Shadow boards consist of emerging leaders who provide innovative insights and challenge traditional decision-making, enhancing organizational agility. Corporate governance boards focus on oversight, risk management, and strategic guidance to ensure accountability and long-term sustainability. Explore how integrating shadow boards can complement corporate governance for dynamic and effective management.
Why it is important
Understanding the difference between Shadow Boards and Corporate Governance Boards is crucial because Shadow Boards consist of younger employees providing fresh perspectives, while Corporate Governance Boards oversee legal and strategic decision-making at the highest level. Shadow Boards promote innovation and agility by representing emerging talent, whereas Corporate Governance Boards ensure compliance, risk management, and accountability to stakeholders. Distinguishing between these boards enables effective integration of innovative ideas with formal governance structures, driving sustainable organizational growth. Knowing their roles enhances strategic alignment and supports balanced decision-making processes.
Comparison Table
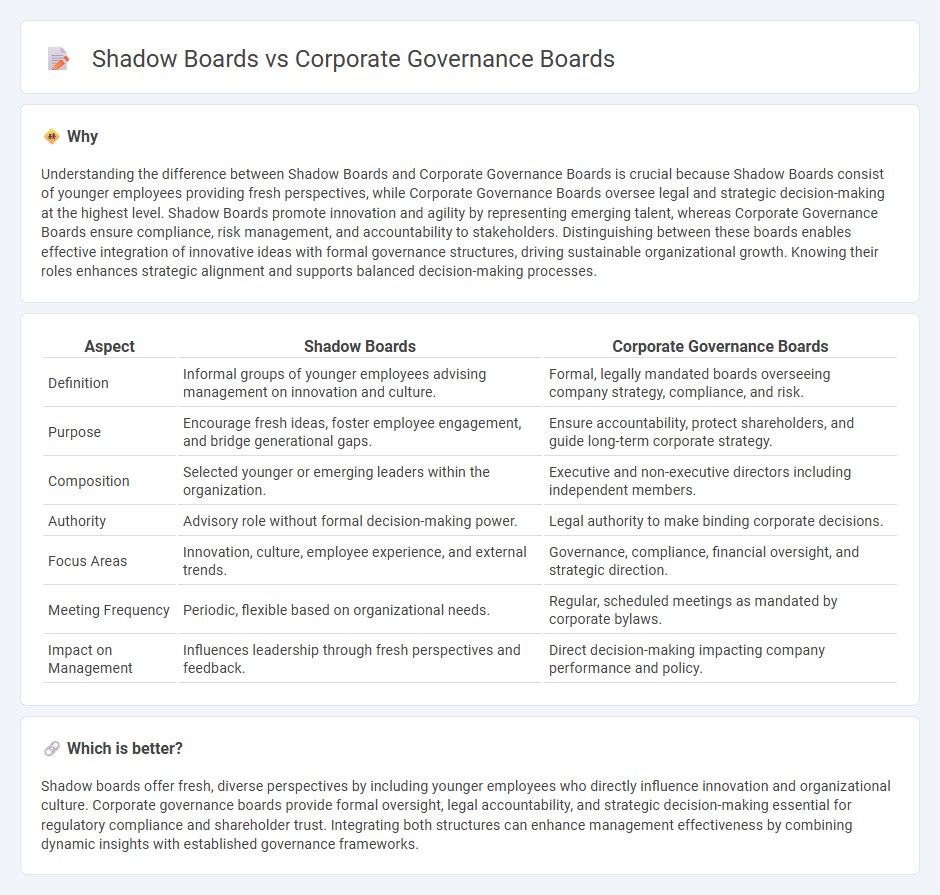
| Aspect | Shadow Boards | Corporate Governance Boards |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Informal groups of younger employees advising management on innovation and culture. | Formal, legally mandated boards overseeing company strategy, compliance, and risk. |
| Purpose | Encourage fresh ideas, foster employee engagement, and bridge generational gaps. | Ensure accountability, protect shareholders, and guide long-term corporate strategy. |
| Composition | Selected younger or emerging leaders within the organization. | Executive and non-executive directors including independent members. |
| Authority | Advisory role without formal decision-making power. | Legal authority to make binding corporate decisions. |
| Focus Areas | Innovation, culture, employee experience, and external trends. | Governance, compliance, financial oversight, and strategic direction. |
| Meeting Frequency | Periodic, flexible based on organizational needs. | Regular, scheduled meetings as mandated by corporate bylaws. |
| Impact on Management | Influences leadership through fresh perspectives and feedback. | Direct decision-making impacting company performance and policy. |
Which is better?
Shadow boards offer fresh, diverse perspectives by including younger employees who directly influence innovation and organizational culture. Corporate governance boards provide formal oversight, legal accountability, and strategic decision-making essential for regulatory compliance and shareholder trust. Integrating both structures can enhance management effectiveness by combining dynamic insights with established governance frameworks.
Connection
Shadow boards complement corporate governance boards by providing fresh perspectives and innovative ideas that enhance strategic decision-making processes. While corporate governance boards focus on oversight, risk management, and compliance, shadow boards simulate real board functions with emerging leaders, enabling accelerated leadership development and dynamic organizational agility. This synergy promotes robust governance practices and fosters a future-ready corporate culture aligned with stakeholder interests.
Key Terms
Decision-Making Authority
Corporate governance boards hold formal decision-making authority, establishing company policies, overseeing management, and ensuring regulatory compliance, while shadow boards function as advisory groups that influence strategic planning without official voting power. Shadow boards consist of emerging leaders or key stakeholders who provide diverse perspectives and challenge traditional governance, enhancing innovation and responsiveness. Explore the dynamics between these boards to understand their distinct roles in shaping organizational success.
Stakeholder Representation
Corporate governance boards legally oversee company strategy, ensuring accountability to shareholders, regulators, and stakeholders by setting policies and monitoring performance. Shadow boards, often composed of emerging leaders or consultants, provide alternative perspectives and future-oriented insights without formal decision-making power, enhancing stakeholder representation by voicing diverse concerns. Explore how these two governance models impact stakeholder engagement and corporate transparency in modern organizations.
Strategic Innovation
Corporate governance boards ensure compliance, risk management, and accountability, predominantly focusing on fiduciary duties and long-term value creation. Shadow boards, consisting of emerging leaders or external experts, prioritize strategic innovation by challenging conventional decision-making and fostering agile, forward-thinking initiatives. Discover how integrating shadow boards can enhance your company's innovation potential and governance practices.
Source and External Links
Types of Board Structure in Corporate Governance - Describes the differences between one-tier (unitary) and two-tier (supervisory + management) board structures, with examples from the U.S., U.K., Germany, and the Netherlands.
Board Governance Best Practices for Modern Organizations - Outlines common board types including governing, working, advisory, and policy boards, highlighting their distinct roles in organizational oversight.
What is a board of directors? - Explains that a board of directors represents shareholders, sets corporate policies, forms specialized committees (audit, finance, ESG, etc.), and oversees executive compensation and recruitment.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com