Leadership in management involves various styles that influence team performance and organizational success. Gig leadership emphasizes agile, project-based guidance suited for flexible work environments, while situational leadership adapts leadership approaches based on team members' maturity and task complexity. Explore these leadership models to determine which best fits your organizational needs.
Why it is important
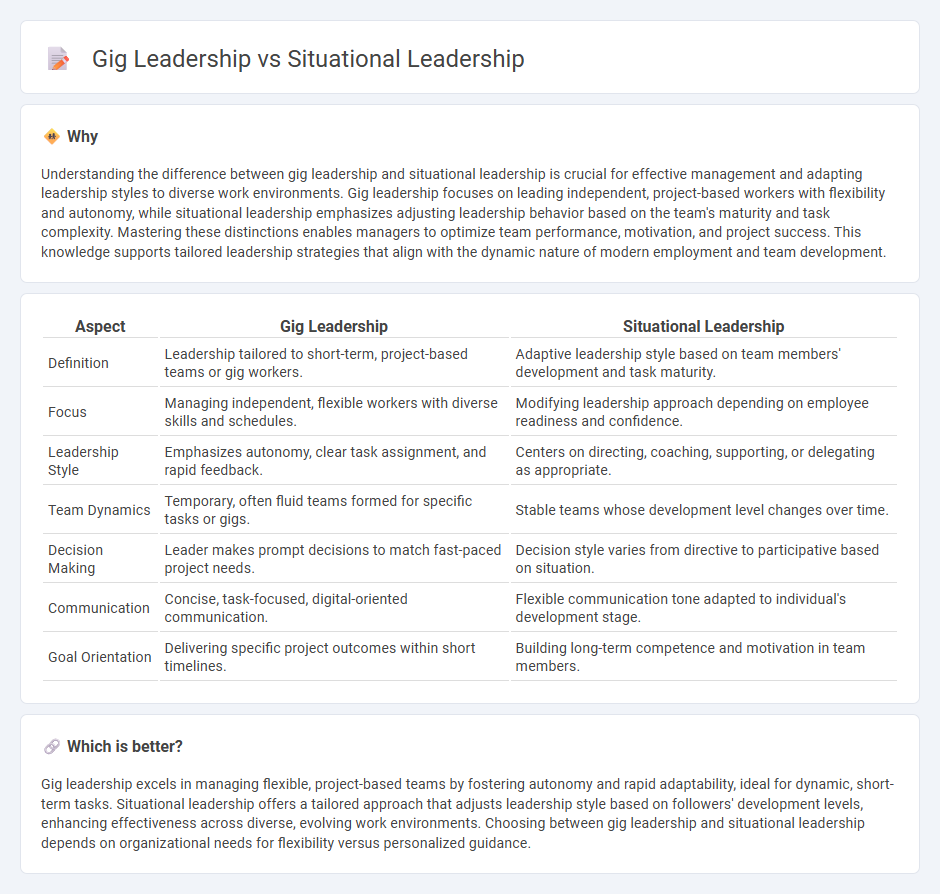
Understanding the difference between gig leadership and situational leadership is crucial for effective management and adapting leadership styles to diverse work environments. Gig leadership focuses on leading independent, project-based workers with flexibility and autonomy, while situational leadership emphasizes adjusting leadership behavior based on the team's maturity and task complexity. Mastering these distinctions enables managers to optimize team performance, motivation, and project success. This knowledge supports tailored leadership strategies that align with the dynamic nature of modern employment and team development.
Comparison Table
| Aspect | Gig Leadership | Situational Leadership |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Leadership tailored to short-term, project-based teams or gig workers. | Adaptive leadership style based on team members' development and task maturity. |
| Focus | Managing independent, flexible workers with diverse skills and schedules. | Modifying leadership approach depending on employee readiness and confidence. |
| Leadership Style | Emphasizes autonomy, clear task assignment, and rapid feedback. | Centers on directing, coaching, supporting, or delegating as appropriate. |
| Team Dynamics | Temporary, often fluid teams formed for specific tasks or gigs. | Stable teams whose development level changes over time. |
| Decision Making | Leader makes prompt decisions to match fast-paced project needs. | Decision style varies from directive to participative based on situation. |
| Communication | Concise, task-focused, digital-oriented communication. | Flexible communication tone adapted to individual's development stage. |
| Goal Orientation | Delivering specific project outcomes within short timelines. | Building long-term competence and motivation in team members. |
Which is better?
Gig leadership excels in managing flexible, project-based teams by fostering autonomy and rapid adaptability, ideal for dynamic, short-term tasks. Situational leadership offers a tailored approach that adjusts leadership style based on followers' development levels, enhancing effectiveness across diverse, evolving work environments. Choosing between gig leadership and situational leadership depends on organizational needs for flexibility versus personalized guidance.
Connection
Gig leadership and situational leadership both emphasize adaptability in managing diverse teams and dynamic work environments. Gig leadership focuses on flexible, project-based team management within the gig economy, while situational leadership adjusts leadership styles based on team members' development levels and task requirements. Integrating situational leadership principles enhances gig leaders' ability to tailor their approach for optimal team performance and engagement.
Key Terms
Adaptability
Situational Leadership emphasizes adapting leadership style based on employee maturity and task complexity, promoting flexibility in direction and support. Gig Leadership focuses on rapid adaptability to dynamic, short-term project demands and the unique needs of gig workers in decentralized teams. Explore how mastering adaptability in these models enhances leadership effectiveness in diverse work environments.
Autonomy
Situational leadership adjusts autonomy levels based on follower maturity and task complexity, providing more guidance when necessary and increasing independence as skills develop. Gig leadership emphasizes high autonomy by empowering gig workers to self-manage tasks and schedules, fostering flexibility and rapid adaptability. Explore how these leadership styles impact team performance and worker satisfaction in diverse work environments.
Flexibility
Situational leadership emphasizes adaptability by encouraging leaders to modify their style based on the team's development level, enhancing employee performance and engagement. Gig leadership prioritizes flexibility through project-based, short-term assignments, allowing leaders to quickly adjust strategies to meet dynamic market demands and diverse gig workers' needs. Explore more about how these leadership models foster flexibility in modern organizations.
Source and External Links
What is Situational Leadership? (4 Styles and Examples) - Situational leadership is a flexible approach where leaders adapt their style based on the current work environment and the specific needs of their team, demonstrating skills like direction, flexibility, encouragement, delegation, coaching, and honesty to foster growth and productivity.
The Four Leadership Styles of Situational Leadership(r) | CLS - Situational leaders use one of four styles (Telling, Selling, Participating, Delegating) depending on the task complexity and the follower's ability and willingness, balancing directive and supportive behaviors to maximize success in each scenario.
Situational Leadership(r) | What Is ... - The model centers on analyzing the work to be done, assessing the follower's competence and commitment, and choosing a leadership approach that aligns with these factors, demanding leaders to be self-aware and capable of accurately reading others to make sound decisions.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com