Vertical forests integrate dense vegetation on building facades to improve urban air quality and biodiversity, while biophilic design emphasizes connecting occupants with nature through natural materials, light, and spatial arrangements. Both approaches enhance real estate value by promoting sustainable living environments and improving occupant well-being. Discover how these innovative design strategies are transforming urban real estate landscapes.
Why it is important
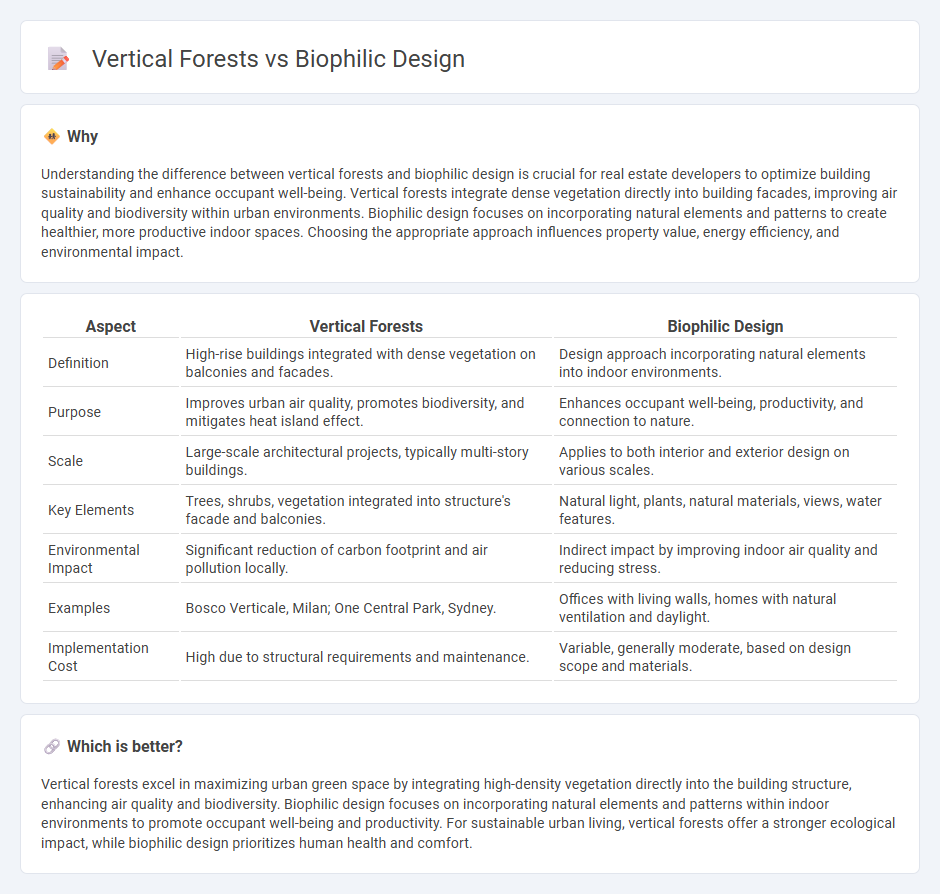
Understanding the difference between vertical forests and biophilic design is crucial for real estate developers to optimize building sustainability and enhance occupant well-being. Vertical forests integrate dense vegetation directly into building facades, improving air quality and biodiversity within urban environments. Biophilic design focuses on incorporating natural elements and patterns to create healthier, more productive indoor spaces. Choosing the appropriate approach influences property value, energy efficiency, and environmental impact.
Comparison Table
| Aspect | Vertical Forests | Biophilic Design |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | High-rise buildings integrated with dense vegetation on balconies and facades. | Design approach incorporating natural elements into indoor environments. |
| Purpose | Improves urban air quality, promotes biodiversity, and mitigates heat island effect. | Enhances occupant well-being, productivity, and connection to nature. |
| Scale | Large-scale architectural projects, typically multi-story buildings. | Applies to both interior and exterior design on various scales. |
| Key Elements | Trees, shrubs, vegetation integrated into structure's facade and balconies. | Natural light, plants, natural materials, views, water features. |
| Environmental Impact | Significant reduction of carbon footprint and air pollution locally. | Indirect impact by improving indoor air quality and reducing stress. |
| Examples | Bosco Verticale, Milan; One Central Park, Sydney. | Offices with living walls, homes with natural ventilation and daylight. |
| Implementation Cost | High due to structural requirements and maintenance. | Variable, generally moderate, based on design scope and materials. |
Which is better?
Vertical forests excel in maximizing urban green space by integrating high-density vegetation directly into the building structure, enhancing air quality and biodiversity. Biophilic design focuses on incorporating natural elements and patterns within indoor environments to promote occupant well-being and productivity. For sustainable urban living, vertical forests offer a stronger ecological impact, while biophilic design prioritizes human health and comfort.
Connection
Vertical forests integrate biophilic design principles by incorporating living plants and trees into urban architecture, enhancing air quality and biodiversity. This approach creates healthier environments, improves occupant well-being, and mitigates urban heat island effects. Real estate developments adopting vertical forests benefit from increased property value and appeal to eco-conscious buyers.
Key Terms
**Biophilic Design:**
Biophilic design integrates natural elements such as plants, natural light, and organic materials within built environments to enhance human well-being and productivity. This approach fosters a stronger connection between occupants and nature, promoting mental health and reducing stress. Explore how implementing biophilic design can transform spaces and improve quality of life.
Nature Integration
Biophilic design emphasizes the integration of natural elements like light, plants, and water within indoor environments to enhance human well-being and productivity, while vertical forests incorporate dense vegetation directly into building facades to improve urban air quality and biodiversity. Both approaches promote nature integration but differ in scale and application, with biophilic design primarily influencing interiors and vertical forests reshaping urban skylines. Explore more to understand how these strategies redefine our connection with nature in architecture.
Wellbeing
Biophilic design integrates natural elements into built environments to enhance occupants' wellbeing by improving air quality, reducing stress, and boosting productivity. Vertical forests incorporate dense vegetation on building facades, actively filtering pollutants and promoting mental health through direct interaction with greenery. Explore further to understand how these approaches uniquely contribute to healthier urban living.
Source and External Links
The six elements of biophilic design - Biophilic design is a methodology for incorporating natural elements into the built environment to enhance human health and well-being by fostering a connection with nature.
What Is and Is Not Biophilic Design - Biophilic design focuses on connecting people with natural elements that contribute to health and productivity, emphasizing our evolved affinity for nature in modern environments.
Biophilic Design Is Good for Your Health - Biophilic design is a human-centric approach that brings natural elements and patterns into interior spaces to improve health and aesthetic appeal.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com