Co-living developments offer shared living spaces designed for community engagement and affordability, attracting young professionals and students seeking flexible lease terms and social interaction. Condominiums provide private ownership of individual units with full control over property customization, appealing to investors and homeowners prioritizing long-term value and personal space. Explore the key differences between co-living and condominium investments to determine the best fit for your lifestyle and financial goals.
Why it is important
Understanding the difference between co-living developments and condominiums is crucial for investors and residents due to variations in ownership structure, community dynamics, and cost efficiency. Co-living spaces offer shared amenities and a collaborative living environment, typically with flexible lease terms, while condominiums provide individual ownership with exclusive control over one's unit and longer-term investment potential. Real estate professionals emphasize that recognizing these distinctions can optimize property investment strategies and lifestyle compatibility. Knowledge of local zoning laws and management policies further affects decision-making in these residential options.
Comparison Table
| Aspect | Co-Living Developments | Condominiums |
|---|---|---|
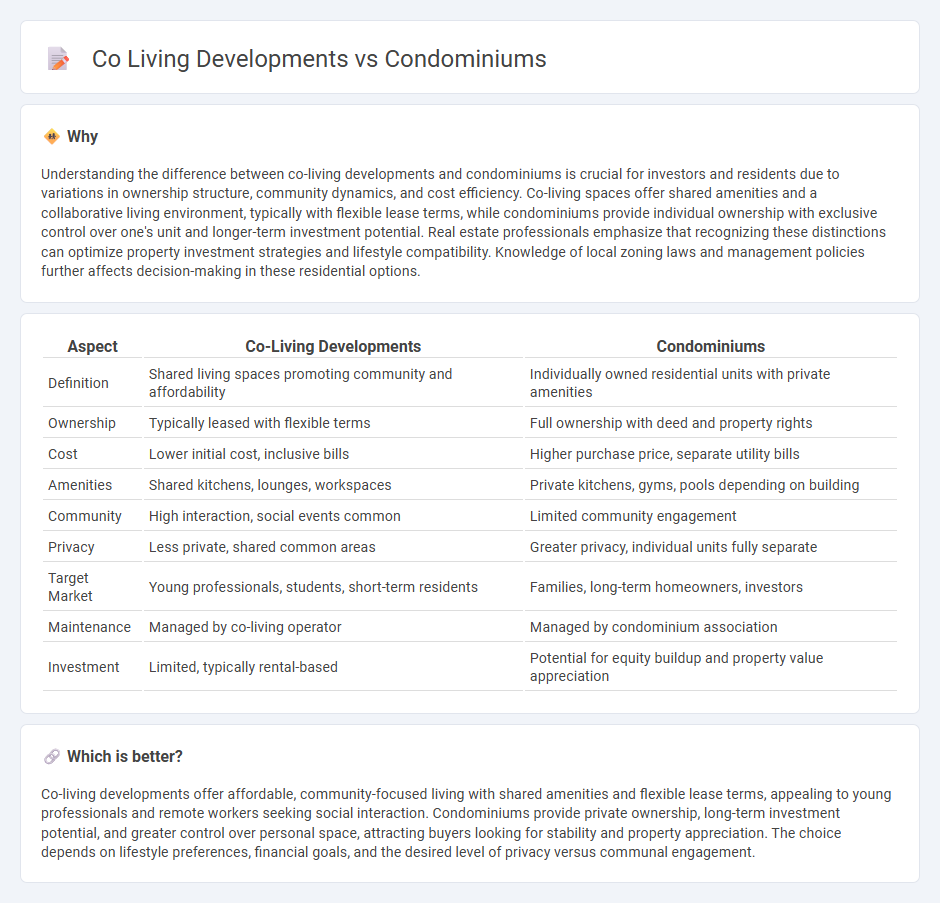
| Definition | Shared living spaces promoting community and affordability | Individually owned residential units with private amenities |
| Ownership | Typically leased with flexible terms | Full ownership with deed and property rights |
| Cost | Lower initial cost, inclusive bills | Higher purchase price, separate utility bills |
| Amenities | Shared kitchens, lounges, workspaces | Private kitchens, gyms, pools depending on building |
| Community | High interaction, social events common | Limited community engagement |
| Privacy | Less private, shared common areas | Greater privacy, individual units fully separate |
| Target Market | Young professionals, students, short-term residents | Families, long-term homeowners, investors |
| Maintenance | Managed by co-living operator | Managed by condominium association |
| Investment | Limited, typically rental-based | Potential for equity buildup and property value appreciation |
Which is better?
Co-living developments offer affordable, community-focused living with shared amenities and flexible lease terms, appealing to young professionals and remote workers seeking social interaction. Condominiums provide private ownership, long-term investment potential, and greater control over personal space, attracting buyers looking for stability and property appreciation. The choice depends on lifestyle preferences, financial goals, and the desired level of privacy versus communal engagement.
Connection
Co-living developments and condominiums both represent evolving residential models that optimize urban living by maximizing space efficiency and fostering community interaction. These housing options share common features such as shared amenities, centralized management, and flexible ownership or rental agreements, appealing to millennials and young professionals seeking affordability and convenience. The growth of co-living spaces often complements condominium markets by offering alternative, socially-driven urban housing solutions within the same metropolitan zones.
Key Terms
Ownership Structure
Condominiums offer individual ownership of units with shared access to common areas, while co-living developments emphasize communal living with leased spaces rather than ownership. In condominiums, residents hold a deed to their specific unit, allowing for investment value and resale opportunities, whereas co-living arrangements typically involve flexible, short-term leases targeting affordability and community engagement. Explore more about how these ownership structures impact lifestyle and investment potential.
Shared Amenities
Condominiums typically offer private ownership with shared amenities such as gyms, pools, and community lounges maintained by a homeowners association, providing residents exclusive access and a sense of long-term investment. Co-living developments emphasize communal living with extensive shared spaces including co-working areas, kitchens, and social hubs designed to foster interaction and collaboration among tenants. Explore how shared amenities shape lifestyle choices by diving deeper into the differences between condominiums and co-living developments.
Governance Model
Condominiums rely on homeowner associations with elected boards that enforce bylaws and manage shared amenities, ensuring residents have a stake in governance and property upkeep. Co-living developments typically operate under professional management companies that handle daily operations and community rules, offering flexible leases and streamlined services for residents. Explore further to understand how these governance models impact resident experience and investment value.
Source and External Links
What is a condo? - This webpage provides an overview of condominiums, explaining their structure, the role of homeowners associations, and the pros and cons of condo ownership.
Condominium - This article defines condominiums as a type of common interest development where each unit owner holds title and becomes a member of the governing association.
Condominium - This Wikipedia entry details the history and legal framework of condominiums, including their origins and widespread adoption in the United States.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com