Zero trust leadership emphasizes transparency, continuous verification, and accountability to foster agile decision-making and enhance organizational resilience. Bureaucratic leadership relies on hierarchical structures, fixed rules, and formal procedures, often leading to slower responses and reduced innovation. Explore how adopting zero trust principles can transform leadership effectiveness and drive business success.
Why it is important
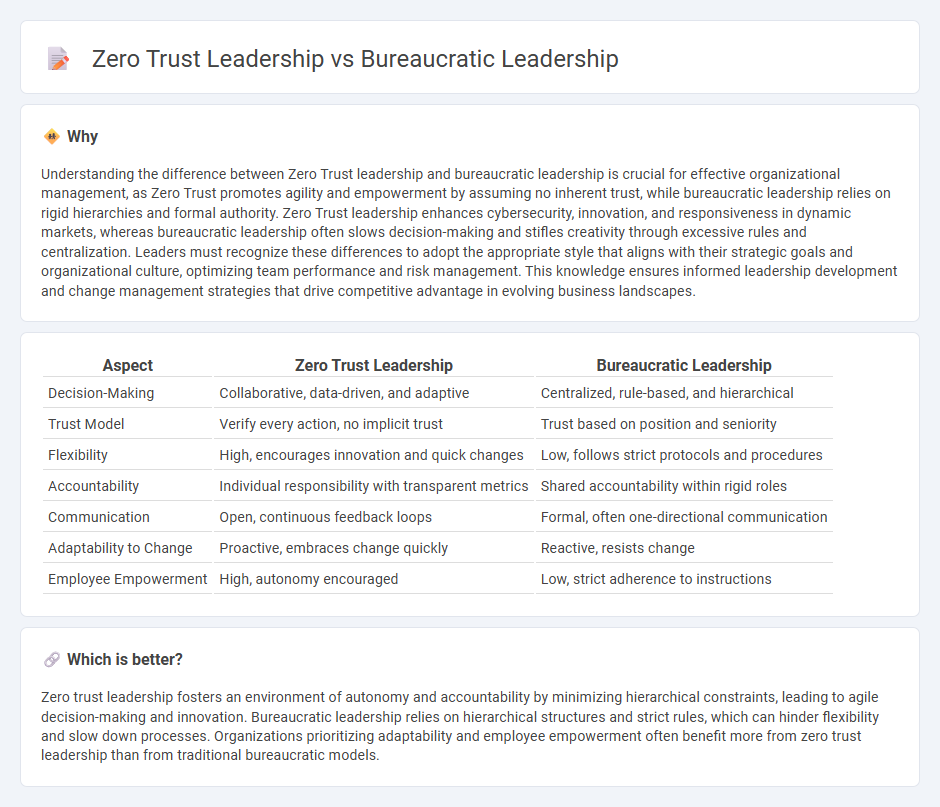
Understanding the difference between Zero Trust leadership and bureaucratic leadership is crucial for effective organizational management, as Zero Trust promotes agility and empowerment by assuming no inherent trust, while bureaucratic leadership relies on rigid hierarchies and formal authority. Zero Trust leadership enhances cybersecurity, innovation, and responsiveness in dynamic markets, whereas bureaucratic leadership often slows decision-making and stifles creativity through excessive rules and centralization. Leaders must recognize these differences to adopt the appropriate style that aligns with their strategic goals and organizational culture, optimizing team performance and risk management. This knowledge ensures informed leadership development and change management strategies that drive competitive advantage in evolving business landscapes.
Comparison Table
| Aspect | Zero Trust Leadership | Bureaucratic Leadership |
|---|---|---|
| Decision-Making | Collaborative, data-driven, and adaptive | Centralized, rule-based, and hierarchical |
| Trust Model | Verify every action, no implicit trust | Trust based on position and seniority |
| Flexibility | High, encourages innovation and quick changes | Low, follows strict protocols and procedures |
| Accountability | Individual responsibility with transparent metrics | Shared accountability within rigid roles |
| Communication | Open, continuous feedback loops | Formal, often one-directional communication |
| Adaptability to Change | Proactive, embraces change quickly | Reactive, resists change |
| Employee Empowerment | High, autonomy encouraged | Low, strict adherence to instructions |
Which is better?
Zero trust leadership fosters an environment of autonomy and accountability by minimizing hierarchical constraints, leading to agile decision-making and innovation. Bureaucratic leadership relies on hierarchical structures and strict rules, which can hinder flexibility and slow down processes. Organizations prioritizing adaptability and employee empowerment often benefit more from zero trust leadership than from traditional bureaucratic models.
Connection
Zero trust leadership and bureaucratic leadership intersect through their emphasis on structured oversight and accountability within organizations. Both models rely on clearly defined roles and stringent protocols to maintain control, reduce risks, and ensure compliance with organizational policies. This connection highlights a shared focus on minimizing vulnerabilities by implementing systematic checks and balances in decision-making processes.
Key Terms
Hierarchy vs. Decentralization
Bureaucratic leadership emphasizes a strict hierarchical structure with clear levels of authority and centralized decision-making, ensuring control and uniformity across the organization. Zero trust leadership promotes decentralization by distributing decision-making power, cultivating trust through transparency, and encouraging autonomy at all levels. Explore in-depth the benefits and challenges of hierarchy compared to decentralization in leadership models.
Rule-based Control vs. Trust but Verify
Bureaucratic leadership relies heavily on rule-based control, emphasizing strict adherence to policies and hierarchical procedures to maintain order and predictability. Zero trust leadership adopts a "trust but verify" approach, where assumptions of trust are replaced with continuous verification and validation of actions, enhancing security and accountability. Discover more about how these contrasting leadership styles impact organizational efficiency and security.
Formal Authority vs. Adaptive Autonomy
Bureaucratic leadership relies heavily on formal authority, structured hierarchies, and strict adherence to established protocols to maintain control and ensure organizational stability. Zero trust leadership emphasizes adaptive autonomy by fostering decentralized decision-making, continuous validation, and trust based on actions rather than position. Explore how integrating these leadership styles can optimize governance and innovation in complex organizations.
Source and External Links
Bureaucratic Leadership: Definition, Pros, and Cons - Bureaucratic leadership is characterized by a hierarchical structure, clear roles, and adherence to established procedures, which can enhance efficiency but may limit flexibility.
What is Bureaucratic Leadership? - This style emphasizes structured decision-making, clear roles, and adherence to policies, ensuring operational efficiency and regulatory compliance.
What Is Bureaucratic Leadership? Plus Examples - Bureaucratic leadership involves a formal hierarchical structure with clear roles and rules, promoting efficiency and fairness but potentially stifling creativity.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com