Energy positive buildings generate more energy than they consume by integrating renewable energy systems like solar panels and advanced energy storage technologies, setting them apart from traditional green buildings that primarily focus on reducing environmental impact through energy efficiency and sustainable materials. These structures contribute to lowering carbon footprints and energy costs while enhancing occupant comfort and resilience against power outages. Discover how energy positive buildings are revolutionizing sustainable real estate development.
Why it is important
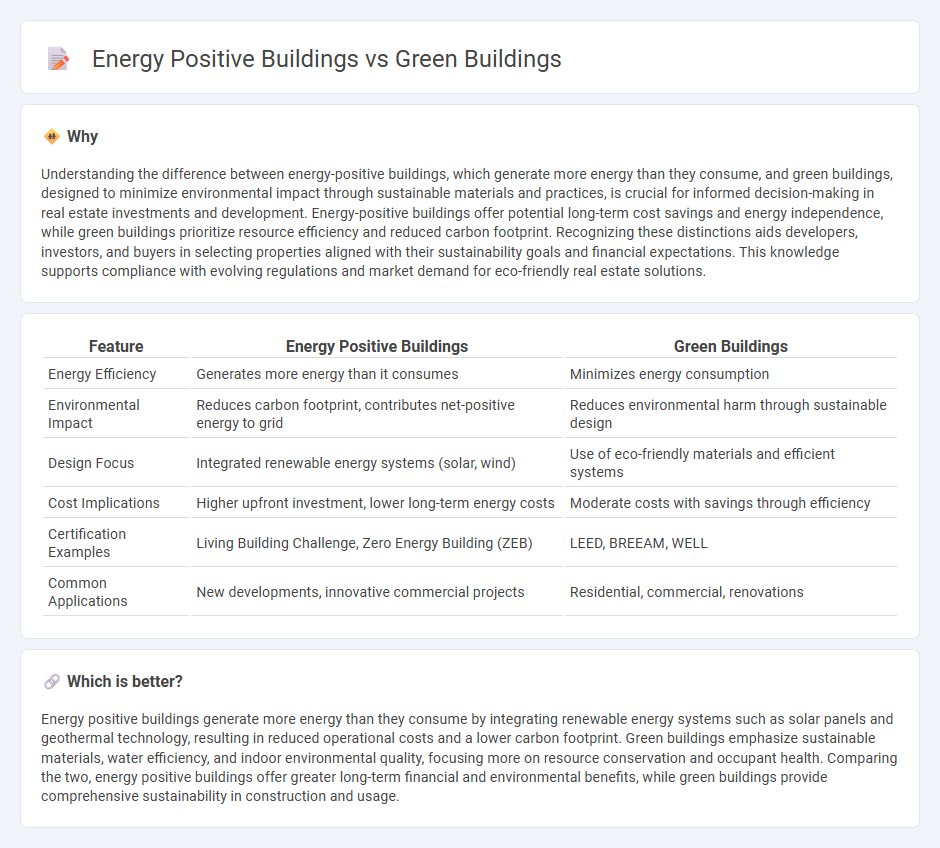
Understanding the difference between energy-positive buildings, which generate more energy than they consume, and green buildings, designed to minimize environmental impact through sustainable materials and practices, is crucial for informed decision-making in real estate investments and development. Energy-positive buildings offer potential long-term cost savings and energy independence, while green buildings prioritize resource efficiency and reduced carbon footprint. Recognizing these distinctions aids developers, investors, and buyers in selecting properties aligned with their sustainability goals and financial expectations. This knowledge supports compliance with evolving regulations and market demand for eco-friendly real estate solutions.
Comparison Table
| Feature | Energy Positive Buildings | Green Buildings |
|---|---|---|
| Energy Efficiency | Generates more energy than it consumes | Minimizes energy consumption |
| Environmental Impact | Reduces carbon footprint, contributes net-positive energy to grid | Reduces environmental harm through sustainable design |
| Design Focus | Integrated renewable energy systems (solar, wind) | Use of eco-friendly materials and efficient systems |
| Cost Implications | Higher upfront investment, lower long-term energy costs | Moderate costs with savings through efficiency |
| Certification Examples | Living Building Challenge, Zero Energy Building (ZEB) | LEED, BREEAM, WELL |
| Common Applications | New developments, innovative commercial projects | Residential, commercial, renovations |
Which is better?
Energy positive buildings generate more energy than they consume by integrating renewable energy systems such as solar panels and geothermal technology, resulting in reduced operational costs and a lower carbon footprint. Green buildings emphasize sustainable materials, water efficiency, and indoor environmental quality, focusing more on resource conservation and occupant health. Comparing the two, energy positive buildings offer greater long-term financial and environmental benefits, while green buildings provide comprehensive sustainability in construction and usage.
Connection
Energy positive buildings contribute to green building practices by generating more energy than they consume, significantly reducing carbon footprints. These buildings integrate renewable energy systems, advanced insulation, and energy-efficient technologies, aligning with green building certifications such as LEED and BREEAM. The synergy between energy positive and green buildings drives sustainable urban development and supports climate goals.
Key Terms
Sustainability
Green buildings minimize environmental impact through energy efficiency, water conservation, and sustainable materials, aiming to reduce carbon footprints. Energy positive buildings go beyond by producing more energy than they consume, integrating renewable technologies like solar panels and energy storage systems. Explore how these innovative approaches drive sustainability forward and transform urban environments.
Net Zero Energy
Green buildings prioritize reducing environmental impact through efficient resource use and sustainable materials, while energy positive buildings generate more energy than they consume. Net Zero Energy buildings achieve a balance by producing as much energy as they use annually, serving as a crucial benchmark between these concepts. Explore more to understand how Net Zero Energy drives innovation in sustainable architecture.
Renewable Energy Integration
Energy positive buildings generate more renewable energy than they consume, often using solar panels, wind turbines, and advanced energy storage systems to achieve net energy surplus. Green buildings emphasize sustainable design and resource efficiency, incorporating renewable energy as part of a broader environmental strategy but not necessarily producing excess energy. Explore how renewable energy integration differentiates these building types and drives the future of sustainable architecture.
Source and External Links
What Is Green Building? - Green building is a resource-efficient approach to construction that reduces environmental impact and enhances human health by optimizing energy use, water efficiency, indoor air quality, and incorporating smart technologies like IoT sensors and renewable energy sources.
Green building - Green building refers to environmentally responsible and resource-efficient structures throughout their life-cycle, focusing on energy, water, and material savings and certified by systems like LEED, BREEAM, and others to ensure sustainability and occupant health.
Green Buildings | PNNL - Green buildings reduce negative environmental impacts by using less water and energy, employing renewable sources, and enhancing indoor environmental quality, aiming to minimize harm and maximize positive effects on nature and human occupants.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com