Intelligent automation enhances management efficiency by integrating AI-driven processes that streamline tasks and reduce manual intervention, surpassing traditional Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) systems which primarily focus on data integration and resource coordination. While ERP centralizes business operations through structured software suites, intelligent automation elevates decision-making with real-time analytics and adaptive workflows. Explore how combining these technologies revolutionizes management strategies for modern enterprises.
Why it is important
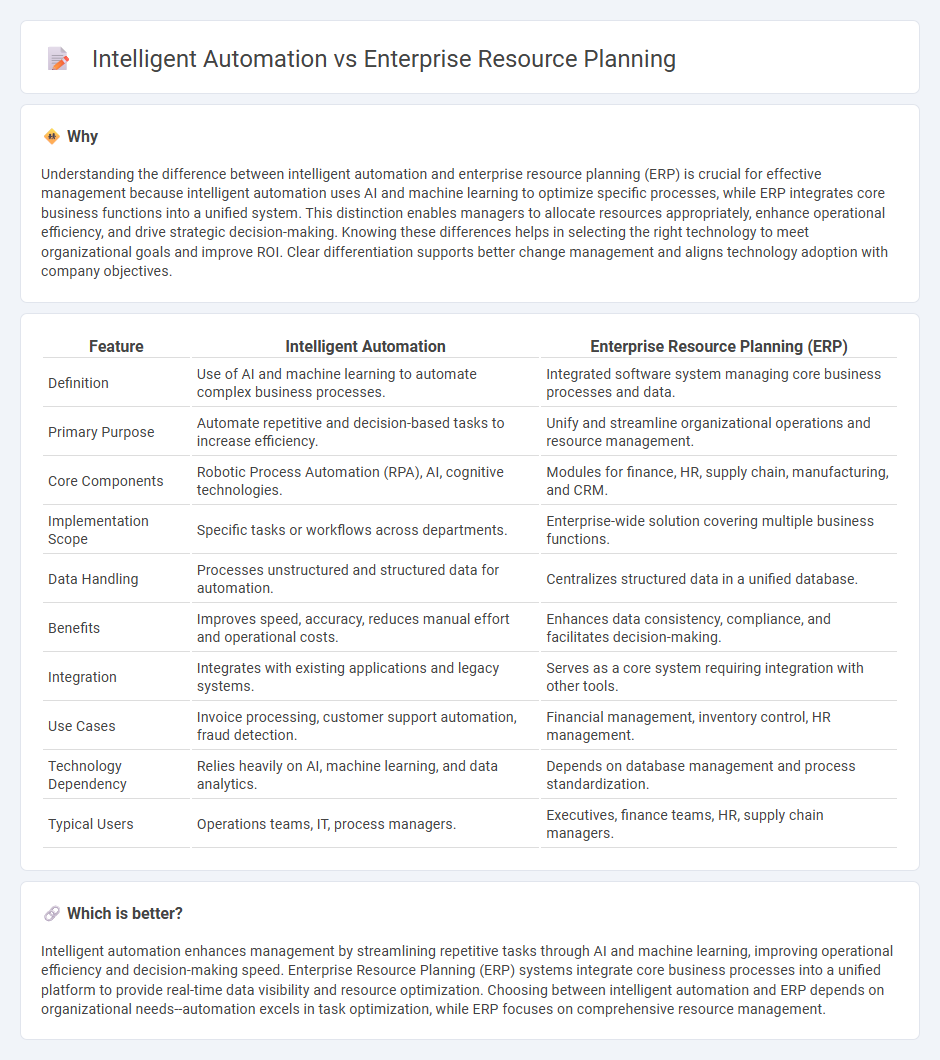
Understanding the difference between intelligent automation and enterprise resource planning (ERP) is crucial for effective management because intelligent automation uses AI and machine learning to optimize specific processes, while ERP integrates core business functions into a unified system. This distinction enables managers to allocate resources appropriately, enhance operational efficiency, and drive strategic decision-making. Knowing these differences helps in selecting the right technology to meet organizational goals and improve ROI. Clear differentiation supports better change management and aligns technology adoption with company objectives.
Comparison Table
| Feature | Intelligent Automation | Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Use of AI and machine learning to automate complex business processes. | Integrated software system managing core business processes and data. |
| Primary Purpose | Automate repetitive and decision-based tasks to increase efficiency. | Unify and streamline organizational operations and resource management. |
| Core Components | Robotic Process Automation (RPA), AI, cognitive technologies. | Modules for finance, HR, supply chain, manufacturing, and CRM. |
| Implementation Scope | Specific tasks or workflows across departments. | Enterprise-wide solution covering multiple business functions. |
| Data Handling | Processes unstructured and structured data for automation. | Centralizes structured data in a unified database. |
| Benefits | Improves speed, accuracy, reduces manual effort and operational costs. | Enhances data consistency, compliance, and facilitates decision-making. |
| Integration | Integrates with existing applications and legacy systems. | Serves as a core system requiring integration with other tools. |
| Use Cases | Invoice processing, customer support automation, fraud detection. | Financial management, inventory control, HR management. |
| Technology Dependency | Relies heavily on AI, machine learning, and data analytics. | Depends on database management and process standardization. |
| Typical Users | Operations teams, IT, process managers. | Executives, finance teams, HR, supply chain managers. |
Which is better?
Intelligent automation enhances management by streamlining repetitive tasks through AI and machine learning, improving operational efficiency and decision-making speed. Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) systems integrate core business processes into a unified platform to provide real-time data visibility and resource optimization. Choosing between intelligent automation and ERP depends on organizational needs--automation excels in task optimization, while ERP focuses on comprehensive resource management.
Connection
Intelligent automation integrates with enterprise resource planning (ERP) systems by streamlining data processing, reducing manual tasks, and enhancing decision-making processes through real-time analytics. ERP platforms leverage robotic process automation (RPA) and artificial intelligence (AI) to optimize supply chain management, financial reporting, and customer relationship management. This synergy boosts operational efficiency, minimizes errors, and supports scalable business growth in dynamic markets.
Key Terms
**Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP):**
Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) systems integrate core business processes such as finance, supply chain, human resources, and manufacturing into a unified platform, enhancing data accuracy and operational efficiency. ERP software provides real-time data analytics, streamlines workflows, and supports compliance management, making it essential for large and growing enterprises. Explore how ERP advancements are transforming business operations to drive strategic growth and innovation.
Integration
Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) systems centralize business processes by integrating core functions such as finance, supply chain, and human resources into a unified platform, enhancing data consistency and operational efficiency. Intelligent automation leverages AI, machine learning, and robotic process automation (RPA) to streamline workflows, reduce manual errors, and accelerate complex decision-making across integrated systems. Explore how combining ERP and intelligent automation can drive seamless integration and digital transformation in your organization.
Modules
Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) systems integrate core business modules such as finance, human resources, supply chain, and manufacturing to streamline operations and centralize data management. Intelligent Automation enhances these modules by embedding capabilities like AI-driven decision-making, robotic process automation (RPA), and predictive analytics to improve efficiency and reduce manual intervention. Explore the specific modules and functionalities where ERP and Intelligent Automation converge to optimize your business processes.
Source and External Links
Enterprise Resource Planning - Wikipedia - Enterprise resource planning (ERP) is a business management software that integrates various business processes, facilitating real-time data management and interpretation.
Latest Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) Insights - Gartner - Gartner provides insights and guidance on ERP strategies to optimize business operations, addressing challenges and incorporating technologies like AI.
What Is ERP? - Oracle - ERP is a software system that integrates business processes such as accounting, procurement, and supply chain management to enhance organizational efficiency and agility.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com