
| Parties Involved | Landlord and tenant focused on eco-friendly operations | Landowner and lessee focusing on land use and development |
| Financial Impact | Potential cost savings through reduced utilities and incentives | Tenant pays rent for land; may fund improvements at own expense |
| Ownership | Tenant owns improvements, landlord owns building and land | Tenant owns improvements; land remains with landlord |
| Common Use Cases | Office buildings, retail spaces focusing on sustainability | Commercial developments, hotels, retail on leased land |
Which is better?
Green leases promote sustainability by integrating energy efficiency and environmental responsibility into tenant agreements, reducing operating costs and enhancing property value. Ground leases provide long-term land use rights, allowing tenants to develop or build while landlords retain ownership of the land, often resulting in stable income without property management responsibilities. Comparing the two, green leases focus on environmental benefits and operational savings, whereas ground leases prioritize land control and long-term financial security.
Connection
Green leases and ground leases intersect in sustainable real estate development by promoting eco-friendly building practices on leased land. Ground leases grant tenants long-term rights to use land, while green leases integrate environmental performance clauses to ensure energy efficiency, waste reduction, and sustainability compliance throughout the lease term. This connection supports aligned incentives for landlords and tenants to invest in greener infrastructure, reducing carbon footprints and enhancing property value.
Key Terms
Landlord-Tenant Agreement
Ground leases establish long-term agreements allowing tenants to develop and use land while the landlord retains ownership, often spanning 30 to 99 years. Green leases integrate sustainability clauses, aligning landlord and tenant responsibilities to reduce environmental impacts, improve energy efficiency, and share cost savings related to green building practices. Explore how these lease structures optimize property management and environmental goals.
Sustainability Clauses
Ground leases typically involve long-term land rental agreements that often lack specific sustainability clauses, focusing instead on basic land use and rights. Green leases incorporate explicit sustainability provisions, such as energy efficiency standards, waste reduction, and renewable energy integration, aimed at reducing environmental impact and promoting sustainable building operations. Explore more about how sustainability clauses in leases can drive eco-friendly property management and investment strategies.
Rent Structure
A ground lease typically involves a fixed or escalating rent paid by the tenant for land use, allowing investors to retain ownership while the tenant develops or operates improvements. Green leases incorporate rent structures tied to sustainability performance metrics, incentivizing tenants to reduce energy consumption and environmental impact, often including clauses for cost-sharing of energy-efficient upgrades. Explore the nuances of rent structures in ground and green leases to optimize lease agreements and promote sustainable property management.
Source and External Links
Key Considerations in a Ground Lease - This webpage discusses the complexities and key considerations involved in negotiating and preparing a ground lease, highlighting its benefits for landlords and tenants.
What Is A Ground Lease? Benefits And Risks - This article explains what a ground lease is, its benefits for both parties, and the associated risks, including the long-term nature and responsibility distribution.
What Is A Ground Lease | Definition & Examples - This webpage provides a definition of a ground lease, explaining how it works, typical terms, and the responsibilities of both parties involved.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com