Brownfield redevelopment transforms previously contaminated or abandoned industrial sites into valuable real estate, boosting urban renewal and reducing environmental hazards. Adaptive reuse repurposes existing structures for new functions, preserving architectural heritage while optimizing space efficiency and sustainability. Explore the differences and benefits of these transformative real estate strategies to enhance urban growth.
Why it is important
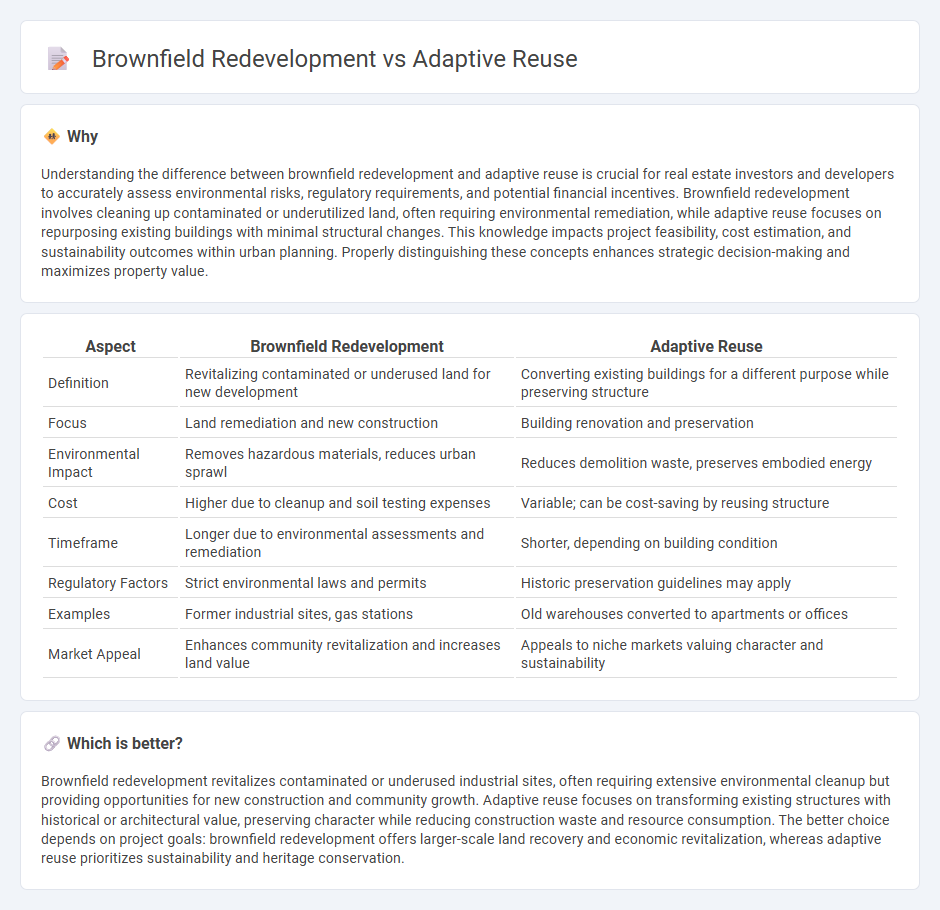
Understanding the difference between brownfield redevelopment and adaptive reuse is crucial for real estate investors and developers to accurately assess environmental risks, regulatory requirements, and potential financial incentives. Brownfield redevelopment involves cleaning up contaminated or underutilized land, often requiring environmental remediation, while adaptive reuse focuses on repurposing existing buildings with minimal structural changes. This knowledge impacts project feasibility, cost estimation, and sustainability outcomes within urban planning. Properly distinguishing these concepts enhances strategic decision-making and maximizes property value.
Comparison Table
| Aspect | Brownfield Redevelopment | Adaptive Reuse |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Revitalizing contaminated or underused land for new development | Converting existing buildings for a different purpose while preserving structure |
| Focus | Land remediation and new construction | Building renovation and preservation |
| Environmental Impact | Removes hazardous materials, reduces urban sprawl | Reduces demolition waste, preserves embodied energy |
| Cost | Higher due to cleanup and soil testing expenses | Variable; can be cost-saving by reusing structure |
| Timeframe | Longer due to environmental assessments and remediation | Shorter, depending on building condition |
| Regulatory Factors | Strict environmental laws and permits | Historic preservation guidelines may apply |
| Examples | Former industrial sites, gas stations | Old warehouses converted to apartments or offices |
| Market Appeal | Enhances community revitalization and increases land value | Appeals to niche markets valuing character and sustainability |
Which is better?
Brownfield redevelopment revitalizes contaminated or underused industrial sites, often requiring extensive environmental cleanup but providing opportunities for new construction and community growth. Adaptive reuse focuses on transforming existing structures with historical or architectural value, preserving character while reducing construction waste and resource consumption. The better choice depends on project goals: brownfield redevelopment offers larger-scale land recovery and economic revitalization, whereas adaptive reuse prioritizes sustainability and heritage conservation.
Connection
Brownfield redevelopment and adaptive reuse are connected through their focus on revitalizing underutilized or contaminated properties by repurposing existing structures. Both approaches aim to reduce urban sprawl, lower construction costs, and preserve historical or architectural value while addressing environmental remediation. This synergy enhances sustainable real estate development by transforming neglected sites into valuable commercial or residential spaces.
Key Terms
Zoning
Adaptive reuse transforms existing structures, optimizing land use while complying with zoning regulations that often favor preservation in urban areas. Brownfield redevelopment involves cleaning and repurposing contaminated sites, with zoning challenges centered on environmental restrictions and allowable land uses under municipal codes. Explore zoning strategies that facilitate each approach to maximize sustainable urban growth.
Environmental Remediation
Adaptive reuse preserves existing structures, reducing landfill waste and minimizing the carbon footprint compared to demolition, often requiring targeted environmental remediation to address contaminants within aging building materials. Brownfield redevelopment specifically targets previously contaminated lands, necessitating comprehensive soil and groundwater remediation to meet environmental safety standards before new construction or reuse can occur. Explore detailed strategies and case studies in environmental remediation within adaptive reuse and brownfield redevelopment to understand their sustainable impacts.
Historic Preservation
Adaptive reuse breathes new life into historic buildings by repurposing structures for modern use while preserving architectural heritage and cultural significance. Brownfield redevelopment involves cleaning and revitalizing previously contaminated or underutilized industrial sites, often improving environmental health and community safety in historic urban areas. Explore key strategies and benefits of both approaches in historic preservation to safeguard heritage and promote sustainable development.
Source and External Links
Adaptive Reuse - Wikipedia - Adaptive reuse involves repurposing existing buildings for new uses, maintaining their historic features while extending their lifespan in a sustainable manner.
What is adaptive reuse? - Ube - Adaptive reuse is a process where existing buildings are reused in a different capacity than their original purpose to reduce environmental impact and demolition.
A Complete Guide to Adaptive Reuse in 2023 - MBH Architects - This guide outlines adaptive reuse as a sustainable strategy to renovate old buildings for new purposes, highlighting various types of such projects.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com